|
Secnidazole
Secnidazole (trade names Flagentyl, Sindose, Secnil, Solosec) is a nitroimidazole anti-infective used to treat bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis. It is taken orally. Structurally it actually methyl-metronidazole. Effectiveness in the treatment of dientamoebiasis has been reported. It has also been tested against ''Atopobium vaginae''. In the United States, secnidazole is FDA-approved for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. About 70% of affected people do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms occur, they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms ca ... in adult women. It was approved in the United States in 2017. References Further reading * {{Agents against amoebozoa Nitroimidazole antibiotics Antiprotozoal agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an infection of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urination may occur. Itching is uncommon. Occasionally, there may be no symptoms. Having BV approximately doubles the risk of infection by a number of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV/AIDS. It also increases the risk of early delivery among pregnant women. BV is caused by an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. There is a change in the most common type of bacteria and a hundred to thousandfold increase in total numbers of bacteria present. Typically, bacteria other than ''Lactobacilli'' become more common. Risk factors include douching, new or multiple sex partners, antibiotics, and using an intrauterine device, among others. However, it is not considered a sexually transmitted infection and, unlike g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitroimidazole
Nitroimidazoles are the group of organic compound, organic compounds consisting of an imidazole ring with at least one nitro group substituent. The term also refers to the class of antibiotics that have nitroimidazole in their structures. These antibiotics commonly include the 5-nitroimidazole positional isomer. Synthesis Imidazole undergoes a nitration reaction with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to give 5-nitroimidazole. Nitroimidazole antibiotics From the chemistry perspective, nitroimidazole antibiotics can be classified according to the location of the nitro functional group. Structures with names 4- and 5-nitroimidazole are equivalent from the perspective of drugs since these tautomers readily interconvert. Drugs of the 5-nitro variety include metronidazole, tinidazole, nimorazole, dimetridazole, pretomanid, ornidazole, megazol, and azanidazole. Drugs based on 2-nitroimidazoles include benznidazole and azomycin. Nitroimidazole antibiotics have been used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-infective
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasitic worms. Infectious diseases remain a significant global health concern, causing approximately 9.2 million deaths in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
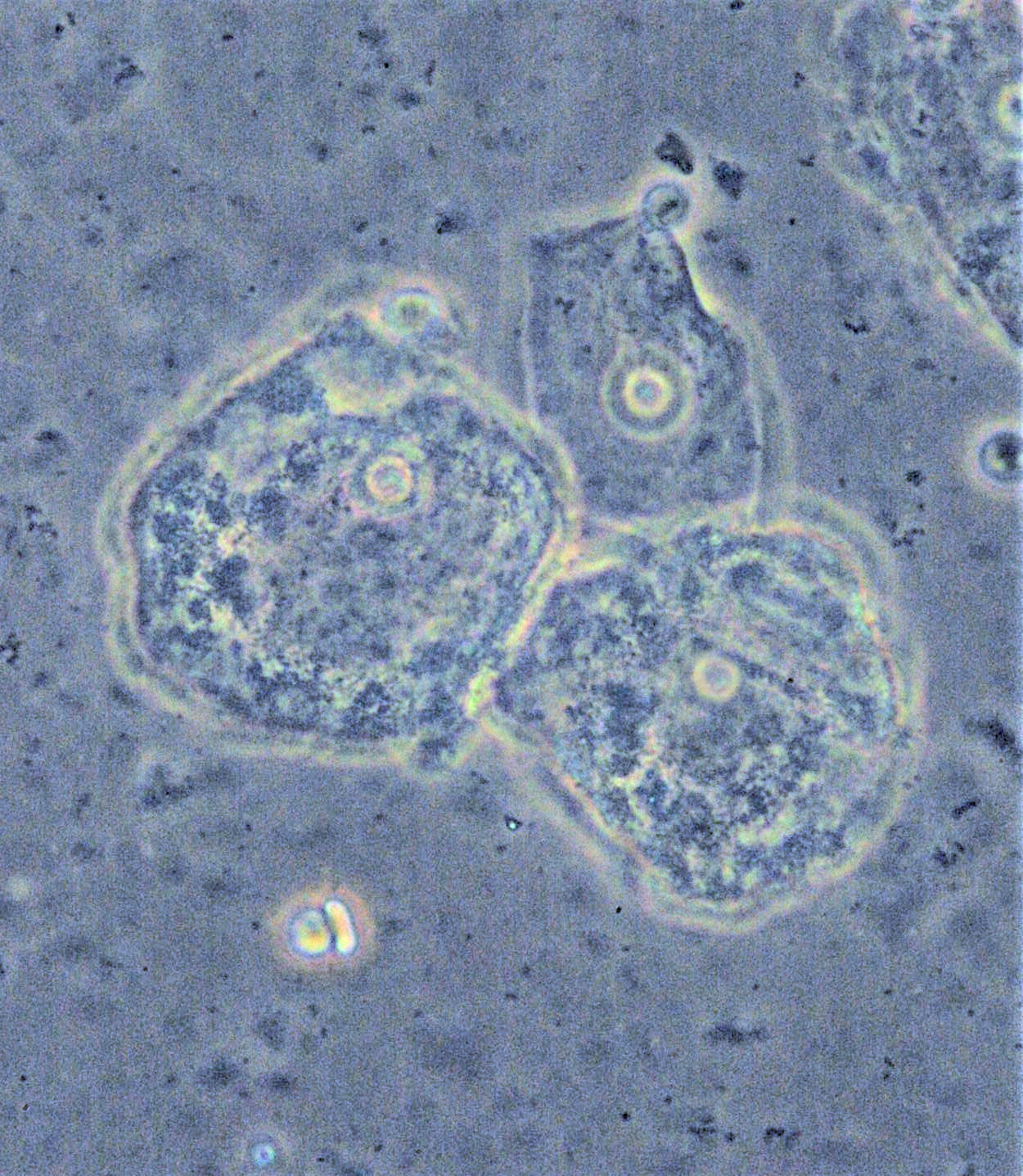
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (trich) is an infectious disease caused by the parasite ''Trichomonas vaginalis''. About 70% of affected people do not have symptoms when infected. When symptoms occur, they typically begin 5 to 28 days after exposure. Symptoms can include itching in the genital area, a bad smelling thin vaginal discharge, burning with urination, and pain with sex. Having trichomoniasis increases the risk of getting HIV/AIDS. It may also cause complications during pregnancy. Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) most often spread by vaginal, oral, or anal sex. It can also spread through genital touching (manual sex). Infected people may spread the disease even when symptoms are absent. Diagnosis is by finding the parasite in the vaginal fluid using a microscope, microbial culture, culturing the vaginal fluid or urine, or testing for the parasite's DNA. If present, other STIs should be tested for. Methods of prevention include sexual abstinence, not having sex, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dientamoebiasis
Dientamoebiasis is a medical condition caused by infection with ''Dientamoeba fragilis'', a single-cell parasite that infects the lower gastrointestinal tract of humans. It is an important cause of traveler's diarrhea, chronic abdominal pain, chronic fatigue, and failure to thrive in children. Signs and symptoms The most commonly reported symptoms in conjunction with infection with ''D. fragilis'' include abdominal pain (69%) and diarrhea (61%). Diarrhea may be intermittent and may not be present in all cases. It is often chronic, lasting over two weeks. The degree of symptoms may vary from asymptomatic to severe, and can include weight loss, vomiting, fever, and involvement of other digestive organs. Symptoms may be more severe in children. Additional symptoms reported have included: # Weight loss # Fatigue # Nausea and vomiting # Fever # Urticaria (skin rash) # Pruritus (itchiness) # Biliary infection Cause Genetic diversity As many individuals are asymptomatic carriers of ''D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atopobium Vaginae
''Fannyhessea vaginae'' is a species of bacteria in the family ''Atopobiaceae''. It is a facultative anaerobic organism, anaerobic, Gram-positive rod-shaped or elliptical coccobacillus found as single elements or in pairs or short chains. It is typically isolated from 80% of women with bacterial vaginosis and it is implicated in treatment failures. Invasive infections such as bacteremia have been reported. See also * List of bacterial orders * List of bacteria genera References Further reading * * * * External links * Type strain of ''Atopobium vaginae'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Coriobacteriaceae Bacterial vaginosis Bacteria described in 1999 {{actinobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitroimidazole Antibiotics
Nitroimidazoles are the group of organic compounds consisting of an imidazole ring with at least one nitro group substituent. The term also refers to the class of antibiotics that have nitroimidazole in their structures. These antibiotics commonly include the 5-nitroimidazole positional isomer. Synthesis Imidazole undergoes a nitration reaction with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid to give 5-nitroimidazole. Nitroimidazole antibiotics From the chemistry perspective, nitroimidazole antibiotics can be classified according to the location of the nitro functional group. Structures with names 4- and 5-nitroimidazole are equivalent from the perspective of drugs since these tautomers readily interconvert. Drugs of the 5-nitro variety include metronidazole, tinidazole, nimorazole, dimetridazole, pretomanid, ornidazole, megazol, and azanidazole. Drugs based on 2-nitroimidazoles include benznidazole and azomycin. Nitroimidazole antibiotics have been used to combat ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |