|
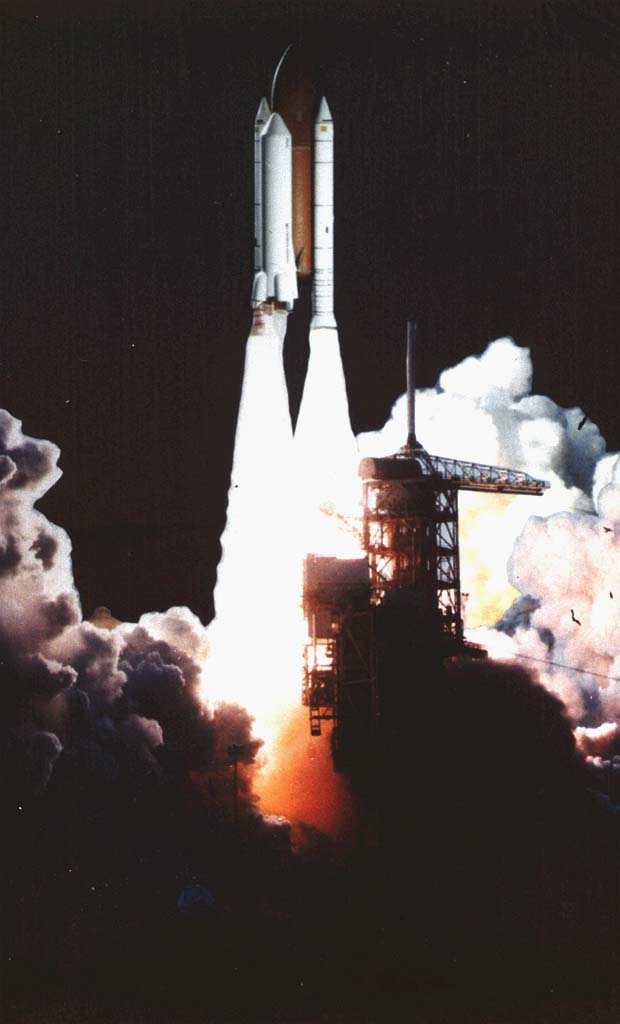
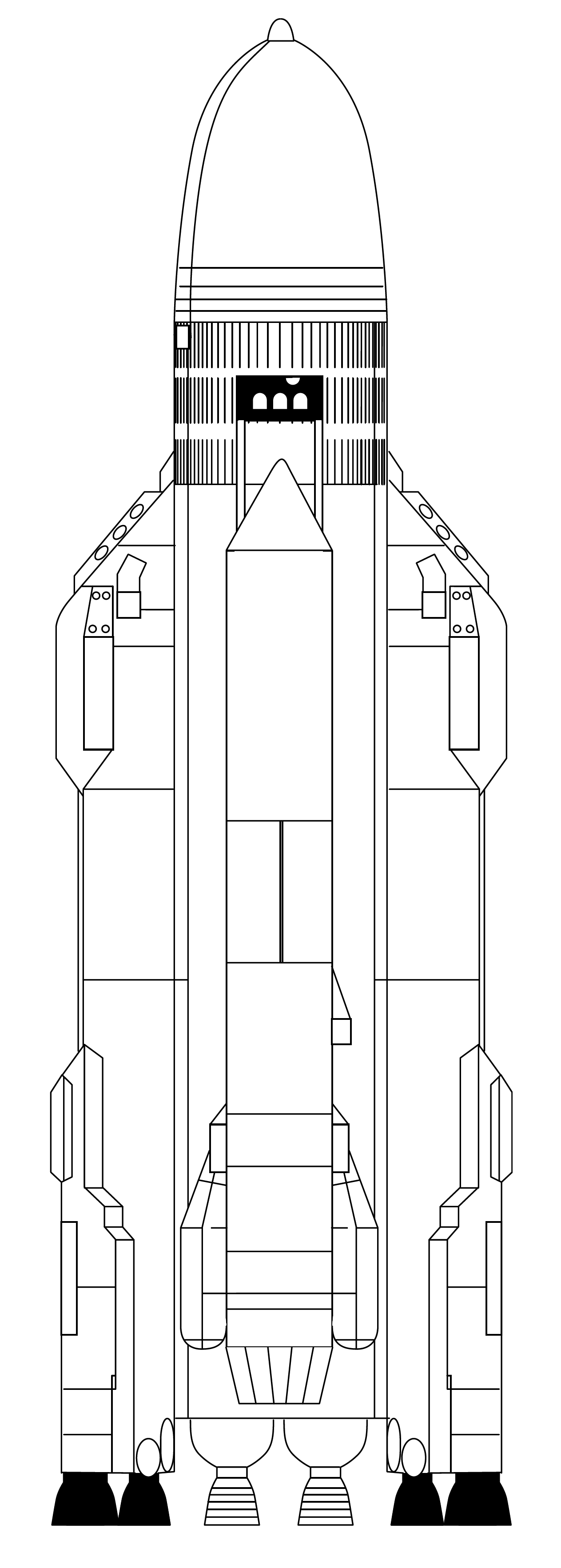
Shuttle-c Launch Painting
The Shuttle-C was a study by NASA to turn the Space Shuttle launch stack into a dedicated uncrewed cargo launcher. The Space Shuttle external tank and Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs) would be combined with a cargo module to take the place of the Shuttle orbiter and include the main engines. Various Shuttle-C concepts were investigated between 1984 and 1995. The Shuttle-C concept would theoretically cut development costs for a heavy launch vehicle by re-using technology developed for the shuttle program. End-of-life and Space Shuttle hardware would also have been used. One proposal even involved converting ''Columbia'' or ''Enterprise'' into a single-use cargo launcher. Before the loss of Space Shuttle ''Challenger'', NASA had expected about 24 shuttle flights a year. In the aftermath of the ''Challenger'' incident, it became clear that this launch rate was not feasible for a variety of reasons. With the Shuttle-C, it was thought that the lower maintenance and safety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Program
The Space Shuttle program was the fourth human spaceflight program carried out by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished routine transportation for Earth-to-orbit crew and cargo from 1981 to 2011. Its official name, Space Transportation System (STS), was taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft of which it was the only item funded for development. It flew 135 missions and carried 355 astronauts from 16 countries, many on multiple trips. The Space Shuttle—composed of an orbiter launched with two reusable solid rocket boosters and a disposable external fuel tank—carried up to eight astronauts and up to of payload into low Earth orbit (LEO). When its mission was complete, the orbiter would reenter the Earth's atmosphere and land like a glider at either the Kennedy Space Center or Edwards Air Force Base. The Shuttle is the only winged crewed spacecraft to have achieved orbit and landing, and the first r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Space Launch System Designs
Even before the launch of Sputnik 1, there were various types of launch vehicle designs. The launch vehicle designs described below are either canceled or never left the drawing board. 20th century 21st century See also *Comparison of orbital launch systems *Non-rocket spacelaunch *List of orbital launch systems * List of private spaceflight companies#Crew and cargo transport vehicles *Spaceplane *List of crewed lunar lander designs Further reading * ''SP-4221 The Space Shuttle Decision'Chapter 8(NASA) * *T.A. Heppenheime(NASA, 1998) External links{cbignore, bot=medic* ttp://www.spacefuture.com/vehicles/designs.shtml Space Future - Vehicle Designsbr>Proposed or planned spacecraft (Wikimedia Commons) |
Energia (rocket)
Energia (russian: Энергия, Energiya, Energy; GRAU 11K25) was a 1980s super-heavy lift launch vehicle. It was designed by NPO Energia of the Soviet Union as part of the Buran program for a variety of payloads including the Buran spacecraft. Control system main developer enterprise was the Khartron NPO "Electropribor". The Energia used four strap-on boosters each powered by a four-chamber RD-170 engine burning kerosene/ LOX, and a central core stage with four single-chamber RD-0120 (11D122) engines fueled by liquid hydrogen/LOX. The launch vehicle had two functionally different operational variants: Energia-Polyus, the initial test configuration, in which the Polyus system was used as a final stage intended to put the payload into orbit, and Energia-Buran, in which the ''Buran'' orbiter was the payload and the source of the orbit insertion impulse. The launch vehicle had the capacity to place about 100 tonnes in Low Earth orbit, up to 20 tonnes to geostationary orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle
A heavy-lift launch vehicle, HLV or HLLV, is an orbital launch vehicle capable of lifting between (by NASA classification) or between (by Russian classification) into low Earth orbit (LEO).50t payloads" , operational heavy-lift launch vehicles include the Ariane 5, the Long March 5, the Proton-M and the Delta IV Heavy. In addition, the Angara A5, the Falcon 9 Full Thrust, and the Falcon Heavy are designed to provide heavy-lift capabilities in at least some configurations but have not yet been proven to carry a 20-tonne payload into LEO. Several other heavy-lift rockets are in development. An HLV is between medium-lift launch vehicles and super heavy-lift launch vehicles. Rated launch vehicles See also * Comparison of orbital launch systems * List of orbital launch systems * Comparison of orbital rocket engines * Comparison of space station cargo vehicles * Medium-lift launch vehicle, capable of lifting between 2,000 and 20,000 kg (4,400 to 44,100 lb) of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle
The Shuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle ("HLV") was an alternate super heavy-lift launch vehicle proposal for the NASA Constellation program. It was first presented to the Augustine Commission on 17 June 2009. Based on the Shuttle-C concept which has been the subject of various studies since the 1980s, the HLV was a Shuttle-Derived Launch Vehicle (SDLV) that proposed to replace the winged Orbiter from the Space Shuttle stack with a side-mounted payload carrier. The Space Shuttle's External Tank (ET) and four-segment Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs) would have remained the same. According to initial estimates, the HLV could have been developed within 4 years for about US$6.6 billion, which was about 20% of the costs estimated for the Ares I and Ares V vehicle development. Origin An uncrewed side-mounted concept of the Space Shuttle named Shuttle-C was investigated between 1984 and 1995. The Shuttle-C cargo only option was not funded in the 1980s and 1990s due to N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnum (rocket)
The Magnum was a large super-heavy-lift rocket designed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center during the mid-1990s. The Magnum, which never made it past the preliminary design phase, would have been a launcher some 96 meters (315 feet) tall, on the scale of the Saturn V and was originally designed to carry a human expedition to Mars. It was to have used two strap-on side boosters, similar to the Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs), but using liquid fuel instead. Some designs had the strap-on boosters using wings and jet engines, which would enable them to fly back to the launch area after they were jettisoned in flight. The Magnum was designed to carry around 80 tons of payload into low Earth orbit (LEO). See also * Shuttle-C * Shuttle-derived vehicle ** Shuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle presented 2009 * National Launch System, studied from 1991 to 1993 * Constellation program, developed from 2005 to 2009 - cancelled * Space Launch System, developed and buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuttle SERV
SERV, short for Single-stage Earth-orbital Reusable Vehicle, was a proposed space launch system designed by Chrysler's Space Division for the Space Shuttle project. SERV was so radically different from the two-stage spaceplanes that almost every other competitor entered into the Shuttle development process that it was never seriously considered for the shuttle program. SERV was to be a single-stage to orbit spacecraft that would take off from the existing Saturn V complexes and land vertically at Kennedy for re-use. SERV looked like a greatly expanded Apollo capsule, with an empty central core able to carry of cargo. SERV could be launched uncrewed for cargo missions, ejecting a cargo capsule and returning to Earth. For crewed missions, a separate spaceplane, MURP (Manned Upper-stage Reusable Payload), could be carried atop the vehicle. The name "SERV" was also used by an entirely unrelated NASA project, the "Space Emergency Re-entry Vehicle". History Background In 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George W
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he previously served as the 46th governor of Texas from 1995 to 2000. While in his twenties, Bush flew warplanes in the Texas Air National Guard. After graduating from Harvard Business School in 1975, he worked in the oil industry. In 1978, Bush unsuccessfully ran for the House of Representatives. He later co-owned the Texas Rangers of Major League Baseball before he was elected governor of Texas in 1994. As governor, Bush successfully sponsored legislation for tort reform, increased education funding, set higher standards for schools, and reformed the criminal justice system. He also helped make Texas the leading producer of wind powered electricity in the nation. In the 2000 presidential election, Bush defeated Democratic incumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |