|
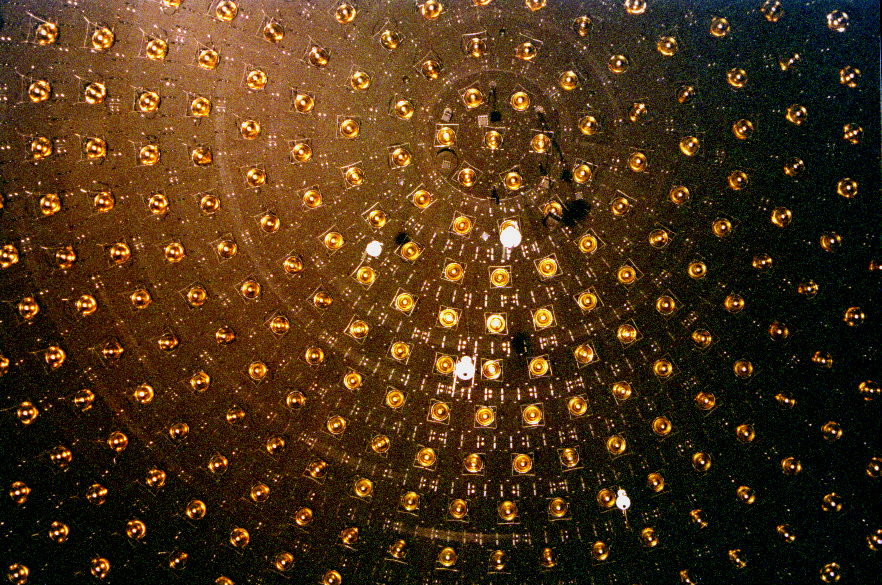
Soviet–American Gallium Experiment
SAGE (Soviet–American Gallium Experiment, or sometimes Russian-American Gallium Experiment) is a collaborative experiment devised by several prominent physicists to measure the solar neutrino flux. The experiment SAGE was devised to measure the Radiochemistry, radio-chemical solar neutrino flux based on the inverse beta decay Nuclear reaction, reaction, 71Ga + \nu_e \rightarrow e^+ 71Ge. The target for the reaction was 50-57 tonnes of liquid gallium metal stored deep (2100 meters) underground at the Baksan Neutrino Observatory in the Caucasus Mountains in Russia. The laboratory containing the SAGE-experiment is called gallium-germanium neutrino telescope (GGNT) laboratory, GGNT being the name of the SAGE experimental apparatus. About once a month, the neutrino induced Germanium, Ge is extracted from the Gallium, Ga. 71Ge is unstable with respect to electron capture (t_=11.43 days) and, therefore, the amount of extracted germanium can be determined from its activity as measured in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicists
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of Phenomenon, phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of Physics#Research fields, research fields, spanning all length scales: from atom, sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to physical cosmology, cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: Experimental physics, experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrino Oscillations
Neutrino oscillation is a quantum mechanical phenomenon in which a neutrino created with a specific lepton family number ("lepton flavor": electron, muon, or tau) can later be measured to have a different lepton family number. The probability of measuring a particular flavor for a neutrino varies between three known states, as it propagates through space. First predicted by Bruno Pontecorvo in 1957, reproduced and translated in reproduced and translated in neutrino oscillation has since been observed by a multitude of experiments in several different contexts. Most notably, the existence of neutrino oscillation resolved the long-standing solar neutrino problem. Neutrino oscillation is of great theoretical and experimental interest, as the precise properties of the process can shed light on several properties of the neutrino. In particular, it implies that the neutrino has a non-zero mass, which requires a modification to the Standard Model of particle physics. The experim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Gavrin
Vladimir (, , pre-1918 orthography: ) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin, widespread throughout all Slavic nations in different forms and spellings. The earliest record of a person with the name is Vladimir of Bulgaria (). Etymology The Old East Slavic form of the name is Володимѣръ ''Volodiměr'', while the Old Church Slavonic form is ''Vladiměr''. According to Max Vasmer, the name is composed of Slavic владь ''vladĭ'' "to rule" and ''*mēri'' "great", "famous" (related to Gothic element ''mērs'', ''-mir'', cf. Theode''mir'', Vala''mir''). The modern ( pre-1918) Russian forms Владимиръ and Владиміръ are based on the Church Slavonic one, with the replacement of мѣръ by миръ or міръ resulting from a folk etymological association with миръ "peace" or міръ "world". Max Vasmer, ''Etymological Dictionary of Russian Language'' s.v. "Владимир"starling.rinet.ru [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-life
Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay. Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to: Film * Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang * ''Half Life: A Parable for the Nuclear Age'', a 1985 Australian documentary film Literature * Half Life (Jackson novel), ''Half Life'' (Jackson novel), a 2006 novel by Shelley Jackson * Half-Life (Krach novel), ''Half-Life'' (Krach novel), a 2004 novel by Aaron Krach * Halflife (Michalowski novel), ''Halflife'' (Michalowski novel), a 2004 novel by Mark Michalowski * ''Rozpad połowiczny'' (), a 1988 award-winning dystopia novel by Edmund Wnuk-Lipiński Music *Half Life (3 album), ''Half Life'' (3 album) (2001) *Halflife (EP), ''Halflife'' (EP), an EP by Lacuna Coil and the title track *''Half-Life E.P.'', an EP by Local H * "Half Life", a song by 10 Years from ''The Autumn Effect'' * "Half Life", a song by Come from ''Near-Life Experience'' * "Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (physics)
In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place in a collision of two particles. For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted (sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process. When two discrete particles interact in classical physics, their mutual cross section is the area transverse to their relative motion within which they must meet in order to scatter from each other. If the particles are hard inelastic sphere A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It is the second most abundant trace metal in humans after iron, an import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterile Neutrino
Sterile neutrinos (or inert neutrinos) are hypothetical particles (neutral leptons – neutrinos) that interact only via gravity and not via any of the other fundamental interactions of the Standard Model. The term ''sterile neutrino'' is used to distinguish them from the known, ordinary ''active neutrinos'' in the Standard Model, which carry an isospin charge of and engage in the weak interaction. The term typically refers to neutrinos with right-handed chirality (see '), which may be inserted into the Standard Model. Particles that possess the quantum numbers of sterile neutrinos and masses great enough such that they do not interfere with the current theory of Big Bang nucleosynthesis are often called neutral heavy leptons (NHLs) or heavy neutral leptons (HNLs). The existence of right-handed neutrinos is theoretically well-motivated, because the known active neutrinos are left-handed and all other known fermions have been observed with both left and right chirality. They could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GALLEX
GALLEX or Gallium Experiment was a radiochemical neutrino detection experiment that ran between 1991 and 1997 at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS). This project was performed by an international collaboration of French, German, Italian, Israeli, Polish and American scientists led by the Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg. After brief interruption, the experiment was continued under a new name GNO (Gallium Neutrino Observatory) from May 1998 to April 2003. It was designed to detect solar neutrinos and prove theories related to the Sun's energy creation mechanism. Before this experiment (and the SAGE experiment that ran concurrently), there had been no observation of low energy solar neutrinos. Location The experiment's main components, the tank and the counters, were located in the underground astrophysical laboratory Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in the Italian Abruzzo province, near L'Aquila, and situated inside the 2912-metre-high Gran Sasso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BN-600 Reactor
The BN-600 reactor is a sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor, built at the Beloyarsk Nuclear Power Station, in Zarechny, Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia. It has a 600 MWe gross capacity and a 560 MWe net capacity, provided to the Middle Urals power grid. It has been in operation since 1980 and represents an improvement to the preceding BN-350 reactor. In 2014, its larger sister reactor, the BN-800 reactor, began operation. The plant is a pool type LMFBR, where the reactor, coolant pumps, intermediate heat exchangers and associated piping are all located in a common liquid sodium pool. The reactor system is housed in a concrete rectilinear building and provided with filtration and gas containment. In the first 24 years of operations, there have been 12 water-into-sodium leaks in the steam generators, routinely addressed by isolating the faulty module with gate valves. These incidents did not have off-site impact, did not generate radioactive material (sodium in the secondary circui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Oxide
Calcium oxide (formula: Ca O), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term '' lime'' connotes calcium-containing inorganic compounds, in which carbonates, oxides, and hydroxides of calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminium, and iron predominate. By contrast, ''quicklime'' specifically applies to the single compound calcium oxide. Calcium oxide that survives processing without reacting in building products, such as cement, is called free lime. Quicklime is relatively inexpensive. Both it and the chemical derivative calcium hydroxide (of which quicklime is the base anhydride) are important commodity chemicals. Preparation Calcium oxide is usually made by the thermal decomposition of materials, such as limestone or seashells, that contain calcium carbonate (CaCO3; mineral calcite) in a lime kiln. This is accomplished by heating the material to above , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argon-37
Argon (Ar) has 26 known isotopes, from Ar to Ar, of which three are stable (Ar, Ar, and Ar). On Earth, Ar makes up 99.6% of natural argon. The longest-lived radioactive isotopes are Ar with a half-life of 268 years, Ar with a half-life of 32.9 years, and Ar with a half-life of 35.04 days. All other isotopes have half-lives of less than two hours, and most less than one minute. The naturally occurring K, with a half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay. Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to: Film * Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang * ''Half Life: ... of 1.248 years, decays to stable Ar by electron capture (10.72%) and by positron emission (0.001%), and also to stable Ca via beta decay (89.28%). These properties and ratios are used to determine the age of rock (geology), rocks through potassium–argon dating. Despite the trapping of Ar in many rocks, it can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |