|
Slavery In China
Slavery in China has taken various forms throughout history. Slavery was nominally abolished in 1910,Hallet, Nicole.China and Antislavery". ''Encyclopedia of Antislavery and Abolition'', Vol. 1, p. 154156. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007. . although the practice continued until at least 1949.Rodriguez, Junius.China, Late Imperial". ''The Historical Encyclopedia of World Slavery'', Vol. 1, p. 146. ABC-CLIO, 1997. . The Chinese term for slave () can also be roughly translated into 'debtor', 'dependent', or 'subject'. Despite a few attempts to ban it, slavery existed continuously throughout pre-modern China, sometimes serving a key role in politics, economics, and historical events. However slaves in China were a very small part of the population due to a large peasant population that mitigated the need for large scale slave labor. The slave population included war prisoners and kidnapped victims or people who had been sold. General history In Chinese society, slaves were grouped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yongzheng Emperor
The Yongzheng Emperor (13 December 1678 – 8 October 1735), also known by his temple name Emperor Shizong of Qing, personal name Yinzhen, was the fourth List of emperors of the Qing dynasty, emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the third Qing emperor to rule over China proper. The fourth son of the Kangxi Emperor, Yongzheng ascended the throne following prolonged disputes over succession. A hard-working ruler, he aimed to create a more effective government, cracked down on corruption and reformed the personnel and financial administration. His reign also saw the formation of the Grand Council (Qing dynasty), Grand Council, an institution that had a major impact on the future of the dynasty. Militarily, Yongzheng continued his father's efforts to consolidate Qing's position in Outer Mongolia and Tibet through force. The Yongzheng Emperor died in 1735 at the age of 56 and was succeeded by his fourth son, who assumed the throne as the Qianlong Emperor. Although his reign was much s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Han
The ''Book of Han'' is a history of China finished in 111 CE, covering the Western, or Former Han dynasty from the first emperor in 206 BCE to the fall of Wang Mang in 23 CE. The work was composed by Ban Gu (32–92 CE), an Eastern Han court official, with the help of his sister Ban Zhao, continuing the work of their father, Ban Biao. They modelled their work on the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (), a cross-dynastic general history, but theirs was the first in this annals-biography form to cover a single dynasty. It is the best source, sometimes the only one, for many topics such as literature in this period. The ''Book of Han'' is also called the ''Book of the Former Han'' () to distinguish it from the '' Book of the Later Han'' () which covers the Eastern Han period (25–220 CE), and was composed in the fifth century by Fan Ye (398–445 CE). Contents This history developed from a continuation of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongguan Hanji
The ''Dongguan Hanji'' () is a Chinese text that is a history of the Eastern Han dynasty. It was compiled in several stages by different people throughout the Eastern Han period. It was considered the standard history of the Eastern Han until the Tang dynasty when it replaced by the ''Book of the Later Han''. Compilation The book started to be written in 72 CE, when Emperor Ming of Han ordered that a history be written of the reign of his father Emperor Guangwu. Ban Gu, Chen Zong (陳宗), , Meng Ji (孟冀), , and were chosen to compile it. They worked on this project in the Orchid Terrace (''Lan tai'', 蘭臺), one of the libraries and archives in the Southern Palace complex in Luoyang. The result was a 28-chapter book entitled ''Jianwu zhu ji'' (建武注記), covering the time from 22 to 57 CE. In 120 CE, Deng Sui, Empress Dowager Deng Sui instructed , , , and to expand the ''Jianwu zhu ji''. They worked in the Eastern Lodge (''Dong guan'', 東觀), another library in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal. In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, i.e. an area that is under the jurisdiction of a sovereign state. As a subdivision, a territory in most countries is an organized division of an area that is controlled by a country but is not formally developed into, or incorporated into, a political unit of that country, which political units are of equal status to one another and are often referred to by words such as "provinces", "regions", or "states". In its narrower sense, it is "a geographic region, such as a colonial possession, that is dependent on an external government." Etymology The origins of the word "territory" begin with the Proto-Indo-European root ''ters'' ('to dry'). From this emerged the Latin word ''terra'' ('earth, land') and later the Latin word ''territorium'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquess
A marquess (; ) is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German-language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman with the rank of a marquess or the wife (or widow) of a marquess is a marchioness () or marquise (). These titles are also used to translate equivalent Asian styles, as in Imperial China and Imperial Japan. Etymology The word ''marquess'' entered the English language from the Old French ("ruler of a border area") in the late 13th or early 14th century. The French word was derived from ("frontier"), itself descended from the Middle Latin ("frontier"), from which the modern English word ''March (territory), march'' also descends. The distinction between governors of frontier territories and interior territories was made as early as the founding of the Roman Empire when some provinces were set aside for administration by the senate and more unpacified or vulnerable provinces were adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legalism (Chinese Philosophy)
''Fajia'' ( zh, s=法家, p=fǎjiā), or the School of ''fa'' (laws, methods), early translated ''Legalism'' for Shang Yang, is a school of thought representing a broader bibliography, collection of primarily Warring States period classical Chinese philosophy, incorporating more administrative works traditionally said to be rooted in Huang-Lao Daoism. Addressing practical governance challenges of the unstable feudal system, their ideas 'contributed greatly to the formation of the Chinese empire' and bureaucracy, advocating concepts including rule by fa (concept), law, sophisticated administrative fa (concept), technique, and ideas of state power. They are often interpreted in the West along Realism (international relations), realist lines. Though persisting, the Qin to Tang dynasty, Tang were more characterized by the 'centralizing tendencies' of their traditions. The school incorporates the more legalistic ideas of Li Kui (legalist), Li Kui and Shang Yang, and more administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manumission
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing slaves by their owners. Different approaches to manumission were developed, each specific to the time and place of a particular society. Historian Verene Shepherd states that the most widely used term is gratuitous manumission, "the conferment of freedom on the enslaved by enslavers before the end of the slave system". The motivations for manumission were complex and varied. Firstly, it may present itself as a sentimental and benevolent gesture. One typical scenario was the freeing in the master's will (law), will of a devoted servant after long years of service. A trusted bailiff might be manumitted as a gesture of gratitude. For those working as agricultural labourers or in workshops, there was little likelihood of being so noticed. In general, it was more common for older slaves to be given freedom. Legislation under the early Roman Empire put limits on the number of slaves that could be freed in wills (''lex Fufia Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
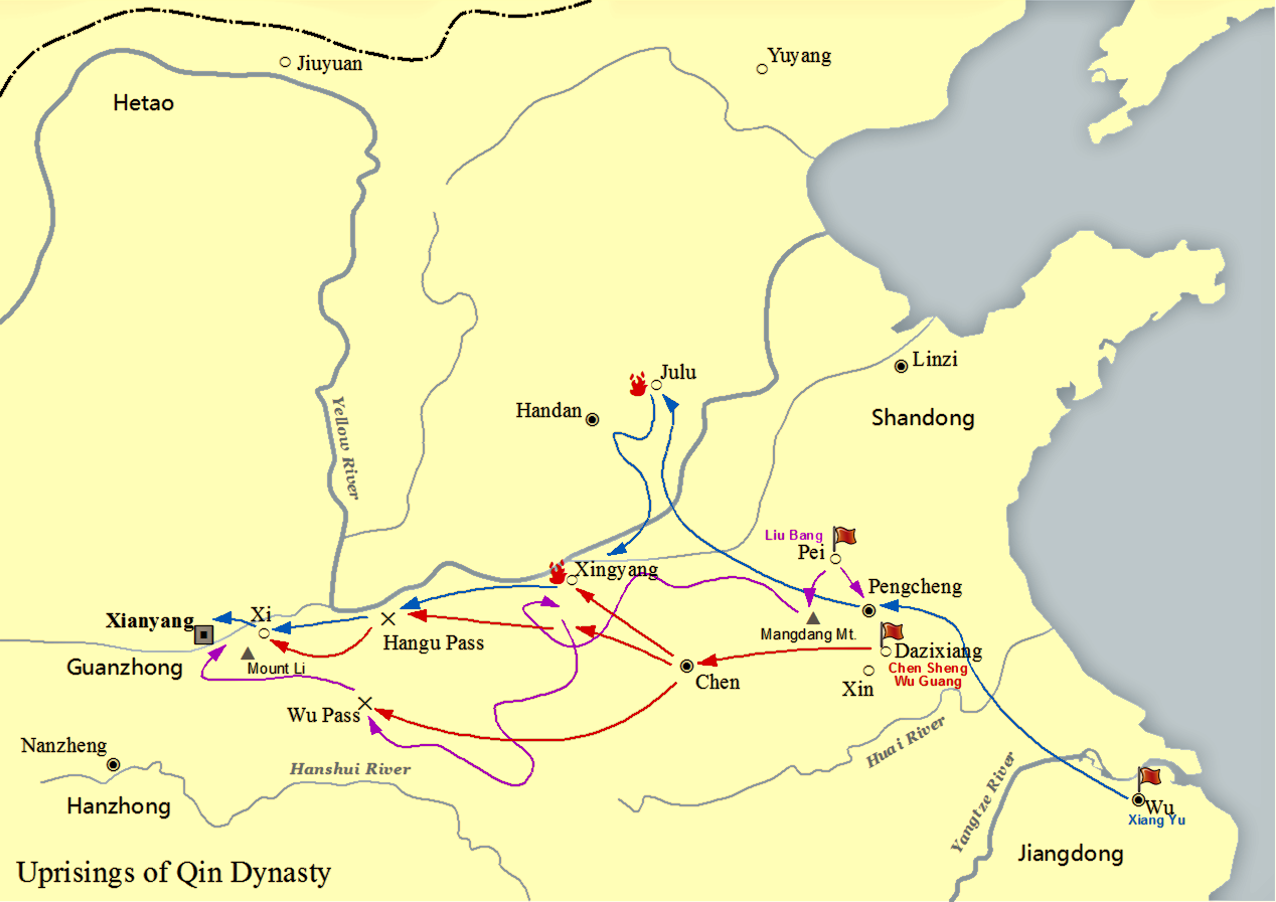
Emperor Gaozu Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (2561 June 195 BC), also known by his given name Liu Bang, was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 202 to 195 BC. He is considered by traditional Chinese historiography to be one of the greatest emperors in history, credited with establishing the first Pax Sinica, one of China's longest golden ages. Liu Bang was among the few dynastic founders to have been born in a peasant family. He initially entered the Qin dynasty bureaucracy as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town in Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. During the political chaos following the death of Qin Shi Huang, who had been the first emperor in Chinese history, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became a rebel leader, taking up arms against the Qin dynasty. He outmanoeuvred rival rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland and forced the surrender of the Qin ruler Ziying in 206 BC. After the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Reclamation
Land reclamation, often known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new Terrestrial ecoregion, land from oceans, list of seas, seas, Stream bed, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamation ground, reclaimed land, or land fill. History In ancient Egypt, the rulers of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt, Twelfth Dynasty (c. 2000–1800 BC) undertook a far-sighted land reclamation scheme to increase agricultural output. They constructed levees and canals to connect the Faiyum Oasis, Faiyum with the Bahr Yussef waterway, diverting water that would have flowed into Lake Moeris and causing gradual evaporation around the lake's edges, creating new farmland from the reclaimed land. A similar land reclamation system using dams and drainage canals was used in the Greek Lake Copais, Copaic Basin during the Middle Helladic period, Middle Helladic Period (c. 1900–1600 BC). Another early large-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |