|
Separation Of Mechanism And Policy
The separation of mechanism and policy is a design principle in computer science. It states that mechanisms (those parts of a system implementation that control the authorization of operations and the allocation of resources) should not dictate (or overly restrict) the policies according to which decisions are made about which operations to authorize, and which resources to allocate. While most commonly discussed in the context of security mechanisms (authentication and authorization), separation of mechanism and policy is applicable to a range of resource allocation problems (e.g. CPU scheduling, memory allocation, quality of service) as well as the design of software abstractions. Per Brinch Hansen introduced the concept of separation of policy and mechanism in operating systems in the RC 4000 multiprogramming system. Artsy and Livny, in a 1987 paper, discussed an approach for an operating system design having an "extreme separation of mechanism and policy". In a 2000 article, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butler W
A butler is a person who works in a house serving and is a domestic worker in a large household. In great houses, the household is sometimes divided into departments, with the butler in charge of the dining room, wine cellar, and pantries, pantry. Some also have charge of the entire parlour floor and Housekeeper (domestic worker), housekeepers caring for the entire house and its appearance. A butler is usually male and in charge of male servants, while a housekeeper is usually female and in charge of female servants. Traditionally, male servants (such as Footman, footmen) were better-paid and of higher status than female servants. The butler, as the senior male servant, has the highest servant status. He can also sometimes function as a chauffeur. In older houses where the butler is the most senior worker, titles such as ''majordomo'', ''butler administrator'', ''house manager'', ''manservant'', ''staff manager'', ''chief of staff'', ''staff captain'', ''estate manager'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael L
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect)">Michael (surname)">he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (fashion designer), Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian football ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomies
A dichotomy () is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are complements. In logic, the partitions are opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multicategorical variables as binary variables is called dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichotomization is temporarily ignored for modeling purposes. Etymology The term ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems. X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at version 11 (hence "X11") since September 1987. The X.Org Foundation leads the X project, with the current reference implementation, X.Org Server, available as free and open-source software under the MIT License and similar permissive licenses. Purpose and abilities X is an architecture-independent system for remote graphical user interfaces and input device capabilities. Each person using a networked computer terminal, terminal has the ability to interact with the display with any type of user input device. In its standard distribution it is a complete, albeit simple, display and interface solution which delivers a standard widget toolkit, toolkit and protocol stack for building graphical user interfaces on most Unix-like operating syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix Philosophy
The Unix philosophy, originated by Ken Thompson, is a set of cultural norms and philosophical approaches to Minimalism (computing), minimalist, Modularity (programming), modular software development. It is based on the experience of leading developers of the Unix operating system. Early Unix developers were important in bringing the concepts of modularity and reusability into software engineering practice, spawning a "software tools" movement. Over time, the leading developers of Unix (and programs that ran on it) established a set of cultural norms for developing software; these norms became as important and influential as the technology of Unix itself, and have been termed the "Unix philosophy." The Unix philosophy emphasizes building simple, compact, clear, modular, and Extensibility, extensible code that can be easily maintained and repurposed by developers other than its creators. The Unix philosophy favors composability as opposed to Monolithic application, monolithic design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separation Of Concerns
In computer science, separation of concerns (sometimes abbreviated as SoC) is a design principle for separating a computer program into distinct sections. Each section addresses a separate '' concern'', a set of information that affects the code of a computer program. A concern can be as general as "the details of the hardware for an application", or as specific as "the name of which class to instantiate". A program that embodies SoC well is called a modular program. Modularity, and hence separation of concerns, is achieved by encapsulating information inside a section of code that has a well-defined interface. Encapsulation is a means of information hiding. Layered designs or packaging by feature in information systems are another embodiment of separation of concerns (e.g., presentation layer, business logic layer, data access layer, persistence layer). Separation of concerns results in more degrees of freedom for some aspect of the program's design, deployment, or usage. Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keycard Lock
A keycard lock is a lock operated by a keycard, a flat, rectangular plastic card. The card typically, but not always, has identical dimensions to that of a credit card, that is ID-1 format. The card stores a physical or digital pattern that the door mechanism accepts before disengaging the lock. There are several common types of keycards in use, including the mechanical holecard, barcode, magnetic stripe, Wiegand wire embedded cards, smart card (embedded with a read/write electronic microchip), RFID, and NFC proximity cards. Keycards are frequently used in hotels as an alternative to mechanical keys. The first commercial use of key cards was to raise and lower the gate at automated parking lots where users paid a monthly fee. Overview Keycard systems operate by physically moving detainers in the locking mechanism with the insertion of the card, by shining LEDs through a pattern of holes in the card and detecting the result, by swiping or inserting a magnetic stripe ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
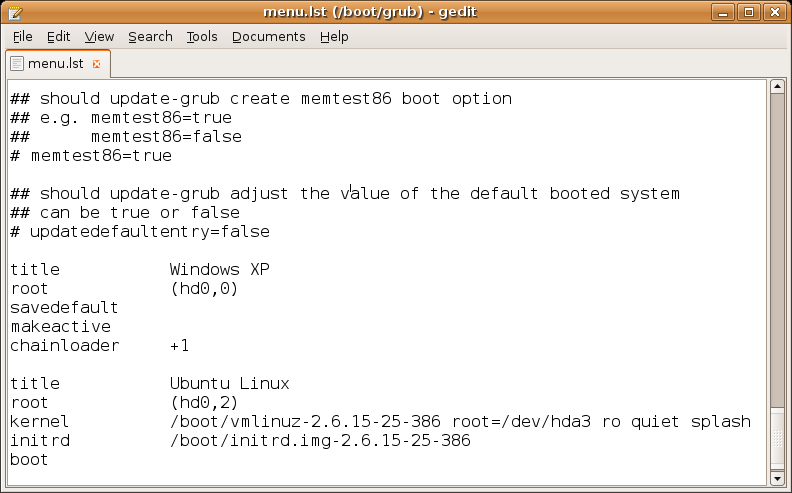
Configuration File
A configuration file, a.k.a. config file, is a computer file, file that stores computer data, data used to configure a software system such as an application software, application, a server (computing), server or an operating system. Some applications provide a tool to create, modify, and verify the syntax of their configuration files sometimes via graphical user interface (GUI). For context, system administrators may be expected to create and modify plain text, text config files via a text editor. For server processes and operating-system settings, there is often no standard tool, but operating systems may provide graphical interfaces such as YaST or debconf. Some computer programs only read their configuration files at Booting, startup. Others periodically check the configuration files for changes. Users can instruct some programs to re-read the configuration files and apply the changes to the current process, or indeed to read arbitrary files as a configuration file. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Binding
In computing, late binding or dynamic linkage—though not an identical process to dynamically linking imported code libraries—is a computer programming mechanism in which the method being called upon an object, or the function being called with arguments, is looked up by name at runtime. In other words, a name is associated with a particular operation or object at runtime, rather than during compilation. The name dynamic binding is sometimes used, but is more commonly used to refer to dynamic scope. With early binding, or static binding, in an object-oriented language, the compilation phase fixes all types of variables and expressions. This is usually stored in the compiled program as an offset in a virtual method table ("v-table"). In contrast, with late binding, the compiler does not read enough information to verify the method exists or bind its slot on the v-table. Instead, the method is looked up by name at runtime. The primary advantage of using late binding in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filesystem Permissions
Typically, a file system maintains permission settings for each stored item commonly computer file, files and directory (computer), directories that either grant or deny the ability to manipulate file system items. Often the settings allow controlling access based on function such as read, change, navigate, and Execution (computing), execute and to different computer user, users and groups of users. One well-established technology was developed for Unix and later codified by POSIX. Another common technology is an access-control list (ACL) with multiple variants implemented in file systems and one codified by POSIX. Since POSIX defines both the older Unix-based technology as well as ACLs, the former is called ''traditional POSIX permissions'' for clarity even though it is not a well-known term. A permission-driven user interface tailors the functionality available to the user based on file system item permissions. For example, the interface might hide menu options that are not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |