|
Sikh Art
Sikh art, also known as the Sikh School, is the artwork created by or associated with Sikhs. Sikh artwork exists in many forms, such as miniature, oil, and watercolour paintings, murals, and wood carvings. Terminology Naqqash The word 'naqqash' is equivalent to the meaning of ''chitrakar'', and means "decorator" or "illuminator" and refers to a painter or artist. Naqqash artists were employed to illuminate Perso-Arabic manuscripts, ornamentation of addresses, letter heads, ''nikah-namahs'' (marriage certificates), ''idis, janam patris'' (horoscopes) and other kinds of records, and the embellishment of calligraphy. The Sikh school of naqqash was initially influenced by Muslim and Vaishnavist Naqqash artists since the initial ones employed to work at the Harmandir Sahib complex during the beautification project by Ranjit Singh were of this background. Some Naqqashi artists belonged to a familial lineage of artists whilst others had been trained specifically by an existing naqq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'. Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh'' ('lion'/'tiger') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world. Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar'' ('baptism by Khanda (Sikh symbol), Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajput Painting
Rajput painting, also called Rajasthan painting, evolved and flourished in the royal courts of Rajputana in northern India, mainly during the 17th century. Artists trained in the tradition of the Mughal miniature were dispersed from the imperial Mughal court and developed styles also drawing from local traditions of painting, especially those illustrating the Hindu religious epics, the ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana''. Subjects varied, but portraits of the ruling family, often engaged in hunting or their daily activities, were generally popular, as were narrative scenes from the epics or Hindu mythology, as well as some genre scenes of unnamed people. The colors were extracted from certain minerals, plant sources, and conch shells, and were even derived by processing precious stones. Gold and silver were used. The preparation of desired colors was a lengthy process, sometimes taking up to two weeks. Traditionally, fine brushes were the norm. Content While there exist a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phulkian Dynasty
The Phulkian (or Phoolkian) Maharajas were Jat-Sikh rulers and aristocrats in the Punjab region of India. They governed the states of Faridkot, Jind, Nabha, Malaudh and Patiala, allying themselves with the British Raj as per the Cis-Sutlej treaty. Lineage The rulers of the Phulkian states shared a common ancestor, the 18th-century Chaudhary Phul Singh Sidhu-Brar. Chaudhary Phul was born in 1629, to Chaudhary Rup Chand and Mat Ambi. He lived through the times of Guru Hargobind Ji, the sixth guru of the Sikh religion as well as Guru Har Rai Ji , the seventh Guru. The legends of Phul say that Chaudhary Phul Singh was given blessings from both Guru Hargobind Ji and Guru Har Rai Ji. Guru Hargobind Ji declared that Phul would have many "blossoms" like a flower (Phul or "phool" is a Punjabi word for flower). Phul's descendants went on to pursue this blessing by ruling the states of Nabha, Jind, Faridkot, Kaithal and Patiala. The Maharajas of all three Phulkian states had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patiala State
Patiala State was a self-governing princely state of the British Empire in India, and one of the Phulkian States, that acceded to the Union of India upon Indian independence and partition. Patiala Kingdom/State was founded by Sidhu Jat Sikhs. Early proposals of a Sikh nation of ‘Sikhistan’ led by Maharaja of Patiala were published by Dr VS Bhatti in 1940 for a “Khalistan led by the Maharaja of Patiala with the aid of a cabinet consisting of representative federating units.”. These would consist of the central districts of Punjab province then directly administered by the British, including Ludhiana, Jalandhar, Ambala, Ferozpur, Amritsar and Lahore; the 'princely states' of the Cis-Sutlej, including Patiala, Nabha, Faridkot and Malerkolta; and the 'Shimla Group' of states. After partition of India in 1947, The Liberator, a Sikh publication advocated for Khalistan which would include East Punjab merged with PEPSU led by Maharaja of Patiala as it’s Monarch. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durbar (court)
Durbar is a Persian-derived term (from fa, دربار - ''darbār'') meaning the kings’ or rulers’ noble court or a formal meeting where the king held all discussions regarding the state. It was used in India for a ruler's court or feudal levy as the latter came to be ruled and later administered by foreigners. A durbar may be either a feudal state council for administering the affairs of a princely state, or a purely ceremonial gathering, as in the time of the British Empire in India. The most famous Durbars belonged to great Emperors and Kings. In the north of India cities like Baroda, Gwalior, Udaipur, Jaipur, Jodhpur, Jaiselmer, and Agra and the city of Lahore in Pakistan, have palaces and forts that adorn such magnificent halls. The Mughal Emperor Akbar had two halls; one for his ministers and the other for the general public. Usually Durbar halls are lavishly decorated with the best possible materials available at the time. In the south of India, the Mysore Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malwa (Punjab)
Malwa is a geographical region in the south of Punjab state in India. It is located between Haryana, Rajasthan, Sutlej and Ghaggar rivers. Districts of Malwa The following districts are classified as Malwa: * Barnala * Bathinda * Faridkot * Fatehgarh Sahib * Fazilka * Firozpur * Ludhiana * Malerkotla * Mansa * Moga * Mohali Mohali, officially known as Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, is a planned city in the Mohali district in Punjab (India), Punjab, India, which is an administrative and a commercial hub lying south-west of Chandigarh. It is the headquarters of the Moh ... * Muktsar Sahib * Patiala * Sangrur Parts of these districts also speak Malwai Punjabi, and are considered a part of Malwa * Sirsa * Fatehabad See also * Doaba * Majha * Poadh References * '' Mahankosh'', Bhai Kahn Singh Nabha {{coord, 30.5000, N, 76.0000, E, source:wikidata, display=title Geography of Punjab, India Landforms of Punjab, India Plains of India Regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. Stucco can be applied on construction materials such as metal, expanded metal lath, concrete, cinder block, or clay brick and adobe for decorative and structural purposes. In English, "stucco" sometimes refers to a coating for the outside of a building and " plaster" to a coating for interiors; as described below, however, the materials themselves often have little to no differences. Other European languages, notably Italian, do not have the same distinction; ''stucco'' means ''plaster'' in Italian and serves for both. Composition The basic composition of stucco is cement, water, and sand. The difference in nomenclature between stucco, plaster, and mortar is based more on use than composition. Until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
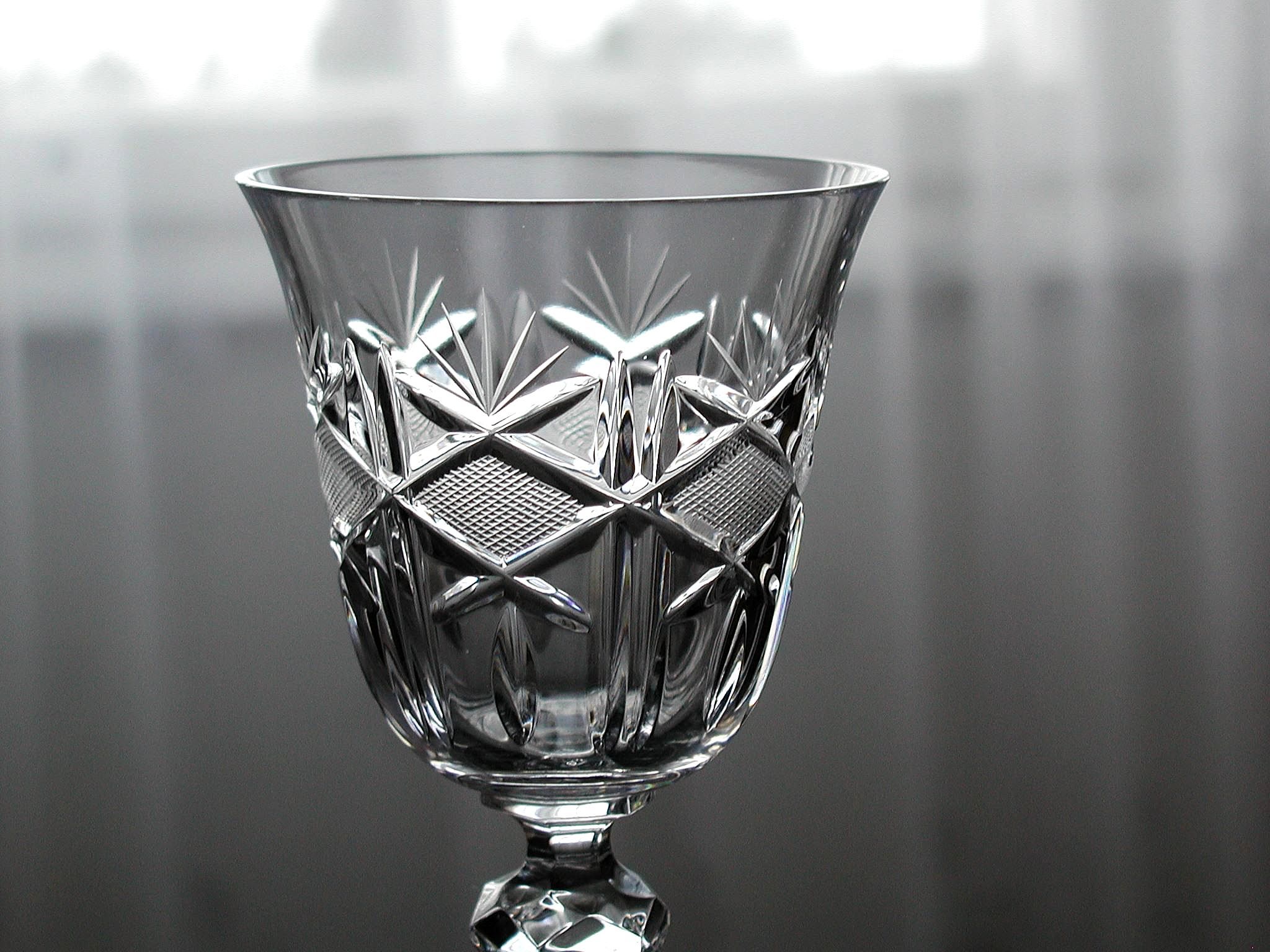
Cut Glass
Cut glass or cut-glass is a technique and a style of decorating glass. For some time the style has often been produced by other techniques such as the use of moulding, but the original technique of cutting glass on an abrasive wheel is still used in luxury products. On glassware vessels, the style typically consists of furrowed faces at angles to each other in complicated patterns, while for lighting fixtures, the style consists of flat or curved facets on small hanging pieces, often all over. Historically, cut glass was shaped using "coldwork" techniques of grinding or drilling, applied as a secondary stage to a piece of glass made by conventional processes such as glassblowing. Today, the glass is often mostly or entirely shaped in the initial process by using a mould ( pressed glass), or imitated in clear plastic. Traditional hand-cutting continues, but gives a much more expensive product. Lead glass has long been misleadingly called "crystal" by the industry, evoking the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word ''fresco'' ( it, affresco) is derived from the Italian adjective ''fresco'' meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting. The word ''fresco'' is commonly and inaccurately used in English to refer to any wall painting regardless of the plaster technology or binding medium. This, in part, contributes to a misconception that the most geographically and temporally common wall painting technology was the painting into wet lime plaster. Even in app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Roman world. Mosaic today includes not just murals and pavements, but also artwork, hobby crafts, and industrial and construction forms. Mosaics have a long history, starting in Mesopotamia in the 3rd millennium BC. Pebble mosaics were made in Tiryns in Mycenean Greece; mosaics with patterns and pictures became widespread in classical times, both in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome. Early Christian basilicas from the 4th century onwards were decorated with wall and ceiling mosaics. Mosaic art flourished in the Byzantine Empire from the 6th to the 15th centuries; that tradition was adopted by the Norman Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century, by the eastern-influenced Republic of Venice, and among the Rus. Mosaic fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839), popularly known as Sher-e-Punjab or "Lion of Punjab", was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire, which ruled the northwest Indian subcontinent in the early half of the 19th century. He survived smallpox in infancy but lost sight in his left eye. He fought his first battle alongside his father at age 10. After his father died, he fought several wars to expel the Afghans in his teenage years and was proclaimed as the "Maharaja of Punjab" at age 21. His empire grew in the Punjab region under his leadership through 1839. Prior to his rise, the Punjab region had numerous warring misls (confederacies), twelve of which were under Sikh rulers and one Muslim. Ranjit Singh successfully absorbed and united the Sikh misls and took over other local kingdoms to create the Sikh Empire. He repeatedly defeated invasions by outside armies, particularly those arriving from Afghanistan, and established friendly relations with the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronage
Patronage is the support, encouragement, privilege, or financial aid that an organization or individual bestows on another. In the history of art, arts patronage refers to the support that kings, popes, and the wealthy have provided to artists such as musicians, painters, and sculptors. It can also refer to the right of bestowing offices or church benefices, the business given to a store by a regular customer, and the guardianship of saints. The word "patron" derives from the la, patronus ("patron"), one who gives benefits to his clients (see Patronage in ancient Rome). In some countries the term is used to describe political patronage or patronal politics, which is the use of state resources to reward individuals for their electoral support. Some patronage systems are legal, as in the Canadian tradition of the Prime Minister to appoint senators and the heads of a number of commissions and agencies; in many cases, these appointments go to people who have supported the politic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)

_(31023042187)_CROP.jpg)