|
SpaceX CRS-28
SpaceX CRS-28, also known as SpX-28, is a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS) scheduled to be launched in January 2023. The mission is contracted by NASA and will be flown by SpaceX using a Cargo Dragon. This will be the seventh flight for SpaceX under NASA's CRS Phase 2. Cargo Dragon SpaceX plans to reuse the Cargo Dragons up to five times. The Cargo Dragon will launch without SuperDraco abort engines, without seats, cockpit controls and the life support system required to sustain astronauts in space. Dragon 2 improves on Dragon 1 in several ways, including lessened refurbishment time, leading to shorter periods between flights. The new Cargo Dragon capsules under the NASA CRS Phase 2 contract will land east of Florida in the Atlantic Ocean. Payload NASA contracted for the CRS-28 mission from SpaceX and therefore determines the primary payload, date of launch, and orbital parameters for the Cargo Dragon. ISS Roll Out Solar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which Scientific research on the International Space Station, scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The International Space Station programme, ISS programme evolved from the Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
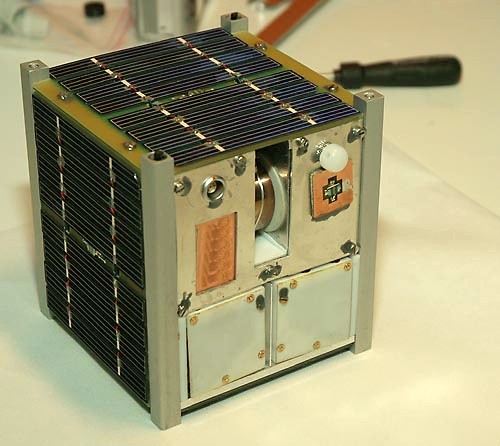
CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncrewed Spaceflights To The International Space Station
Uncrewed spaceflights to the International Space Station (ISS) are made primarily to deliver cargo, however several Russian modules have also docked to the outpost following uncrewed launches. Resupply missions typically use the Russian Progress spacecraft, European Automated Transfer Vehicles, Japanese Kounotori vehicles, and the American Dragon and Cygnus spacecraft. The primary docking system for Progress spacecraft is the automated Kurs system, with the manual TORU system as a backup. ATVs also use Kurs, however they are not equipped with TORU. Progress and ATV can remain docked for up to six months. The other spacecraft — the Japanese HTV, the SpaceX Dragon (under CRS phase 1) and the Northrop Grumman Cygnus — rendezvous with the station before being grappled using Canadarm2 and berthed at the nadir port of the Harmony or Unity module for one to two months. Under CRS phase 2, Cargo Dragon will dock autonomously at IDA-2 or 3 as the case may be. As of December 2022, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and ''amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 1 per cent of Canada's population. The terms "northern Canada" or "the North" may be used in contrast with ''the far north'', which may refer to the Canadian Arctic, the portion of Canada that lies north of the Arctic Circle, east of Alaska and west of Greenland. However, in many other uses the two areas are treated as a single unit. __TOC__ Definitions Subdivisions As a social rather than political region, the Canadian North is often subdivided into two distinct regions based on climate, the ''near north'' and the ''far north''. The different climates of these two regions result in vastly different vegetation, and therefore very different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildfire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identified as a bushfire( in Australia), desert fire, grass fire, hill fire, peat fire, prairie fire, vegetation fire, or veld fire. Some natural forest ecosystems depend on wildfire. Wildfires are distinct from beneficial human usage of wildland fire, called controlled burning, although controlled burns can turn into wildfires. Fossil charcoal indicates that wildfires began soon after the appearance of terrestrial plants approximately 419 million years ago during the Silurian period. Earth's carbon-rich vegetation, seasonally dry climates, atmospheric oxygen, and widespread lightning and volcanic ignitions create favorable conditions for fires. The occurrence of wildfires throughout the history of terrestrial life invites conjecture tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
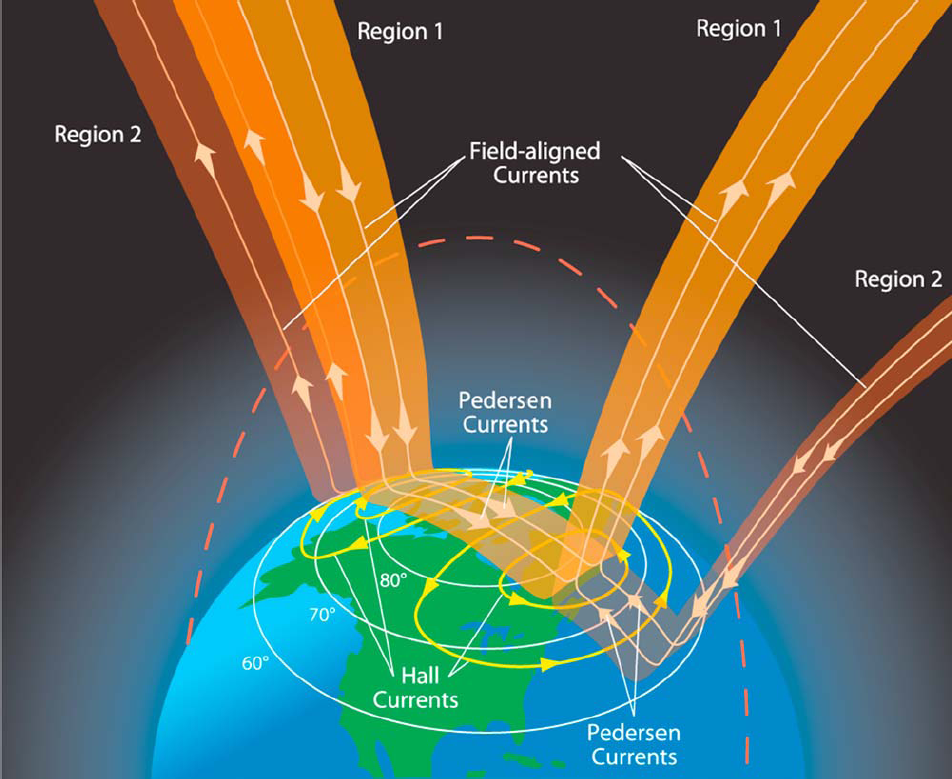
Birkeland Current
A Birkeland current (also known as field-aligned current) is a set of electrical currents that flow along geomagnetic field lines connecting the Earth's magnetosphere to the Earth's high latitude ionosphere. In the Earth's magnetosphere, the currents are driven by the solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field and by bulk motions of plasma through the magnetosphere (convection indirectly driven by the interplanetary environment). The strength of the Birkeland currents changes with activity in the magnetosphere (e.g. during substorms). Small scale variations in the upward current sheets (downward flowing electrons) accelerate magnetospheric electrons which, when they reach the upper atmosphere, create the Auroras Borealis and Australis. In the high latitude ionosphere (or auroral zones), the Birkeland currents close through the region of the auroral electrojet, which flows perpendicular to the local magnetic field in the ionosphere. The Birkeland currents occur in two pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomena of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ' refers to iron because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4. All substances exhibit some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Space Agency
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA; french: Agence spatiale canadienne, ASC) is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the ''Canadian Space Agency Act''. The president is Lisa Campbell, who took the position on September 3, 2020. The agency is responsible to the minister of innovation, science and industry. The CSA's headquarters are located at the John H. Chapman Space Centre in Longueuil, Quebec. The agency also has offices in Ottawa, Ontario, and small liaison offices in Houston; Washington, D.C.; and Paris. History The origins of the Canadian upper atmosphere and space program can be traced back to the end of the Second World War. Between 1945 and 1960, Canada undertook a number of small launcher and satellite projects under the aegis of defence research, including the development of the Black Brant rocket as well as series of advanced studies examining both orbital rendezvous and re-entry. In 1957, scientists and engineers at the Canadian Defence Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |