|
Slovak Sign Language
The Slovak Sign Language (, SPJ) is the sign language of the deaf community in Slovakia. It belongs to the French sign-language family. Bickford (2005) found that Slovak, Czech, and Hungarian Sign formed a cluster with Romanian, Bulgarian, and Polish Sign.Bickford, 2005''The Signed Languages of Eastern Europe''/ref> Despite the similarity of oral Slovak and Czech, SSL is not particularly close to Czech Sign Language Czech Sign Language (, ČZJ) is the sign language of the deaf community in the Czech Republic. It presumably emerged around the time of the first deaf school in Bohemia (1786). It belongs to the French sign-language family and is partially intel .... References French Sign Language family Languages of Slovakia {{sign-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , hosting a population exceeding 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of the present-day Slovakia in the 5th and 6th centuries. From the late 6th century, parts of modern Slovakia were incorporated into the Pannonian Avars, Avar Khaghanate. In the 7th century, the Slavs played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. When the Avar Khaghanate dissolved in the 9th century, the Slavs established the Principality of Nitra before it was annexed by the Great Moravia, Principality of Moravia, which later became Great Moravia. When Great Moravia fell in the 10th century, the territory was integrated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
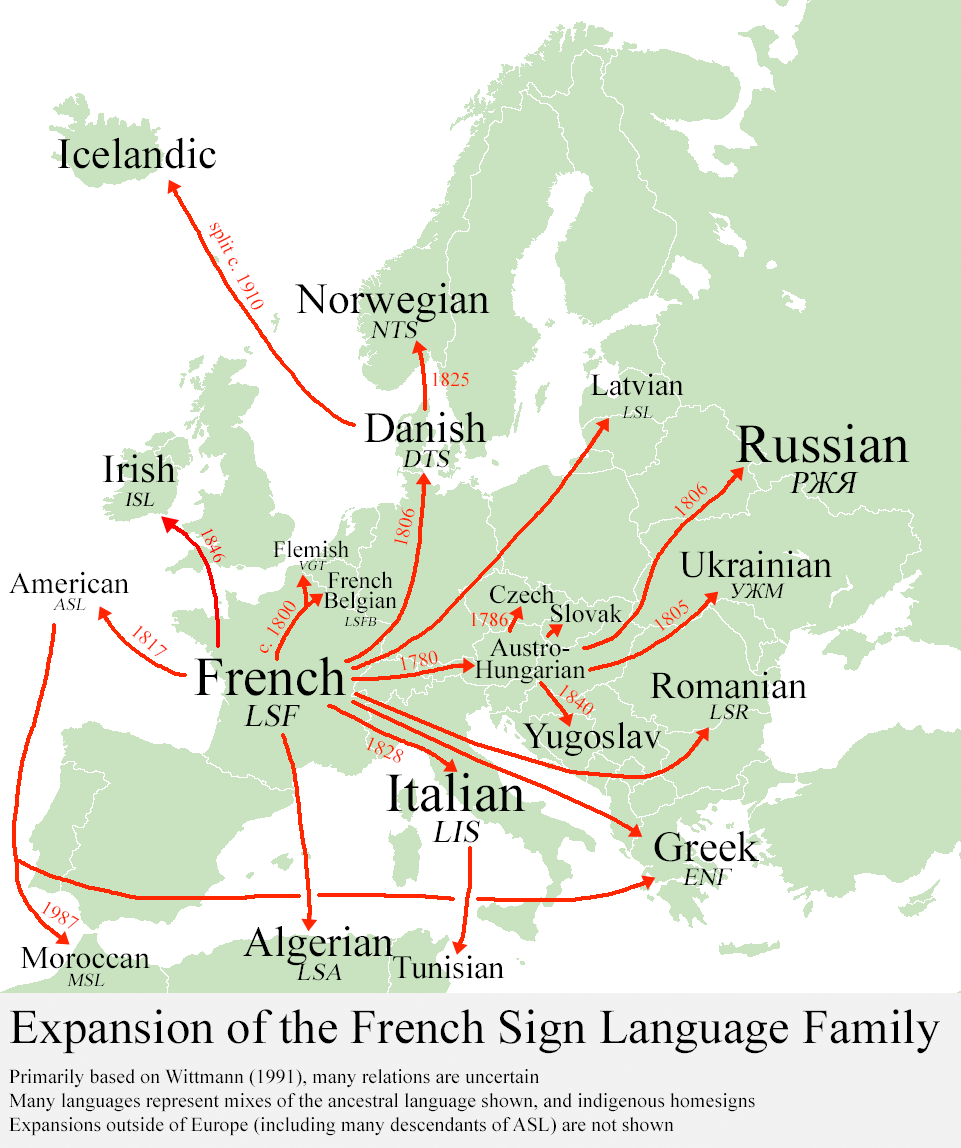
French Sign Language Family
The French Sign Language (LSF, from ) or Francosign family is a language family of sign languages which includes French Sign Language and American Sign Language. The LSF family descends from Old French Sign Language (VLSF), which developed among the deaf community in Paris. The earliest mention of Old French Sign Language is by the abbé Charles-Michel de l'Épée in the late 18th century, but it could have existed for centuries prior. Several European sign languages, such as Russian Sign Language, derive from it, as does American Sign Language, established when French educator Laurent Clerc taught his language at the American School for the Deaf. Others, such as Spanish Sign Language, are thought to be related to French Sign Language even if they are not directly descendent from it. Language family tree Anderson (1979) Anderson (1979) postulated the following classification of LSF and its relatives, with derivation from Medieval monks' sign systems, though some lineages are ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian Sign Language
Austrian Sign Language (, ÖGS) is the sign language used by the Austrian Deaf community—approximately 10,000 people (see Krausneker 2006). Classification ÖGS and Hungarian Sign Language seem to be related for historical reasons (First School for the Deaf in Vienna), but HSL forms a cluster with neighboring languages rather than with ÖGS. Although there are no detailed studies of the extent of relatedness, ÖGS shares aspects of its grammar with German Sign Language and Swiss Sign Language, while the vocabulary differs (see Skant et al. 2002); Wittmann (1991) places it in the French Sign Language family). Research Linguistic research on ÖGS started in the 1990s and is primarily conducted at the University of Klagenfurt and University of Graz. The Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt (AAU) worked on the "Deaf learning" project (September 1, 2015 – August 31, 2018) financed under Erasmus+ as a cooperation for innovation and the exchange of good practices, strategic Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with #Non-manual elements, non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, although there are similarities among different sign languages. Linguists consider both spoken and signed communication to be types of natural language, meaning that both emerged through an abstract, protracted aging process and evolved over time without meticulous planning. This is supported by the fact that there is substantial overlap between the neural substrates of sign and spoken language processing, despite the obvious differences in modality. Sign language should not be confused with body language, a type of non verbal communicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deaf
Deafness has varying definitions in cultural and medical contexts. In medical contexts, the meaning of deafness is hearing loss that precludes a person from understanding spoken language, an audiological condition. In this context it is written with a lower case ''d''. It later came to be used in a cultural context to refer to those who primarily communicate with a deafness aid or through sign language regardless of hearing ability, often capitalized as ''Deaf'' and referred to as "big D Deaf" in speech and sign. The two definitions overlap but are not identical, as hearing loss includes cases that are not severe enough to impact spoken language comprehension, while cultural Deafness includes hearing people who use sign language, such as children of deaf adults. Medical context In a medical context, deafness is defined as a degree of hearing difficulties such that a person is unable to understand speech, even in the presence of amplification. In profound deafness, even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech Sign Language
Czech Sign Language (, ČZJ) is the sign language of the deaf community in the Czech Republic. It presumably emerged around the time of the first deaf school in Bohemia (1786). It belongs to the French sign-language family and is partially intelligible with French sign language. Despite the similarity of oral Czech and Slovak, it is not particularly close to Slovak Sign Language. References French Sign Language family Languages of the Czech Republic {{sign-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Sign Language
Hungarian Sign Language (, ) is the sign language of deaf people in Hungary Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and .... There is historical evidence that Hungarian and Austrian Sign Language are related, but Bickford (2005) found that Hungarian, Slovak, and Czech Sign formed a cluster with Romanian, Bulgarian, and Polish Sign rather than with Austrian. Bickford also noted that there are about seven dialects of Hungarian Sign Language, with the variation connected to the residential deaf school where it is taught. In November 2009, the Hungarian Parliament unanimously passed Act CXXV of 2009 on Hungarian Sign Language and the use of Hungarian Sign Language. In 2020, the act was amended to place HSL on equal footing with spoken Hungarian when it comes to state-recognized exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Sign Language
The Romanian Sign Language (, LSR) is the sign language used by deaf people in Romania Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to .... In Romania, the first organization dedicated to people with hearing impairments was the Romanian Society of the Deaf-Mute, established on 9 November 1919. It was continued by the Romanian Association of the Deaf-Mute (1952), and the (, ANSR, 1995). References French Sign Language family Languages of Romania {{sign-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Sign Language
Bulgarian Sign Language (, BZhE) is the language, or perhaps languages, of the deaf community in Bulgaria Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t .... Primary schools were established for the deaf. Russian Sign Language was introduced in 1910, and allowed in the classroom in 1945, and Wittmann (1991) classifies it as a descendant of Russian Sign. However, Bickford (2005) found that Bulgarian Sign formed a cluster with Slovak, Czech, Hungarian, Romanian, and Polish Sign.Bickford, 2005''The Signed Languages of Eastern Europe''/ref> The language of the classroom is different from that used by adults outside, and it is not clear if Wittmann and Bickford looked at the same language; nor, if one is derived from Russian Sign, if it is a dialect or if it creolized to form a new la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Sign Language
Polish Sign Language (, ) is the language of the deaf community in Poland. Polish Sign Language uses a distinctive one-handed manual alphabet based on the alphabet used in Old French Sign Language and therefore appears to be related to French Sign Language. It may also have common features with Russian Sign Language and German Sign Language, which is related to the history of Poland during the Partitions, when Russification and Germanization influenced the Polish language, and may also have borrowings from the sign language used in the Austrian partition. Its lexicon and grammar are distinct from the Polish language, although there is a manually coded version of Polish known as (, or Signed Polish), which is often used by interpreters on television and by teachers in schools. Polish Sign Language was first formed/became prevalent around 1817. Around that time, thInstytut Głuchoniemych(Institute for the Deaf-Mute) was founded by Jakub Falkowski, who began teaching deaf chil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |