|
Significant Figures
Significant figures, also referred to as significant digits, are specific digits within a number that is written in positional notation that carry both reliability and necessity in conveying a particular quantity. When presenting the outcome of a measurement (such as length, pressure, volume, or mass), if the number of digits exceeds what the measurement instrument can resolve, only the digits that are determined by the resolution are dependable and therefore considered significant. For instance, if a length measurement yields 114.8 mm, using a ruler with the smallest interval between marks at 1 mm, the first three digits (1, 1, and 4, representing 114 mm) are certain and constitute significant figures. Further, digits that are uncertain yet meaningful are also included in the significant figures. In this example, the last digit (8, contributing 0.8 mm) is likewise considered significant despite its uncertainty. Therefore, this measurement contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
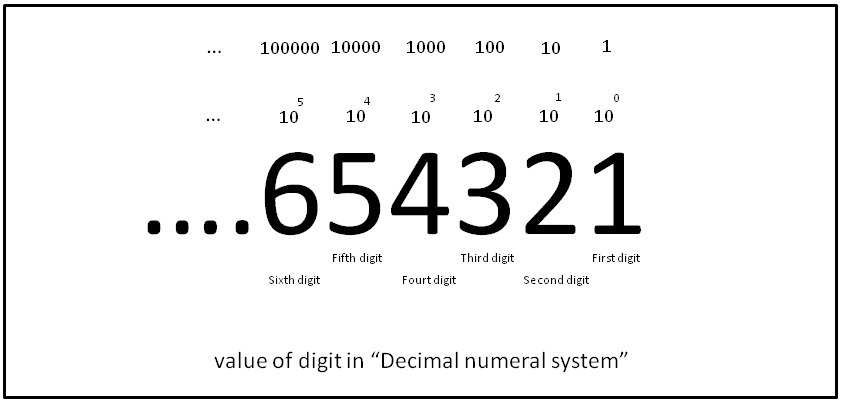
Numerical Digit
A numerical digit (often shortened to just digit) or numeral is a single symbol used alone (such as "1"), or in combinations (such as "15"), to represent numbers in positional notation, such as the common base 10. The name "digit" originates from the Latin ''digiti'' meaning fingers. For any numeral system with an integer base, the number of different digits required is the absolute value of the base. For example, decimal (base 10) requires ten digits (0 to 9), and binary (base 2) requires only two digits (0 and 1). Bases greater than 10 require more than 10 digits, for instance hexadecimal (base 16) requires 16 digits (usually 0 to 9 and A to F). Overview In a basic digital system, a numeral is a sequence of digits, which may be of arbitrary length. Each position in the sequence has a place value, and each digit has a value. The value of the numeral is computed by multiplying each digit in the sequence by its place value, and summing the results. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and in many other branches of mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers, sometimes called "the reals", is traditionally denoted by a bold , often using blackboard bold, . The adjective ''real'', used in the 17th century by René Descartes, distinguishes real numbers from imaginary numbers such as the square roots of . The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real numbers are called irrational numbers. Some irrational numbers (as well as all the rationals) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mic Speed Limit
Mic or MIC may refer to: * Microphone, an acoustic transducer Places * Federated States of Micronesia, UNDP country code * Miami Intermodal Center, a mega-transportation hub in Miami, Florida People * Mic (name), numerous people Arts, entertainment, and media * M.I.C. (band), a Chinese band formed by Taihe Rye Music * Mic (media company), a media company focused on news for millennials * Mic, an abbreviation for referencing the '' Book of Micah'' * ''Made in Chelsea'', a television series Organizations Business * Metal Improvement Company, a company specializing in metal surface treatments * Merida Industry Co., Ltd., a bicycle manufacturing company in Taiwan * Military Industries Corporation (Saudi Arabia), the main armament industry for the Saudi military * Military Industry Corporation, the main armament industry for the Sudanese military * Myanmar Investment Commission, a government-appointed body * Mortgage investment corporation, a Canadian investment and lendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Significant Figures Rules Explained
Significance is a synonym for importance. It can also refer to: * ''Significance'' (magazine), a magazine published by the Royal Statistical Society and the American Statistical Association * Significance (policy debate), a stock issue in policy debate * Significant figures or significant digits, the precision of a numerical value * Statistical significance In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when a result at least as "extreme" would be very infrequent if the null hypothesis were true. More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the ..., the extent to which a result is unlikely to be due to chance alone See also * Meaning (other) * Significand, part of a number in floating-point representation {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal Separator
FIle:Decimal separators.svg, alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for international use. The apostrophe and Arabic decimal separator are also used in certain contexts. A decimal separator is a symbol that separates the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form. Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choice of symbol can also affect the choice of symbol for the #Digit grouping, thousands separator used in digit grouping. Any such symbol can be called a decimal mark, decimal marker, or decimal sign. Symbol-specific names are also used; decimal point and decimal comma refer to a dot (either Baseline dot, baseline or Middle dot, middle) and comma respectively, when it is used as a decimal separator; these are the usual terms used in English, with the aforem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rounding
Rounding or rounding off is the process of adjusting a number to an approximate, more convenient value, often with a shorter or simpler representation. For example, replacing $ with $, the fraction 312/937 with 1/3, or the expression √2 with . Rounding is often done to obtain a value that is easier to report and communicate than the original. Rounding can also be important to avoid false precision, misleadingly precise reporting of a computed number, measurement, or estimate; for example, a quantity that was computed as but is known to be accuracy and precision, accurate only to within a few hundred units is usually better stated as "about ". On the other hand, rounding of exact numbers will introduce some round-off error in the reported result. Rounding is almost unavoidable when reporting many computations – especially when dividing two numbers in integer or fixed-point arithmetic; when computing mathematical functions such as square roots, logarithms, and sines; or whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plus–minus Sign
The plus–minus sign or plus-or-minus sign () and the complementary minus-or-plus sign () are symbols with broadly similar multiple meanings. *In mathematics, the sign generally indicates a choice of exactly two possible values, one of which is obtained through addition and the other through subtraction. *In statistics and experimental sciences, the sign commonly indicates the confidence interval or uncertainty bounding a range of possible errors in a measurement, often the standard deviation or standard error. The sign may also represent an inclusive range of values that a reading might have. *In chess, the sign indicates a clear advantage for the white player; the complementary minus-plus sign () indicates a clear advantage for the black player. Other meanings occur in other fields, including medicine, engineering, chemistry, electronics, linguistics, and philosophy. History A version of the sign, including also the French word ''ou'' ("or"), was used in its mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Significand
The significand (also coefficient, sometimes argument, or more ambiguously mantissa, fraction, or characteristic) is the first (left) part of a number in scientific notation or related concepts in floating-point representation, consisting of its significant digits. For negative numbers, it does not include the initial minus sign. Depending on the interpretation of the exponent, the significand may represent an integer or a fractional number, which may cause the term "mantissa" to be misleading, since the ''mantissa'' of a logarithm is always its fractional part. Although the other names mentioned are common, ''significand'' is the word used by IEEE 754, an important technical standard for floating-point arithmetic. In mathematics, the term "argument" may also be ambiguous, since "the argument of a number" sometimes refers to the length of a circular arc from 1 to a number on the unit circle in the complex plane. Example The number 123.45 can be represented as a decimal floati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Of Measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of System of measurement, systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures are often a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Prefix
A unit prefix is a specifier or mnemonic that is added to the beginning of a unit of measurement to indicate multiples or fractions of the units. Units of various order of magnitude, sizes are commonly formed by the use of such prefixes. The Metric prefix, prefixes of the metric system, such as ''kilo-, kilo'' and ''milli-, milli'', represent multiplication by positive or negative exponentiation, powers of ten. In information technology it is common to use binary prefixes, which are based on power of 2, powers of two. Historically, many prefixes have been used or proposed by various sources, but only a narrow set has been recognised by standards organisations. Metric prefixes The prefixes of the metric system precede a basic unit of measure to indicate a decimal, decadic multiple (mathematics), multiple and fraction (mathematics), fraction of a unit. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is added to the beginning of the unit symbol. Some of the prefixes date back to the introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underline
An underscore or underline is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript as an instruction to the printer. Its use to add emphasis in modern finished documents is generally avoided. The (freestanding) underscore character, , also called a low line, or low dash, originally appeared on the typewriter so that underscores could be typed. To produce an underscored word, the word was typed, the typewriter carriage was moved back to the beginning of the word, and the word was overtyped with the underscore character. In modern usage, underscoring is achieved with a markup language, with the Unicode combining low line or as a standard facility of word processing software. The free-standing underscore character is used to indicate word boundaries in situations where spaces are not allowed, such as in computer filenames, email addresses, and in Internet U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |