|
Sixty-four (ship)
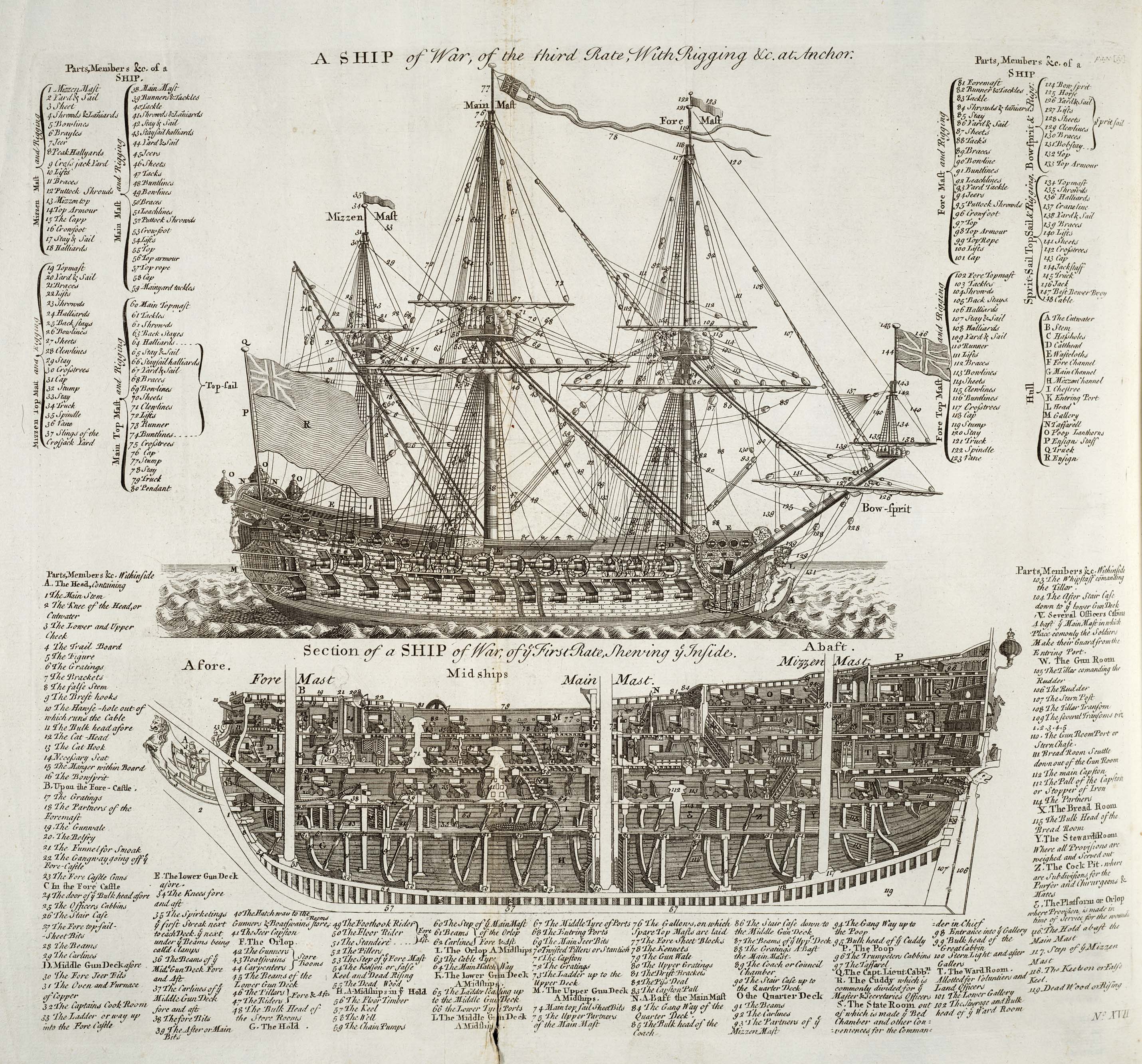
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with second rates having between 90 and 98 guns, while first rates had 100 guns or more, and fourth rates between 48 and 60 guns. By the latter half of the 18th century, they carried between 500 and 720 men. This designation became especially common because it included the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rate Ship-of-the-line 20100306-2
Third or 3rd may refer to: Numbers * 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3 * , a fraction of one third * 1⁄60 of a ''second'', i.e., the third in a series of fractional parts in a sexagesimal number system Places * 3rd Street (other) * Third Avenue (other) * Highway 3 Music Music theory * Interval number of three in a musical interval **Major third, a third spanning four semitones **Minor third, a third encompassing three half steps, or semitones **Neutral third, wider than a minor third but narrower than a major third ** Augmented third, an interval of five semitones **Diminished third, produced by narrowing a minor third by a chromatic semitone *Third (chord), chord member a third above the root *Degree (music), three away from tonic **Mediant, third degree of the diatonic scale **Submediant, sixth degree of the diatonic scale – three steps below the tonic ** Chromatic mediant, chromatic relationship by thirds *Ladder of thirds, similar to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rating System Of The Royal Navy
The rating system of the Royal Navy and its predecessors was used by the Royal Navy between the beginning of the 17th century and the middle of the 19th century to categorise sailing warships, initially classing them according to their assigned complement of men, and later according to the number of their carriage-mounted guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy formally came to an end in the late 19th century by declaration of the Admiralty; rating ships by the number of guns had become obsolete with new types of gun, the introduction of steam propulsion and the use of iron and steel armour. Origins and description The first movement towards a English naval rating system began in the early 16th century, when the largest carracks in the Tudor navy, such as ''Mary Rose'', ''Peter Pomegranate'' and '' Henry Grace à Dieu'', were denoted as "great ships". This was due only to their size, not to their weight, crew or number of guns. When these carracks were superseded by ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Of The Line
A ship of the line was a type of naval warship constructed during the Age of Sail from the 17th century to the mid-19th century. The ship of the line was designed for the naval tactics in the Age of Sail, naval tactic known as the line of battle, which involved the two columns of opposing warships manoeuvering to volley fire with the naval cannon, cannons along their Broadside (naval), broadsides. In conflicts where opposing ships were both able to fire from their broadsides, the faction with more cannons firingand therefore more firepowertypically had an advantage. From the end of the 1840s, the introduction of steam engine, steam power brought less dependence on the wind in battle and led to the construction of propeller, screw-driven wooden-hulled ships of the line; a number of purely sail-powered ships were converted to this propulsion mechanism. However, the rise of the ironclad warship, ironclad frigate, starting in 1859, made steam-assisted ships of the line obsolete. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Deck
The term gun deck used to refer to a deck aboard a ship that was primarily used for the mounting of cannon A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ... to be fired in broadsides. The term is generally applied to decks enclosed under a roof; smaller and Rating system of the Royal Navy#Unrated vessels, unrated vessels carried their guns on the Deck (ship)#Upper deck, upper deck, forecastle and quarterdeck, and these were not described as gun decks.Knight, p 798Cutler, p 107 Slang The term "gun decking" is also naval slang for fabricating or falsifying something. A possible explanation relates to midshipmen retiring to the gun deck to complete their celestial navigation assignments of computing the ship's position three times daily following morning Star-Sighting, star sights, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-decker
A two-decker is a sail warship which carried her guns on two fully armed decks. Usually additional guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous battery and thus not counted as a full gun deck. Two-deckers ranged all the way from the small 40-gun Fifth rate up to 80- or even 90-gun ships of the line, with the third-rate of seventy-four guns, or " seventy-four", being the archetype. See also * Three-decker A three-decker was a sailing warship which carried her principal carriage-mounted guns on three fully armed decks. Usually additional (smaller) guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous ba ... References Naval sailing ship types {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Rate
In 1603 all English warships with a complement of fewer than 160 men were known as 'small ships'. In 1625/26 to establish pay rates for officers, a six-tier naval ship rating system was introduced.Winfield 2009 These small ships were divided into three tiers: fourth-, fifth- and sixth-rates. Up to the end of the 17th century, the number of guns and the complement size were adjusted until the rating system was actually clarified. A 'fourth-rate' was nominally a ship of over thirty guns with a complement of 140 men. In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorize sailing warships in the 18th century, a fourth-rate was a ship of the line with 46 to 60 guns mounted. They were phased out of ship of the line service during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, as their usefulness was declining; though they were still in service, especially on distant stations such as the East Indies. ''Fourth-rates'' took many forms, initially as small two-decked warships, later a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventy-four (ship)
The "seventy-four" was a type of two-gun deck, decked sailing ship of the line, which nominally carried 74 guns. It was developed by the French navy in the 1740s, replacing earlier classes of 60- and 62-gun ships, as a larger complement to the recently developed 64-gun ships. Impressed with the performance of several captured French seventy-fours, the British Royal Navy quickly adopted similar designs, classing them as third rates. The type then spread to the Spanish, Dutch, Danish and Russian navies. The design was considered a good balance between firepower and sailing qualities. Hundreds of seventy-fours were constructed, becoming the dominant form of ship-of-the-line. They remained the wikt:mainstay, mainstay of most major fleets into the early 19th century. From the 1820s, they began to be replaced by larger two-decked ships mounting more guns. However, some seventy-fours remained in service until the late 19th century, when they were finally supplanted by ironclad warship, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-decker
A three-decker was a sailing warship which carried her principal carriage-mounted guns on three fully armed decks. Usually additional (smaller) guns were carried on the upper works (forecastle and quarterdeck), but this was not a continuous battery and so did not count as a "fourth deck". Three-deckers were usually "ships of the line", i.e. of sufficient strength to participate in the line of battle, and in the rating system of the Royal Navy were generally classed as first or second rates, although from the mid-1690s until the 1750s the larger of the third rate In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Rating When the rating system was f ...s were also three-deckers. Three-deckers also served in the naval forces of other European states, notably those of France, Russia and Spain. The French definition of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Melville And Graham Island
HMS or hms may refer to: Education * Habib Medical School, of the Islamic University in Uganda * Hartley–Melvin–Sanborn Community School District of Iowa, United States * Harvard Medical School of Harvard University * Heidelberg Middle School, a former American school in Heidelberg, Germany * Hongwanji Mission School, in Hawaii, United States * Horley Methodist School, Teluk Intan, in Malaysia Medicine and science * Hartford Medical Society, an American professional association based in Hartford, Connecticut * Health management system * Hexose monophosphate shunt, an alternative name for the pentose phosphate pathway * Highly migratory species, a classification of fish * Hypermobility spectrum disorder, formerly hypermobility syndrome or HMS * HMS, a brand name of medrysone Technology *Huawei Mobile Services, proprietary apps and services from Huawei bundled with Android devices * HMS Networks, a company in the field of industrial communications * Heavy melting s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Sail
The Age of Sail is a period in European history that lasted at the latest from the mid-16th (or mid-15th) to the mid-19th centuries, in which the dominance of sailing ships in global trade and warfare culminated, particularly marked by the introduction of naval artillery, and ultimately reached its highest extent at the advent of steam power. Enabled by the advances of the related age of navigation, it is identified as a distinctive element of the early modern period and the Age of Discovery. Periodization Like most periodic eras, defining the age is inexact and serves only as a general description. The term is used differently for warships and merchant vessels. By the 14th century naval artillery was employed in Europe, documented at the Battle of Arnemuiden (1338). The 15th century saw the Iberian naval ventures all the way along the African Atlantic coast and across the Atlantic Ocean, starting the Age of Discovery. For warships, the age of sail runs roughly from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |