Configuration File on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 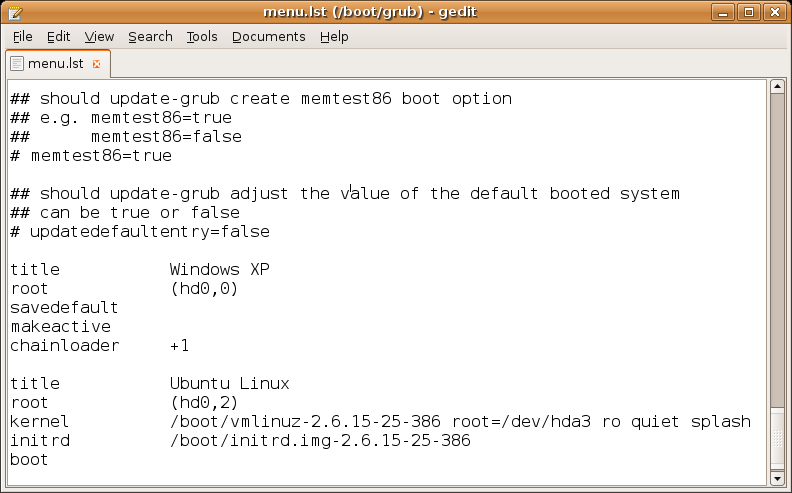
DOS=HIGH,UMB
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE RAM
DEVICEHIGH=C:\DOS\ANSI.SYS
FILES=30
SHELL=C:\DOS\COMMAND.COM C:\DOS /E:512 /P
DOS applications used a wide variety of individual configuration files, most of them binary, proprietary and undocumented - and there were no common conventions or formats.
 The early Microsoft Windows family of operating systems heavily utilized plain-text INI files (from "initialization"). These served as the primary mechanism to configure the operating system and application features.
The early Microsoft Windows family of operating systems heavily utilized plain-text INI files (from "initialization"). These served as the primary mechanism to configure the operating system and application features.Microsoft: Windows NT Workstation Resource Kit
The APIs to read and write from these still exist in Windows, but after 1993, Microsoft began to steer developers away from using INI files and toward storing settings in the Windows Registry, a hierarchical database to store configuration settings, which was introduced that year with
The OS/2 INI Files
' by James J. Weinkam. Two files control system-wide settings: OS2.INI and OS2SYS.INI. Application developers can choose whether to use them or to create a specific file for their applications.
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
, configuration files (commonly known simply as config files) are files used to configure the parameters and initial settings for some computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer progra ...
s. They are used for user applications, server processes and operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
settings.
Some applications provide tools to create, modify, and verify the syntax of their configuration files; these sometimes have graphical interfaces. For other programs, system administrator
A system administrator, or sysadmin, or admin is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems, especially multi-user computers, such as servers. The system administrator seeks to en ...
s may be expected to create and modify files by hand using a text editor, which is possible because many are human-editable plain text files. For server processes and operating-system settings, there is often no standard tool, but operating systems may provide their own graphical interfaces such as YaST or debconf.
Some computer programs only read their configuration files at startup
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses that never intend t ...
. Others periodically check the configuration files for changes. Users can instruct some programs to re-read the configuration files and apply the changes to the current process, or indeed to read arbitrary files as a configuration file. There are no definitive standards or strong conventions.

Configuration files and operating systems
Unix and Unix-like operating systems
Across Unix-like operating systems many different configuration-file formats exist, with each application or service potentially having a unique format, but there is a strong tradition of them being in human-editable plain text, and a simple key–value pair format is common. Filename extensions of.cnf, .conf, .cfg, .cf or .ini are often used.
Almost all formats allow comments
Comment may refer to:
* Comment (linguistics) or rheme, that which is said about the topic (theme) of a sentence
* Bernard Comment (born 1960), Swiss writer and publisher
Computing
* Comment (computer programming), explanatory text or informa ...
, in which case, individual settings can be disabled by prepending with the comment character. Often the default configuration files contain extensive internal documentation in the form of commentshttps://opensource.apple.com/source/postfix/postfix-174.2/Postfix.Config/main.cf.default. http://opensource.apple.com/source/apache/apache-769/httpd.conf. and man files are also typically used to document the format and options available.
System-wide software often uses configuration files stored in /etc
In Unix and operating systems inspired by it, the file system is considered a central component of the operating system. It was also one of the first parts of the system to be designed and implemented by Ken Thompson in the first experimental ...
, while user applications often use a "dotfile
In computing, a hidden folder (sometimes hidden directory) or hidden file is a folder or file which filesystem utilities do not display by default when showing a directory listing. They are commonly used for storing user preferences or preservin ...
" – a file or directory in the home directory prefixed with a period, which in Unix hides the file or directory from casual listing.
Some configuration files run a set of commands upon startup. A common convention is for such files to have "rc" in their name, typically using the name of the program then an "(.)rc" suffix e.g. ".xinitrc", ".vimrc", ".bashrc", "xsane.rc". See run commands for further details.
By contrast, IBM's AIX uses an Object Data Manager (ODM) database to store much of its system settings.
MS-DOS
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few oper ...
itself primarily relied on just one configuration file, CONFIG.SYS. This was a plain text file with simple key–value pairs (e.g. DEVICEHIGH=C:\DOS\ANSI.SYS) until MS-DOS 6, which introduced an INI-file style format. There was also a standard plain text batch file named AUTOEXEC.BAT that ran a series of commands on boot. Both these files were retained up to Windows 98SE, which still ran on top of MS-DOS.
An example CONFIG.SYS for MS-DOS 5:
Microsoft Windows
 The early Microsoft Windows family of operating systems heavily utilized plain-text INI files (from "initialization"). These served as the primary mechanism to configure the operating system and application features.
The early Microsoft Windows family of operating systems heavily utilized plain-text INI files (from "initialization"). These served as the primary mechanism to configure the operating system and application features.The APIs to read and write from these still exist in Windows, but after 1993, Microsoft began to steer developers away from using INI files and toward storing settings in the Windows Registry, a hierarchical database to store configuration settings, which was introduced that year with
Windows NT
Windows NT is a proprietary graphical operating system produced by Microsoft, the first version of which was released on July 27, 1993. It is a processor-independent, multiprocessing and multi-user operating system.
The first version of Wi ...
.
macOS
The Property List is the standard configuration file format inmacOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
(as well as in iOS, NeXTSTEP, GNUstep and Cocoa
Cocoa may refer to:
Chocolate
* Chocolate
* ''Theobroma cacao'', the cocoa tree
* Cocoa bean, seed of ''Theobroma cacao''
* Chocolate liquor, or cocoa liquor, pure, liquid chocolate extracted from the cocoa bean, including both cocoa butter and ...
applications). It uses the filename extension .plist.
IBM OS/2
IBM'sOS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 ...
uses a binary format, also with a .INI suffix, but this differs from the Windows versions. It contains a list
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby uni ...
of lists of untyped key–value pairs.The OS/2 INI Files
' by James J. Weinkam. Two files control system-wide settings: OS2.INI and OS2SYS.INI. Application developers can choose whether to use them or to create a specific file for their applications.
Serialization formats
A number of general-purpose serialization formats exist that can represent complex data structures in an easily stored format, and these are often used as a basis for configuration files, particularly in open-source and platform-neutral software applications and libraries. The specifications describing these formats are routinely made available to the public, thus increasing the availability of parsers and emitters across programming languages. Examples include:JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced ; also ) is an open standard file format and data interchange format that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of attribute–value pairs and arrays (or other s ...
, XML, and YAML.
See also
*.properties
.properties is a file extension for files mainly used in Java-related technologies to store the configurable parameters of an application. They can also be used for storing strings for Internationalization and localization; these are known as P ...
, a file extension mainly used in Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's mo ...
* HOCON, a superset of .properties and JSON
* INI file, a common configuration file format
* JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced ; also ) is an open standard file format and data interchange format that uses human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consisting of attribute–value pairs and arrays (or other s ...
, with support for complex data types and data structures
* Run commands, which explains the historical origin of the "rc" suffix
* TOML, a formally-specified configuration file format
* YAML, with support for complex data types and structures
References