|
Shuyang County
Shuyang () is a Counties of China, county in northern Jiangsu province. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Suqian. Shuyang sits on the Northern Jiangsu Plains and borders the cities of Xuzhou, Lianyungang, and Huai'an to the north, east, and south. Shuyang is a pilot administrative division for "provinces governing county level units directly" in Jiangsu, along with Kunshan and Taixing. Etymology The name of “Shuyang” was first officially used in 549 AD during Eastern Wei. The two Chinese characters in the county's name are “沭” and “阳”, together meaning “in the north of the Shu River”. As the government and commercial center, the county seat was chosen to be constructed in the north of Shuhe River in 549 AD in order to control the land around the river basin. History Prior to its proclamation as the Zhou dynasty, Zhou Dynasty in 1111 BC, the area around the north of Jiangsu was inhabited by the Dongyi, an ancient ethnic group t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of The People's Republic Of China
zh, p=Xiàn, labels=no , alt_name = , map = , caption = , category = Third level administrative division of a unitary state , territory = People's Republic of China , upper_unit = Prefectures, Provinces , start_date = , current_number = 1,319 (1,307 controlled, 11 claimed) , number_date = 2023 , population_range = , area_range = , government = Various, Central Government , subdivision = Town, Township Counties ( zh, s=县, labels=no) are found in the third level of the administrative hierarchy in provinces and autonomous regions and the second level in municipalities and Hainan, a level that is known as "county level" and also contains autonomous counties, county-level cities, banners, autonomous banners and city districts. There are 1,355 counties in mainland China out of a total of 2,851 county-level divisions. The term ''xian'' is sometimes translated as "district" or "prefecture" when put in the context of Chinese history. History ''Xia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lianyungang
Lianyungang () is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province of China, province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its name derives from Lian Island, the largest island in Jiangsu which lies off its coastline, and Yuntai Mountain, the highest peak in Jiangsu, a few miles from the city center, and the fact that it is a port. The name can be literally translated as the Port Connecting the Clouds. Lianyungang was home to 4.65 million inhabitants as of the 2020 census whom 1,210,767 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of Haizhou and Lianyun counties. Lianyungang was known in the West as Haichow (Postal romanization), which means the City of Sea. Haichow was opened to foreign trade by the Qing imperial government in 1905. Geography Lianyungang is between 118°24' and 119°48' east longitude and 34°11' and 35°07' north latitude. Lianyungang covers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
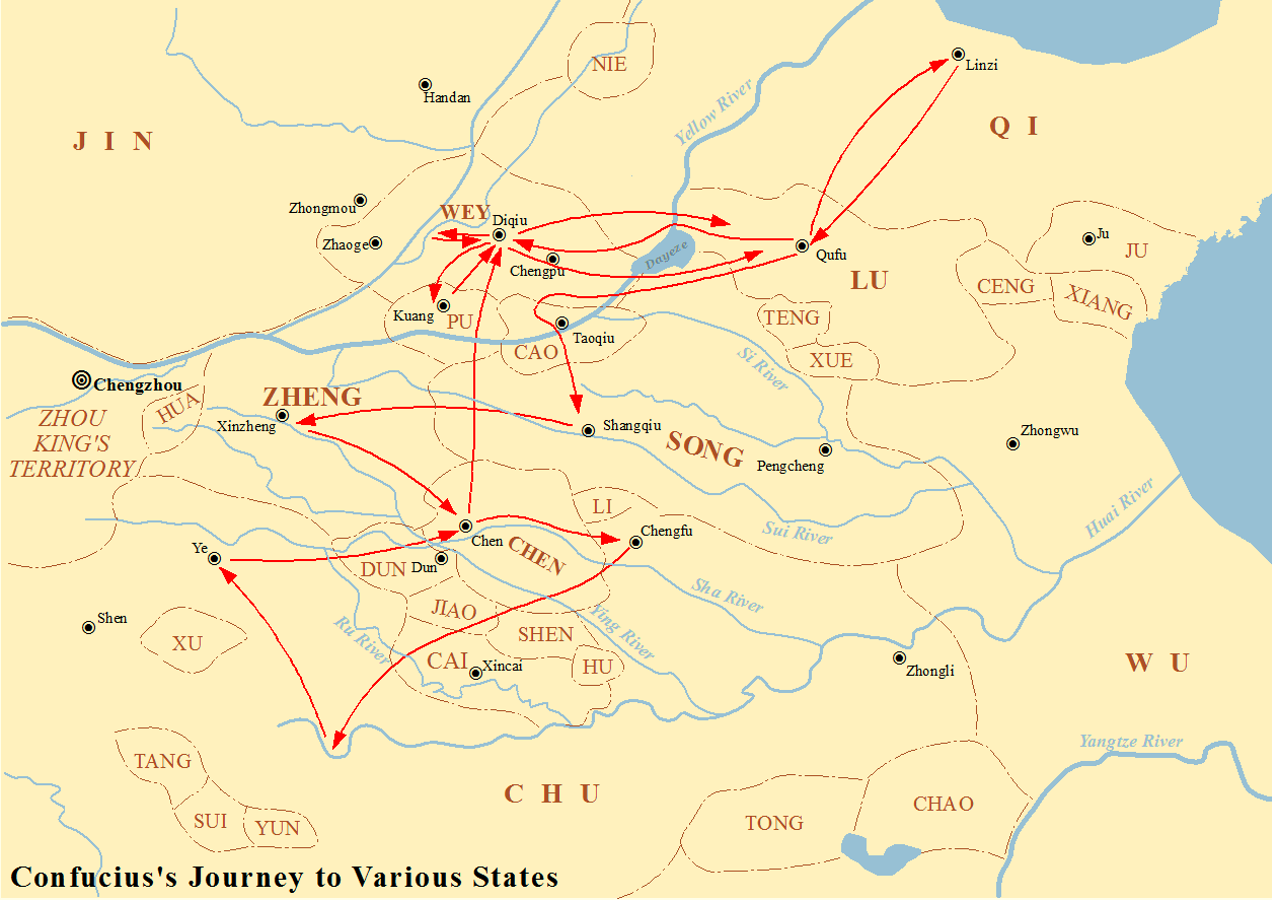
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Annals
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals'' is an ancient Chinese chronicle that has been one of the core Chinese classics since ancient times. ''The Annals'' is the official chronicle of the State of Lu, and covers a 242-year period from 722 to 481 BCE. It is the earliest surviving Chinese historical text to be arranged in annals form. Because it was traditionally regarded as having been compiled by Confucius—after a claim to this effect by Mencius—it was included as one of the Five Classics of Chinese literature. The ''Annals'' records main events that occurred in Lu during each year, such as the accessions, marriages, deaths, and funerals of rulers, battles fought, sacrificial rituals observed, celestial phenomena considered ritually important, and natural disasters. The entries are tersely written, averaging only 10 characters per entry, and contain no elaboration on events or recording of speeches. During the Warring States period (475221 BCE), a number of commentari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu (state)
Lu (; 249 BC) was a vassal Ancient Chinese states, state during the Zhou dynasty of History of China#Ancient China, ancient China located around modern Shandong. Founded in the 11th century BC, its rulers were from a cadet branch of the Jī, House of Ji () that ruled the Zhou dynasty. The first duke was Boqin, a son of the Duke of Zhou, who was brother of King Wu of Zhou and regent to King Cheng of Zhou. Lu was the home state of Confucius as well as Mozi, and, as such, has an outsized cultural influence among the states of the Eastern Zhou and in history. The ''Annals of Spring and Autumn'', for instance, was written with the Lu rulers' years as their basis. Another great work of Chinese history, the ''Zuo Zhuan'' or ''Commentary of Zuo'', was traditionally considered to have been written in Lu by Zuo Qiuming. Geography The state's capital was in Qufu and its territory mainly covered the central and southwest regions of what is now Shandong Province. It was borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
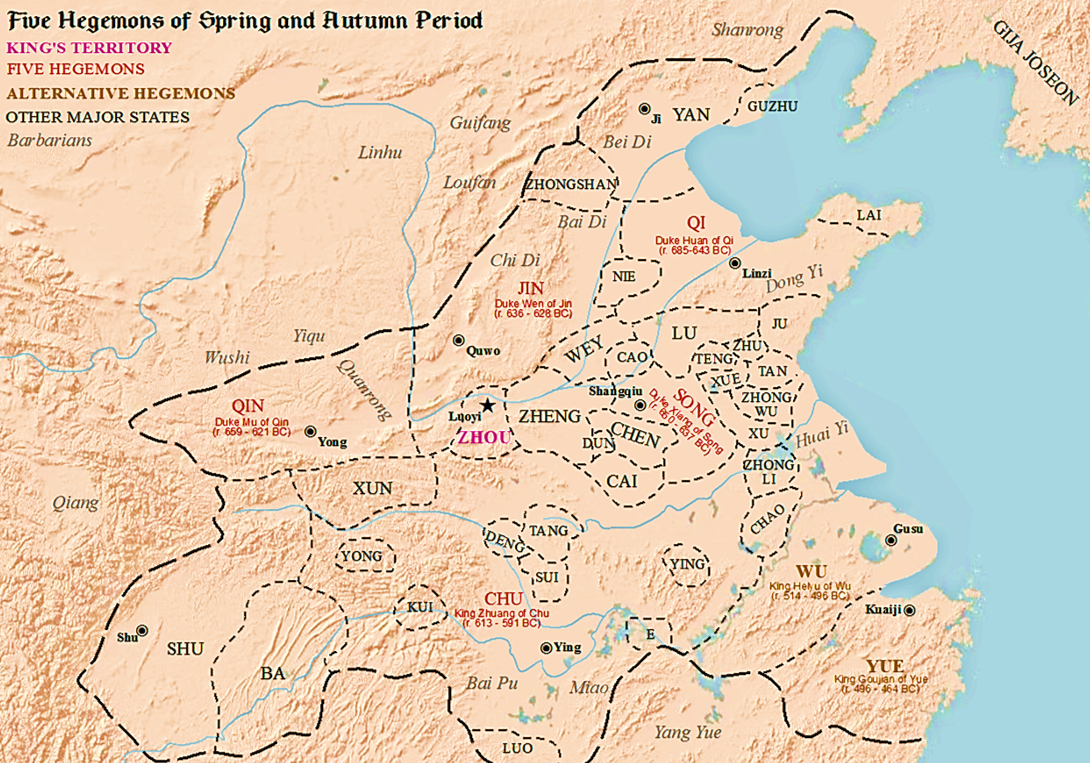
Spring And Autumn Period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject to the Zhou exercised increasing political autonomy. The period's name derives from the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', a chronicle of the state of Lu between 722 and 481 BCE, which tradition associates with Confucius (551–479 BCE). During this period, local polities negotiated their own alliances, waged wars against one another, up to defying the king's court in Luoyang, Luoyi. The gradual Partition of Jin, one of the most powerful states, is generally considered to mark the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the beginning of the Warring States period. The periodization dates to the late Western Han (). Background In 771 BCE, a Quanrong invasion in coalition with the states of Zeng (state), Zeng and Shen (state), Shen— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongyi
The Dongyi or Eastern Yi () was a collective term for ancient peoples found in Chinese records. The definition of Dongyi varied across the ages, but in most cases referred to inhabitants of eastern China, then later, the Korean peninsula and Japanese Archipelago. Dongyi refers to different group of people in different periods. As such, the name "Yí" was something of a catch-all and was applied to different groups over time. According to the earliest Chinese record, the '' Zuo Zhuan'', the Shang dynasty was attacked by King Wu of Zhou while attacking the Dongyi and collapsed afterward. Ancient inhabitants of Eastern China Oracle bone inscriptions from the early 11th century BCE refer to campaigns by the late Shang king Di Yi against the ''Rénfāng'' (), a group occupying the area of southern Shandong and Jianghuai (northern Anhui and Jiangsu). Many Chinese archaeologists apply the historical name "Dongyi" to the archaeological Yueshi culture (1900–1500 BCE). Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period (771 BC), the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military control over territories centered on the Wei River valley and North China Plain. Even as Zhou suzerainty became increasingly ceremonial over the following Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC), the political system created by the Zhou royal house survived in some form for several additional centuries. A date of 1046 BC for the Zhou's establishment is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC. The latter Eastern Zhou period is itself roughly subdivided into two parts. During the Spring and Autumn period (), power became increasingly decentralized as the authority of the royal house diminished. The Warring States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu River
Shu River () is a river in Shandong Province, China, that flows into the Yellow Sea. See also *List of rivers in China Rivers that flow through China are as follows. The list is organized according to the body of water into which each river empties, beginning with the Sea of Okhotsk in the northeast, moving clockwise on a map and ending with the Arctic Ocean. S ... References {{coord missing, China Rivers of Shandong Rivers of Jiangsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Characters
Chinese characters are logographs used Written Chinese, to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represent the only one that has remained in continuous use. Over a documented history spanning more than three millennia, the function, style, and means of writing characters have changed greatly. Unlike letters in alphabets that reflect the sounds of speech, Chinese characters generally represent morphemes, the units of meaning in a language. Writing all of the frequently used vocabulary in a language requires roughly 2000–3000 characters; , nearly have been identified and included in ''The Unicode Standard''. Characters are created according to several principles, where aspects of shape and pronunciation may be used to indicate the character's meaning. The first attested characters are oracle bone inscriptions made during the 13th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Wei
Wei (), known in historiography as the Eastern Wei (), was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei dynasty. One of the Northern and Southern dynasties#Northern dynasties, Northern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period, the Eastern Wei ruled the eastern part of northern China from 534 to 550. As with the Northern Wei, the ruling family of the Eastern Wei were members of the Tuoba clan of the Xianbei. History Gao Huan was the potentate of the eastern half of what was Northern Wei territory. In 534, following the disintegration of the Northern Wei dynasty, he installed Emperor Xiaojing of Eastern Wei, Yuan Shanjian as ruler of Eastern Wei. Yuan Shanjian was a descendant of the Northern Wei. Yuan Shanjian was a puppet ruler, as the real power lay in the hands of Gao Huan. Several military campaigns, such as the Battle of Shayuan, were launched against the neighboring Western Wei in an attemp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |