|
Sequence Number
A sequence number is a consecutive number in a sequence of numbers, usually of real integers (natural numbers). Sequence numbers have many practical applications. They can be used, among other things, as part of serial numbers on manufactured parts, in case management, or in databases as a surrogate key for registering and identifying unique entries in a table (in which case it is used as a primary key). Examples Historically, the Norwegian Mapping Authority have used sequence numbers for land registration as a placeholder in cases where an organization number or national identity number have not been known. In elections in Norway, sequence numbers are used in the duplicate check to prevent votes being counted twice or to detect duplicate ballots. An example of a sequence number being used as a surrogate key is the ''snr'' number used by Statistics Norway since 1970, which uniquely identifies a person even if their social security number changes. The snr number will then be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is called the ''length'' of the sequence. Unlike a set, the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in a sequence, and unlike a set, the order does matter. Formally, a sequence can be defined as a function from natural numbers (the positions of elements in the sequence) to the elements at each position. The notion of a sequence can be generalized to an indexed family, defined as a function from an ''arbitrary'' index set. For example, (M, A, R, Y) is a sequence of letters with the letter "M" first and "Y" last. This sequence differs from (A, R, M, Y). Also, the sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8), which contains the number 1 at two different positions, is a valid sequence. Sequences can be '' finite'', as in these examples, or '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Elections In Norway
Norway elects its legislature on a national level. The parliament, the Storting (or ''Stortinget'' by Norwegian grammar), has 169 members elected for a four-year term (during which it may not be dissolved) by a form of proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies. Norway has a multi-party system, with numerous parties in which no one party often has a chance of gaining power alone, and parties must work with each other to form coalition governments or minority cabinets. In Norway, elections are held every second year, alternating between elections for the Parliament and local elections, both of which are held every four years. Suffrage is universal from the year a person turns 18 years old, even if the person turns 18 later in the year the election is held. Only Norwegian citizens can vote in the Parliamentary elections, but foreigners who have lived in Norway for three years continuously can vote in the local elections. Women's suffrage was adopted in 1913. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Timestamp
A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolute notion of time, however. They can have any epoch, can be relative to any arbitrary time, such as the power-on time of a system, or to some arbitrary time in the past. A distinction is sometimes made between the terms datestamp, timestamp and date-timestamp: * Datestamp or DS: A date, for example -- according to ISO 8601 * Timestamp or TS: A time of day, for example :: using 24-hour clock * Date-timestamp or DTS: Date and time, for example --, :: History The term "timestamp" derives from rubber stamps used in offices to stamp the current date, and sometimes time, in ink on paper documents, to record when the document was received. Common examples of this type of timestamp are a postmark on a letter or the "in" and "out" times on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Opus Number
In music, the opus number is the "work number" that is assigned to a musical composition, or to a set of compositions, to indicate the chronological order of the composer's publication of that work. Opus numbers are used to distinguish among compositions with similar titles; the word is abbreviated as "Op." for a single work, or "Opp." when referring to more than one work. Opus numbers do not necessarily indicate chronological order of composition. For example, posthumous publications of a composer's juvenilia are often numbered after other works, even though they may be some of the composer's first completed works. To indicate the specific place of a given work within a music catalogue, the opus number is paired with a cardinal number; for example, Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 14 in C-sharp minor (1801, nicknamed ''Moonlight Sonata'') is "Opus 27, No. 2", whose work-number identifies it as a companion piece to "Opus 27, No. 1" ( Piano Sonata No. 13 in E-flat major, 1800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
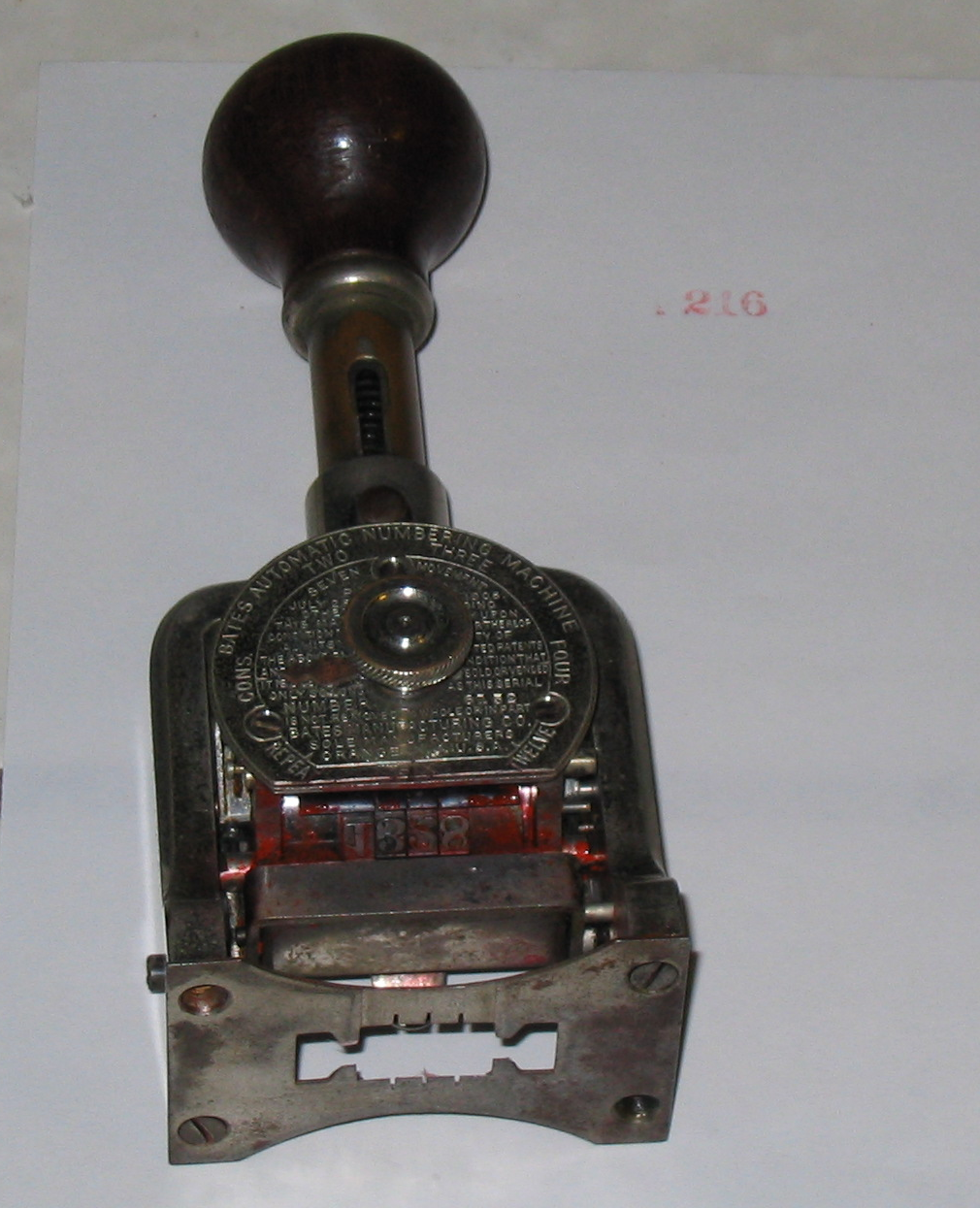 |
Bates Numbering
Bates numbering (also known as Bates stamping, Bates branding, Bates coding or Bates labeling) is a method of sequentially Pagination, numbering pages with a reference number. A hand-operated Bates numbering device is used to "stamp" a number on a page, and the numbers will automatically advance after each stamping. Bates numbering is used in the legal, medical, and business fields to place one or more of identifying numbers, date and time marks on images and documents as they are scanned or processed, for example, during the Discovery (law), discovery stage of preparations for trial or identifying business receipts. Bates stamping can be used to mark and identify images with copyrights by putting a company name, logo, and/or legal copyright on them. This process provides identification, protection, and automatic consecutive numbering of the pages. History The Bates Automatic Numbering-Machine or Bates stamper is named after the inventor Edwin G. Bates, Edwin Granville Bates of Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Check Digit
A check digit is a form of redundancy check used for Error detection and correction, error detection on identification numbers, such as bank account numbers, which are used in an application where they will at least sometimes be input manually. It is analogous to a binary parity bit used to check for errors in computer-generated data. It consists of one or more digits (or letters) computed by an algorithm from the other digits (or letters) in the sequence input. With a check digit, one can detect simple errors in the input of a series of characters (usually digits) such as a single mistyped digit or some permutations of two successive digits. Design Check digit algorithms are generally designed to capture ''human'' transcription errors. In order of complexity, these include the following: * letter/digit errors, such as l → 1 or O → 0 * single-digit errors, such as 1 → 2 * transposition errors, such as 12 → 21 * twin errors, such as 11 → 22 * jump transpositions errors, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
BLS AG
BLS AG is a Swiss railway company created by the 2006 merger of BLS Lötschbergbahn and Regionalverkehr Mittelland AG. Its ownership is divided, with 55.8% of it owned by the canton of Berne, and 21.7% by the Swiss Confederation. It has two main business fields: passenger traffic and infrastructure. BLS has a subsidiary—BLS Cargo—which is responsible for all freight operations. BLS Cargo works in cooperation with the freight subsidiary of , Railion. However, the staff, apart from management and sales, is employed by BLS AG. Part of the BLS locomotive fleet is owned by BLS Cargo. Another subsidiary, BLS Fernverkehr AG, is responsible for long-distance passenger transport. BLS Fernverkehr AG is wholly owned by BLS AG. Infrastructure In 2007 the new, Lötschberg Base Tunnel opened, which is part of the 449 km of infrastructure owned and operated by BLS AG. The Lötschberg base tunnel was built by a wholly owned subsidiary, BLS AlpTransit AG. By mid-2007 this compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Drive Shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power (physics), power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them. As torque carriers, drive shafts are subject to torsion (mechanics), torsion and shear stress, equivalent to the difference between the input torque and the load. They must therefore be strong enough to bear the stress, while avoiding too much additional weight as that would in turn increase their inertia. To allow for variations in the alignment and distance between the driving and driven components, drive shafts frequently incorporate one or more universal joints, jaw couplings, or rag joints, and sometimes a Rotating spline, splined joint or prismatic joint. History The term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
RegioExpress
RegioExpress, commonly abbreviated to RE, is a Train categories in Europe, category of fast regional train service in Switzerland, run by Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS) or other railway companies (such as Treni Regionali Ticino Lombardia, TILO, BLS AG, BLS, transports publics Fribourgeois, tpf, THURBO or Rhätische Bahn, RhB, previously also by Transports publics Neuchâtelois, transN). A few lines also serve stations in Germany, France and Italy. Since 2023, all RE services are numbered for more clarity. It is comparable to the Regional-Express in Rail transport in Germany, Germany, Rail transport in Austria, Austria and Rail transport in Luxembourg, Luxembourg. Its speed is considerably faster than regional trains at the same level, as it does not stop at all stations served by the regional trains. Nonetheless, it is slightly slower than InterRegio trains. Swiss Federal Railways describes the trains as ones that serve "rapidly into the regions". List of services the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Locomotive
A locomotive is a rail transport, rail vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push–pull train, push–pull operation has become common, and in the pursuit for longer and heavier freight trains, companies are increasingly using distributed power: single or multiple locomotives placed at the front and rear and at intermediate points throughout the train under the control of the leading locomotive. Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing motion', and is a shortened form of the term ''locomotive engine'', which was first used in 1814 to distinguish between self-propelled and stationary steam engines. Classifications Prior to locomotives, the motive force for railways had been generated by various lower-technology methods such as human power, horse power, Gravity railroad, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Statistics Norway
Statistics Norway (, abbreviated to ''SSB'') is the Norwegian statistics bureau. It was established in 1876. Relying on a staff of about 1,000, Statistics Norway publish about 1,000 new statistical releases every year on its web site. All releases are published both in Norwegian and English. In addition a number of edited publications are published, and all are available on the web site for free. As the central Norwegian office for official government statistics, Statistics Norway provides the public and government with extensive research and analysis activities. It is administratively placed under the Ministry of Finance but operates independently from all government agencies. Statistics Norway has a board appointed by the government. It relies extensively on data from registers, but are also collecting data from surveys and questionnaires, including from cities and municipalities. History Statistics Norway was originally established in 1876. The Statistics Act of 1989 provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Ballot
A ballot is a device used to cast votes in an election and may be found as a piece of paper or a small ball used in voting. It was originally a small ball (see blackballing) used to record decisions made by voters in Italy around the 16th century. Each voter uses one ballot, and ballots are not shared. In the simplest elections, a ballot may be a scrap of paper on which each voter writes in the name of a candidate, but governmental elections use printed ballots to protect the secrecy of the votes. The voter casts their ballot in a box at a polling station. In British English, this is usually called a "ballot paper". The word ''ballot'' is used for an election process within an organization (such as a trade union "holding a ballot" of its members). Etymology The word ballot comes from Italian ''ballotta'', meaning a "small ball used in voting" or a "secret vote taken by ballots" in Venice, Italy. History In ancient Greece, citizens used pieces of broken pottery to scratch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |