|
Six Arts
The Six Arts formed the basis of education in ancient Chinese culture. These were made and practiced by the Confucians. History During the Zhou dynasty (1122–256 BCE), students were required to master the "liù yì" (六藝) (''Six Arts''): * Rites (禮) * Music (樂) * Archery (射) * Chariotry or Equestrianism (御) * Calligraphy (書) or Literature * Mathematics (數) Men who excelled in these six arts were thought to have reached the state of perfection, becoming a perfect gentleman. The Six Arts were practiced by scholars and existed before Confucius, but became a part of Confucian philosophy. As such, Xu Gan (170–217 CE) discusses them in the ''Balanced Discourses''. The Six Arts were practiced by the 72 disciples of Confucius. The Six Arts concept developed during the pre-imperial period. It incorporated both military and civil components. The civil side was later associated with the four arts ( qin playing, chess, calligraphy and painting). However, the latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as White and Black in chess, "White" and "Black", each control sixteen Chess piece, pieces: one king (chess), king, one queen (chess), queen, two rook (chess), rooks, two bishop (chess), bishops, two knight (chess), knights, and eight pawn (chess), pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "checkmate" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw (chess), draw. The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of chaturanga—also thought to be an ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analects
The ''Analects'', also known as the ''Sayings of Confucius'', is an ancient Chinese philosophical text composed of sayings and ideas attributed to Confucius and his contemporaries, traditionally believed to have been compiled by his followers. The consensus among scholars is that large portions of the text were composed during the Warring States period (475–221 BC), and that the work achieved its final form during the mid-Han dynasty (206 BC220 AD). During the early Han, the ''Analects'' was merely considered to be a commentary on the Five Classics. However, by the dynasty's end the status of the ''Analects'' had grown to being among the central texts of Confucianism. During the late Song dynasty (960–1279 AD) the importance of the ''Analects'' as a Chinese philosophy work was raised above that of the older Five Classics, and it was recognized as one of the "Four Books". The ''Analects'' has been one of the most widely read and studied books in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism (, often shortened to ''lǐxué'' 理學, literally "School of Principle") is a moral, ethical, and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, which originated with Han Yu (768–824) and Li Ao (772–841) in the Tang dynasty, and became prominent during the Song and Ming dynasties under the formulations of Zhu Xi (1130–1200). After the Mongol conquest of China in the thirteenth century, Chinese scholars and officials restored and preserved neo-Confucianism as a way to safeguard the cultural heritage of China. Neo-Confucianism could have been an attempt to create a more rationalist and secular form of Confucianism by rejecting mystical elements of Taoism and Buddhism that had influenced Confucianism during and after the Han dynasty. Although the neo-Confucianists were critical of Taoism and Buddhism, the two did have an influence on the philosophy, and the neo-Confucianists borrowed terms and concepts. However, unlike the Buddhists and Tao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Shijie
Zhu Shijie (, 1249–1314), courtesy name Hanqing (), pseudonym Songting (), was a Chinese mathematician and writer during the Yuan Dynasty. Zhu was born close to today's Beijing. Two of his mathematical works have survived: ''Introduction to Computational Studies'' ( ''Suan-hsüeh Ch'i-mong'') and ''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'' ( ''Ssŭ-yüan Yü-chien''). ''Suanxue Qimeng'' The ''Suanxue Qimeng'' (), written in 1299, is an elementary textbook on mathematics in three volumes, 20 chapters and 259 problems. This book also showed how to measure two-dimensional shapes and three-dimensional solids. The ''Introduction'' strongly influenced the development of Japanese mathematics, mathematics in Japan. The book was once lost in China until the Qing dynasty mathematician Luo Shilin bought a Korean printed edition and republished it in Yangzhou. ''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'' Zhu's second book, ''Jade Mirror of the Four Unknowns'' (1303) was his most important work, advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
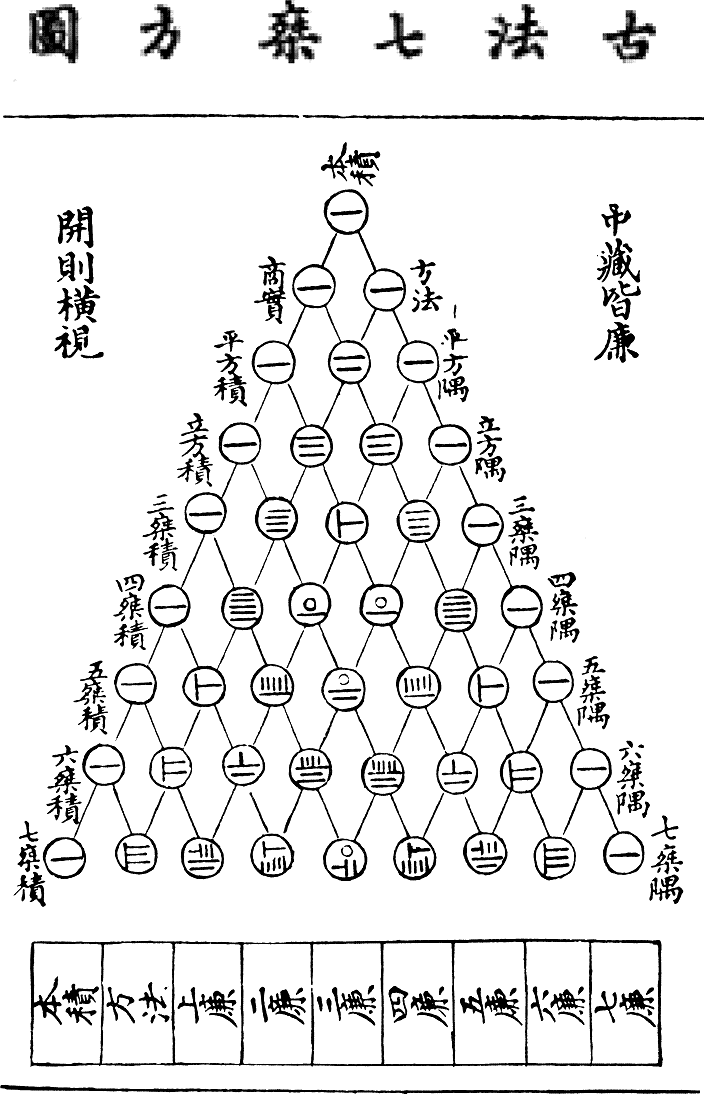
Yang Hui
Yang Hui (, ca. 1238–1298), courtesy name Qianguang (), was a Chinese mathematician and writer during the Song dynasty. Originally, from Qiantang (modern Hangzhou, Zhejiang), Yang worked on magic squares, magic circles and the binomial theorem, and is best known for his contribution of presenting Yang Hui's triangle. This triangle was the same as Pascal's triangle, discovered by Yang's predecessor Jia Xian. Yang was also a contemporary of Qin Jiushao, another well-known Chinese mathematician. Written work The earliest extant Chinese illustration of 'Pascal's triangle' is from Yang's book ''Xiángjiě Jiǔzhāng Suànfǎ '' () of 1261 AD, in which Yang acknowledged that his method of finding square roots and cubic roots using "Yang Hui's triangle" was invented by mathematician Jia XianNeedham, Volume 3, 134-137. who expounded it around 1100 AD, about 500 years before Pascal. His book (now lost), known as ''Rújī Shìsuǒ'' () or ''Piling-up Powers and Unlocking Coeffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo (; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and Art name#China, pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁),Yao (2003), 544. was a Chinese polymath, scientist, and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen was a master in many fields of study including Chinese mathematics, mathematics, history of optics, optics, and horology. In his career as a civil servant, he became a finance minister, governmental state inspector, head official for the Chinese astronomy, Bureau of Astronomy in the Song court, Assistant Minister of Imperial Hospitality, and also served as an Chancellor (education), academic chancellor.Needham (1986), Volume 4, Part 2, 33. At court his political allegiance was to the Reformist faction known as the History of the Song dynasty#Partisans and factions, reformers and conservatives, New Policies Group, headed by Chancellor of China, Chancellor Wang Anshi (1021–1085). In his ''Dream Pool Essays'' or ''Dream Torren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zu Chongzhi
Zu Chongzhi (; 429 – 500), courtesy name Wenyuan (), was a Chinese astronomer, inventor, mathematician, politician, and writer during the Liu Song and Southern Qi dynasties. He was most notable for calculating pi as between 3.1415926 and 3.1415927, a record in precision which would not be surpassed for nearly 900 years. Life and works Chongzhi's ancestry was from modern Baoding, Hebei. To flee from the ravages of war, Zu's grandfather Zu Chang moved to the Yangtze, as part of the massive population movement during the Eastern Jin. Zu Chang () at one point held the position of Chief Minister for the Palace Buildings () within the Liu Song and was in charge of government construction projects. Zu's father, Zu Shuozhi (), also served the court and was greatly respected for his erudition. Zu was born in Jiankang. His family had historically been involved in astronomical research, and from childhood Zu was exposed to both astronomy and mathematics. When he was only a youth, his t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Hui
Liu Hui () was a Chinese mathematician who published a commentary in 263 CE on ''Jiu Zhang Suan Shu ( The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art).'' He was a descendant of the Marquis of Zixiang of the Eastern Han dynasty and lived in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 CE) of China. His major contributions as recorded in his commentary on ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' include a proof of the Pythagorean theorem, theorems in solid geometry, an improvement on Archimedes's approximation of , and a systematic method of solving linear equations in several unknowns. In his other work, '' Haidao Suanjing (The Sea Island Mathematical Manual)'', he wrote about geometrical problems and their application to surveying. He probably visited Luoyang, where he measured the sun's shadow. Mathematical work Liu Hui expressed mathematical results in the form of decimal fractions that utilized metrological units (i.e., related units of length wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Man
A polymath or polyhistor is an individual whose knowledge spans many different subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific problems. Polymaths often prefer a specific context in which to explain their knowledge, but some are gifted at explaining abstractly and creatively. Embodying a basic tenet of Renaissance humanism that humans are limitless in their capacity for development, the concept led to the notion that people should embrace all knowledge and develop their capacities as fully as possible. This is expressed in the term Renaissance man, often applied to the gifted people of that age who sought to develop their abilities in all areas of accomplishment: intellectual, artistic, social, physical, and spiritual. Etymology The word polymath derives from the Greek roots ''poly-'', which means "much" or "many," and ''manthanein'', which means "to learn." Plutarch wrote that the Ancient Greek muse Polyhymnia was sometimes known as Polymathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Go (game)
# Go is an abstract strategy game, abstract strategy board game for two players in which the aim is to fence off more territory than the opponent. The game was invented in China more than 2,500 years ago and is believed to be the oldest board game continuously played to the present day. A 2016 survey by the International Go Federation's 75 member nations found that there are over 46 million people worldwide who know how to play Go, and over 20 million current players, the majority of whom live in East Asia. The Game piece (board game), playing pieces are called ''Go equipment#Stones, stones''. One player uses the white stones and the other black stones. The players take turns placing their stones on the vacant intersections (''points'') on the #Boards, board. Once placed, stones may not be moved, but ''captured stones'' are immediately removed from the board. A single stone (or connected group of stones) is ''captured'' when surrounded by the opponent's stones on all Orthogona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |