|
Socket 495
Socket 495, also known as μPGA2, is a CPU socket used for the Intel Pentium III and Celeron mobile processors. This socket was also used in Microsoft's Xbox console for the List of Intel Pentium_III processors#"Coppermine-128" (180 nm), Xbox CPU, albeit in a ball grid array, BGA (ball grid array) format. It replaces Socket 615 (μPGA1), which was used in Pentium II and early Celeron mobile processors. Technical specifications This socket is a 495 pin CPU socket designed to house any processor in the Socket 495 package. The socket has a 1.27mm pitch and is designed to support a heatsink. See also * List of Intel processors * List of Intel Celeron processors References {{Intelsock Intel CPU sockets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip-chip Pin Grid Array
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") apart, and may or may not cover the entire underside of the package. PGAs are often mounted on printed circuit boards using the through hole method or inserted into a socket. PGAs allow for more pins per integrated circuit than older packages, such as dual in-line package (DIP). Chip mounting The chip can be mounted either on the top or the bottom (the pinned side). Connections can be made either by wire bonding or through flip chip mounting. Typically, PGA packages use wire bonding when the chip is mounted on the pinned side, and flip chip construction when the chip is on the top side. Some PGA packages contain multiple dies, for example Zen 2 and Zen 3 Ryzen CPUs for the AM4 socket. Flip chip A flip-chip pin grid array (FC-P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGTL+
Gunning transceiver logic (GTL) is a type of logic signaling used to drive electronic backplane buses. It has a voltage swing between 0.4 volts and 1.2 volts — much lower than that used in TTL and CMOS logic — and symmetrical parallel resistive termination. The maximum signaling frequency is specified to be 100 MHz, although some applications use higher frequencies. GTL is defined by JEDEC standard JESD 8-3 (1993) and was invented by William Gunning while working for Xerox at the Palo Alto Research Center. All Intel front-side buses use GTL. As of 2008, GTL in these FSBs has a maximum frequency of 1.6 GHz. The front-side bus of the Intel Pentium Pro, Pentium II and Pentium III microprocessors uses GTL+ (or GTLP) developed by Fairchild Semiconductor, an upgraded version of GTL which has defined slew rate In electronics and electromagnetics, slew rate is defined as the change of voltage or current, or any other electrical or electromagnetic quantity, per un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded processors. The most notable differences were the addition of the Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) instruction set (to accelerate floating point and parallel calculations), and the introduction of a controversial serial number embedded in the chip during manufacturing. Even after the release of the Pentium 4 in late 2000, the Pentium III continued to be produced with new models introduced up until early 2003. They were then discontinued in April 2004 for desktop units and May 2007 for mobile units. Processor cores Similarly to the Pentium II it superseded, the Pentium III was also accompanied by the Celeron brand for lower-end versions, and the Xeon for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celeron
Celeron is a series of IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor, microprocessors targeted at low-cost Personal computer, personal computers, manufactured by Intel from 1998 until 2023. The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, 1998, and was based on the Pentium II. Celeron-branded processors released from 2009 to 2023 are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed compared to flagship Intel CPU lines, such as the Pentium or Intel Core, Core brands. They often have less CPU cache, cache or intentionally disabled advanced features, with variable impact on performance. While some Celeron designs have achieved strong performance for their segment, the majority of the Celeron line has exhibited noticeably degraded performance. This has been the primary Market segmentation, justification for the higher cost of other Intel CPU brands versus the Celeron range. In September 2022, Intel announced that the Celeron brand, along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
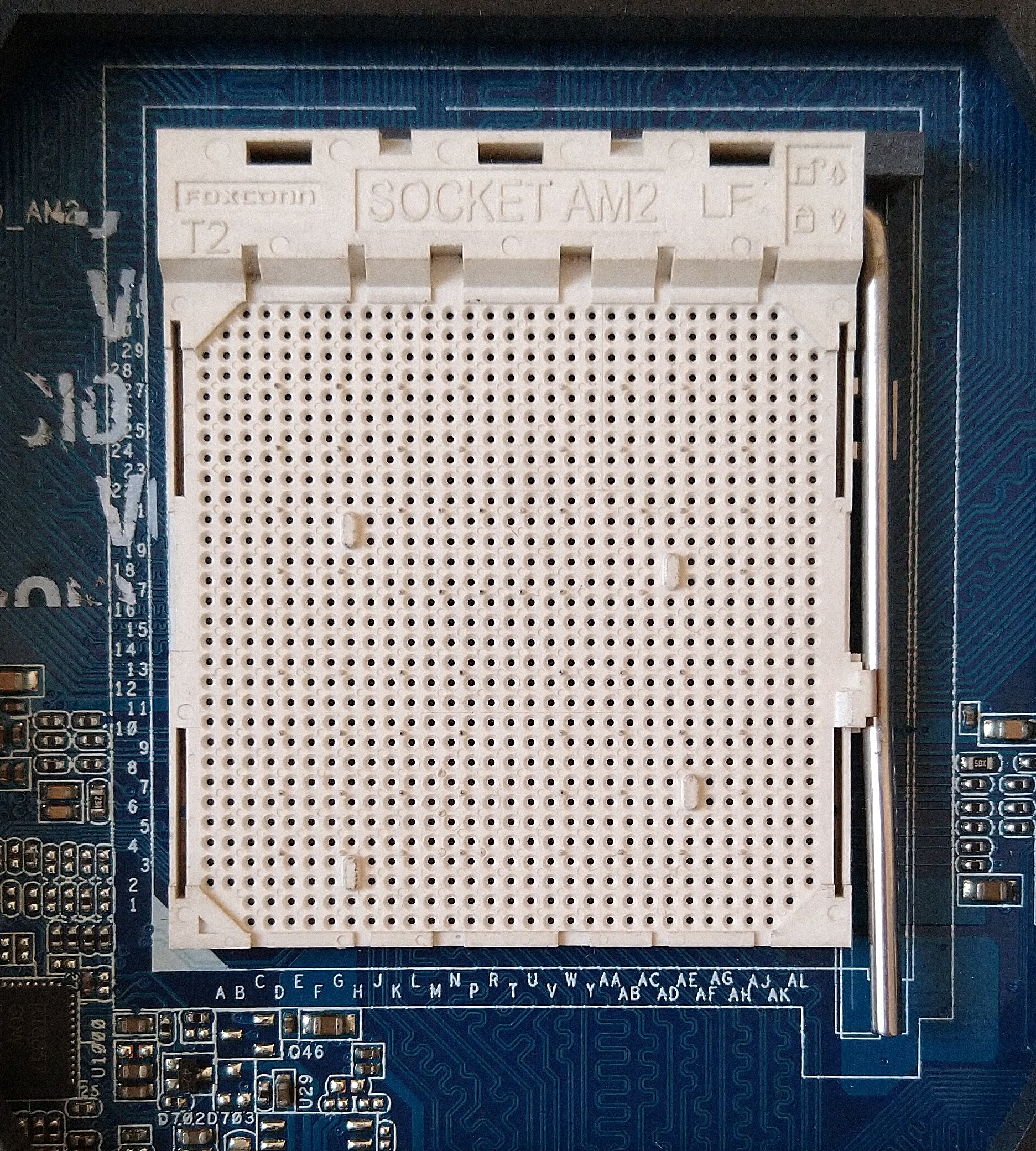
Socket 615
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include pin grid array (PGA) or land grid array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket 479
Socket 479 (mPGA479M) is a CPU socket used by some Intel microprocessors. It is primarily known as the socket used by Pentium M and Celeron M mobile processors normally found in laptops, however the socket has also been used with Tualatin (microprocessor), Tualatin-M Mobile Celeron and Pentium III processors years before it. The official naming by Intel is μFCPGA and μPGA479M. Technical specifications Socket 479 has 479 pin holes. Pentium M processors in PGA package have 479 pins that plug into this zero insertion force socket. Only 478 pins are electrically connected (B2 is reserved and "depopulated on the Micro-FCPGA package"). Although mechanically similar, Socket 478 has one pin fewer, making it impossible to use a Pentium M processor in a Socket 478 board. For this reason, some manufacturers like Asus have made drop-in boards (e.g. CT-479) which allow the use of Socket 479 processors in Socket 478 boards. Conversely, it is impossible to use any Socket 478 desktop Celeron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the central processing unit (CPU) without soldering. Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with many pins, zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets are preferred. Common sockets include pin grid array (PGA) or land grid array (LGA). These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (PGA type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket. Certain devices use Ball Grid Array (BGA) sockets, although these require soldering and are generally not considered user replaceable. CPU sockets are used on the motherboard in desktop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Processor
A mobile processor is a microprocessor designed for mobile devices such as laptops and cell phones. A CPU chip is designed for portable computers to run fanless, under 10 to 15W, which is cool enough without a fan. It is typically housed in a smaller chip package, but more importantly, in order to run cooler, it uses lower voltages than its desktop counterpart and has more sleep mode capability. A mobile processor can be throttled down to different power levels or sections of the chip can be turned off entirely when not in use. Further, the clock frequency may be stepped down under low processor loads. This stepping down conserves power and prolongs battery life. In laptops One of the main characteristics differentiating laptop processors from other CPUs is low-power consumption, which is not without tradeoffs: they also tend to not perform as well as their desktop counterparts. The notebook processor has become an important market segment in the semiconductor industry. No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xbox
Xbox is a video gaming brand that consists of four main home video game console lines, as well as application software, applications (games), the streaming media, streaming service Xbox Cloud Gaming, and online services such as the Xbox network and Xbox Game Pass. The brand is produced by Microsoft Gaming, a division of Microsoft. The brand was 2001 in video gaming#Video game consoles, first introduced in the United States in November 2001, with the launch of the original Xbox console. The Xbox branding was formerly, from 2012 to 2015, used as Microsoft's digital media entertainment brand replacing Zune. In 2022, Microsoft expanded its gaming business and reorganized Xbox to become part of its newly formed Microsoft Gaming division. Under Microsoft Gaming, Xbox's first-party publishers are Xbox Game Studios, ZeniMax Media (Bethesda Softworks), and Activision Blizzard (Activision, Blizzard Entertainment, and King (company), King), who own numerous studios and successful franchis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intel Pentium III Processors
The Pentium III from Intel is a sixth-generation Central processing unit, CPU targeted at the consumer market. Desktop processors Katmai (microprocessor), "Katmai" (250 nm) * 9.5 million transistors * All models support: MMX (instruction set), MMX, Streaming SIMD Extensions, SSE * The 'B' suffix denotes a 133 MHz FSB * The '80525PYxxx512' number denotes an OEM CPU while the 'BX80525xxxx512' or 'BX80525xxxx512E' number denotes a boxed CPU * The L2 cache is off-die and runs at 50% CPU speed. Coppermine (microprocessor), "Coppermine" (180 nm) * 28 million transistors * All models support: MMX (instruction set), MMX, Streaming SIMD Extensions, SSE * The 'B' suffix denotes a 133 MHz FSB when the same speed was also available with a 100 MHz FSB. * The 'E' suffix denotes a processor with support for Intel's Advanced Transfer Cache in Intel documentation; in reality it indicates a Coppermine core when the same speed was available as either Katmai or Copperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Grid Array
A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging (a chip carrier) used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be put on a dual in-line or flat package. The whole bottom surface of the device can be used, instead of just the perimeter. The traces connecting the package's leads to the wires or balls which connect the die to package are also on average shorter than with a perimeter-only type, leading to better performance at high speeds. Soldering of BGA devices requires precise control and is usually done by automated processes such as in computer-controlled automatic reflow ovens. Description The BGA is descended from the pin grid array (PGA), which is a package with one face covered (or partly covered) with pins in a grid pattern which, in operation, conduct electrical signals between the integrated circuit and the printed circuit board (PCB) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |