|
Social Software (social Procedure)
In philosophy and the social sciences, social software is an interdisciplinary research program that borrows mathematical tools and techniques from game theory and computer science in order to analyze and design social procedures. The goals of research in this field are modeling social situations, developing theories of correctness, and designing social procedures.Pacuit (2005), p.10 Work under the term social software has been going on since about 1996, and conferences in Copenhagen, London, Utrecht and New York, have been partly or wholly devoted to it. Much of the work is carried out at the City University of New York under the leadership of Rohit Jivanlal Parikh, who was influential in the development of the field. Goals and tools Current research in the area of social software include the analysis of social procedures and examination of them for fairness, appropriateness, correctness and efficiency. For example, an election procedure could be a simple majority vote, Bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Procedure
The term social procedure is sometimes applied to any of the procedures carried out by people in various areas of society, such as legislative assemblies, judicial systems, and resource arbiters, such as banks or other lending organizations. It has been described as social software and indeed does resemble software. Social procedures include as a subset procedures which are at the foundation of our society, such as procedural law. Similarly many social procedures are explicitly designed to ensure fair treatment to individuals or corporations, as official records of parliamentary debates show. Multiple social procedures can serve to achieve the same end. Justice, as an example, in the U.S. achieved through the use of 2 adversarial lawyers, a neutral judge, and a jury of peers. In Canada, the judge is less neutral. This subtle difference in programming has an effect on the justice outcome. Though game theory is a highly technical subject with no special attention to sports, an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Searle
John Rogers Searle (; born July 31, 1932) is an American philosopher widely noted for contributions to the philosophy of language, philosophy of mind, and social philosophy. He began teaching at UC Berkeley in 1959, and was Willis S. and Marion Slusser Professor Emeritus of the Philosophy of Mind and Language and Professor of the Graduate School at the University of California, Berkeley until 2019. As an undergraduate at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, Searle was secretary of "Students against Joseph McCarthy". He received all his university degrees, BA, MA, and DPhil, from the University of Oxford, where he held his first faculty positions. Later, at UC Berkeley, he became the first tenured professor to join the 1964–1965 Free Speech Movement. In the late 1980s, Searle challenged the restrictions of Berkeley's 1980 rent stabilization ordinance. Following what came to be known as the California Supreme Court's "Searle Decision" of 1990, Berkeley changed its rent co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerzy Tiuryn
Jerzy is the Polish version of the masculine given name George. The most common nickname for Jerzy is Jurek (), which may also be used as an official first name. Occasionally the nickname Jerzyk may be used, which means "swift" in Polish. People *Jerzy, ''nom de guerre'' of Ryszard Białous, Polish World War II resistance fighter * Jerzy Andrzejewski, Polish writer * Jerzy Bartmiński, Polish linguist and ethnologist * Jerzy Braun (other), several people * Jerzy Brzęczek, Polish footballer and manager * Jerzy Buzek, Polish politician and former Prime Minister * Jerzy Dudek, Polish footballer * Jerzy Fedorowicz, Polish actor and theatre director * Jerzy Ficowski, Polish poet and translator * Jerzy Grotowski, Polish theatre director and theorist * Jerzy Hoffman, Polish film director, screenwriter, and producer * Jerzy Jarniewicz, Polish poet, literary critic, translator and essayist * Jerzy Janowicz, Polish tennis player * Jerzy Jurka, Polish-American computational and mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexter Kozen
Dexter Campbell Kozen (born December 20, 1951) is an American theoretical computer scientist. He is Joseph Newton Pew, Jr. Professor in Engineering at Cornell University. He received his B.A. from Dartmouth College in 1974 and his PhD in computer science in 1977 from Cornell University, where he was advised by Juris Hartmanis. He advised numerous Ph.D. students. He is a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery, a Guggenheim Fellow, and has received an Outstanding Innovation Award from IBM Corporation. He has also been named Faculty of the Year by the Association of Computer Science Undergraduates at Cornell. Dexter Kozen was one of the first professors to receive the honor of a professorship at The Radboud Excellence Initiative at Radboud University Nijmegen in the Netherlands. He is known for his work at the intersection of logic and complexity. He is one of the fathers of dynamic logic and developed the version of the modal μ-calculus most used today. Moreover, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
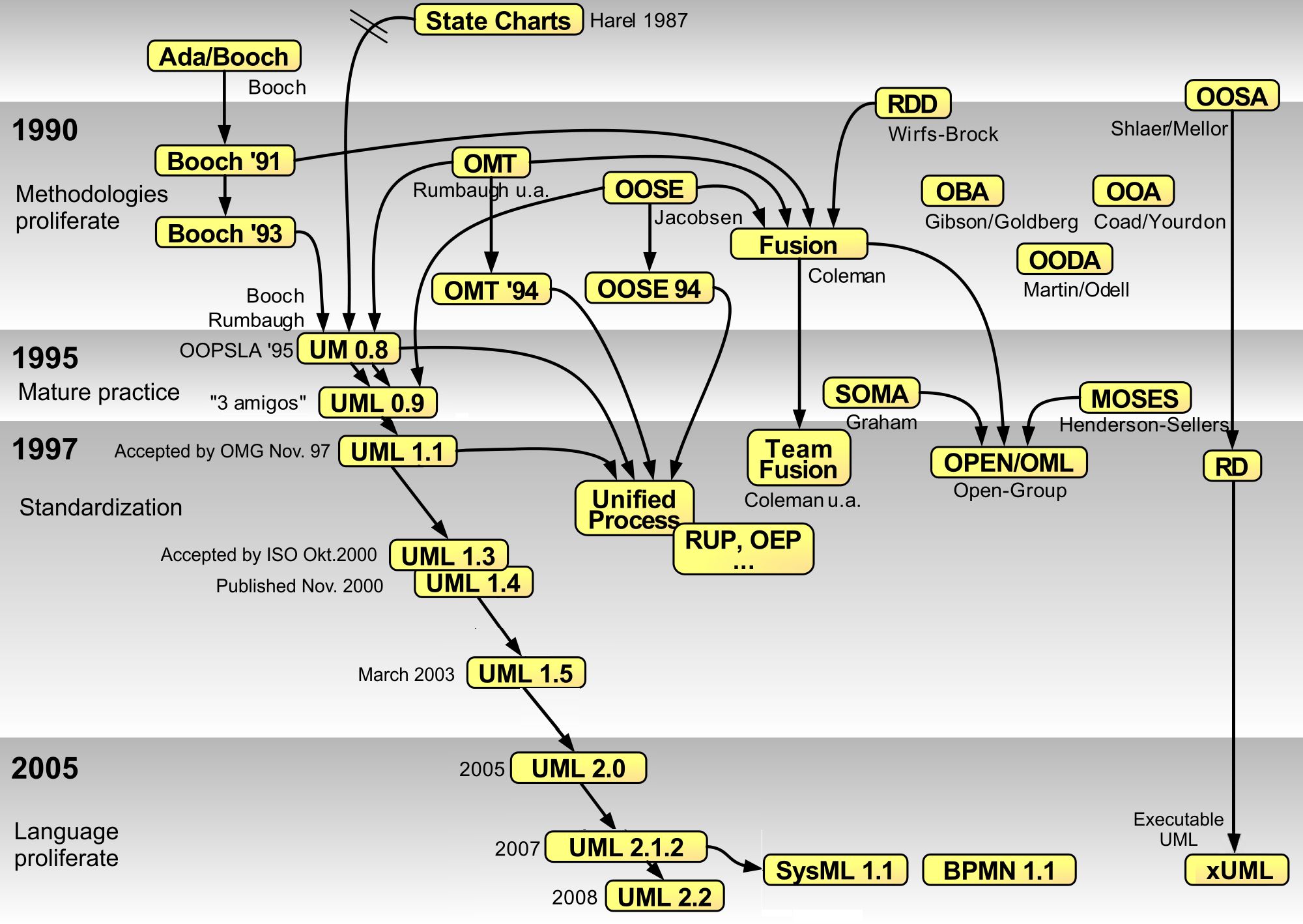
David Harel
David Harel ( he, דוד הראל; born 12 April 1950) is a computer scientist, currently serving as President of the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities. He has been on the faculty of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel since 1980, and holds the William Sussman Professorial Chair of Mathematics. Born in London, England, he was Dean of the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science at the institute for seven years. Biography Harel is best known for his work on dynamic logic, computability, database theory, software engineering and modelling biological systems. In the 1980s he invented the graphical language of Statecharts for specifying and programming reactive systems, which has been adopted as part of the UML standard. Since the late 1990s he has concentrated on a scenario-based approach to programming such systems, launched by his co-invention (with W. Damm) of Live Sequence Charts. He has published expository accounts of computer science, such as his awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshe Vardi
, honorific_suffix = , image = Moshe Vardi IMG 0010.jpg , birth_date = , birth_place = Israel , workplaces = Rice UniversityIBM Research Stanford University , alma_mater = , thesis_title = The Implication Problem for Data Dependencies in the Relational Model , thesis_url = , thesis_year = 1981 , doctoral_advisor = Catriel Beeri , doctoral_students = Kristin Yvonne Rozier , fields = LogicComputation , awards = , website = Moshe Ya'akov Vardi ( he, משה יעקב ורדי) is an Israeli mathematician and computer scientist. He is a Professor of Computer Science at Rice University, United States. He is University Professor, the Karen Ostrum George Professor in Computational Engineering, Distinguished Service Professor, and director of the Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology. His interests focus on applications of logic to computer science, including database theory, finite model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoram Moses
Yoram Moses ( he, יוֹרָם מוֹזֶס) is a Professor in the Electrical Engineering Department at the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology. Yoram Moses received a B.Sc. in mathematics from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in 1981, and a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Stanford University in 1986. Moses is a co-author of the book ''Reasoning About Knowledge'', and is a winner of the 1997 Gödel Prize in theoretical computer science and the 2009 Dijkstra Prize The Edsger W. Dijkstra Paper Prize in Distributed Computing is given for outstanding papers on the principles of distributed computing, whose significance and impact on the theory and/or practice of distributed computing has been evident for at lea ... in Distributed Computing. His major research interests are distributed systems and reasoning about knowledge. He is married to the computer scientist Yael Moses. External linksYoram Moses's homepage Electrical engineering academics Gödel Prize laureates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Halpern
Joseph Yehuda Halpern (born 1953) is an Israeli-American professor of computer science at Cornell University. Most of his research is on reasoning about knowledge and uncertainty. Biography Halpern graduated in 1975 from University of Toronto with a B.S. in mathematics. He went on to earn a Ph.D. in mathematics from Harvard University in 1981 under the supervision of Albert R. Meyer and Gerald Sacks. He has written three books, ''Actual Causality'', ''Reasoning about Uncertainty,'' and ''Reasoning About Knowledge'' and is a winner of the 1997 Gödel Prize in theoretical computer science and the 2009 Dijkstra Prize in distributed computing. From 1997 to 2003 he was editor-in-chief of the Journal of the ACM. In 2002 he was inducted as a Fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery and in 2012 he was selected as an IEEE Fellow. In 2011 he was awarded a Senior Fellowship of the Zukunftskolleg at the University of Konstanz. In 2019, Halpern was elected a member of the Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Fagin
Ronald Fagin (born 1945) is an American mathematician and computer scientist, and IBM Fellow at the IBM Almaden Research Center. He is known for his work in database theory, finite model theory, and reasoning about knowledge. Biography Ron Fagin was born and grew up in Oklahoma City, where he attended Northwest Classen High School. He was later elected to the Northwest Classen Hall of Fame. He completed his undergraduate degree at Dartmouth College. Fagin received his Ph.D. in Mathematics from the University of California, Berkeley in 1973, where he worked under the supervision of Robert Vaught. He joined the IBM Research Division in 1973, spending two years at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center, and then transferred in 1975 to what is now the IBM Almaden Research Center in San Jose, California. He has served as program committee chair for ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems 1984, ACM Symposium on Principles of Database Systems 1984, Theoretical Aspects of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Stokey
Nancy Laura Stokey (born May 8, 1950) has been the Frederick Henry Prince Distinguished Service Professor of Economics at the University of Chicago since 1990 and focuses particularly on mathematical economics while recently conducting research about Growth Theory, economic dynamics, and fiscal/monetary policy. She earned her BA in economics from the University of Pennsylvania in 1972 and her PhD from Harvard University in 1978, under the direction of thesis advisor Kenneth Arrow. She is a Fellow of the Econometric Society, the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and the National Academy of Sciences. She previously served as a co editor of ''Econometrica'' and was a member of the Expert Panel of the Copenhagen Consensus. She received her Honorary Doctor of Laws (L.L.D) in 2012 from the University of Western Ontario. Much of her work has been done by digesting economic dynamics, which most of this work is done as an expositor. She spent a great deal of time recently researching g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Milgrom
Paul Robert Milgrom (born April 20, 1948) is an American economist. He is the Shirley and Leonard Ely Professor of Humanities and Sciences at the Stanford University School of Humanities and Sciences, a position he has held since 1987. He is a professor in the Stanford School of Engineering as well and a Senior Fellow at the Stanford Institute for Economic Research. Milgrom is an expert in game theory, specifically auction theory and pricing strategies. He is the winner of the 2020 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, together with Robert B. Wilson, "for improvements to auction theory and inventions of new auction formats". He is the co-creator of the no-trade theorem with Nancy Stokey. He is the co-founder of several companies, the most recent of which, Auctionomics, provides software and services for commercial auctions and exchanges. Milgrom and his thesis advisor Wilson designed the auction protocol the FCC uses to determine which phone company gets what cellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaakko Hintikka
Kaarlo Jaakko Juhani Hintikka (12 January 1929 – 12 August 2015) was a Finnish philosopher and logician. Life and career Hintikka was born in Helsingin maalaiskunta (now Vantaa). In 1953, he received his doctorate from the University of Helsinki for a thesis entitled ''Distributive Normal Forms in the Calculus of Predicates''. He was a student of Georg Henrik von Wright. Hintikka was a Junior Fellow at Harvard University (1956-1969), and held several professorial appointments at the University of Helsinki, the Academy of Finland, Stanford University, Florida State University and finally Boston University from 1990 until his death. He was the prolific author or co-author of over 30 books and over 300 scholarly articles, Hintikka contributed to mathematical logic, philosophical logic, the philosophy of mathematics, epistemology, language theory, and the philosophy of science. His works have appeared in over nine languages. Hintikka edited the academic journal ''Synthese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |