|
Seborrheic Dermatitis
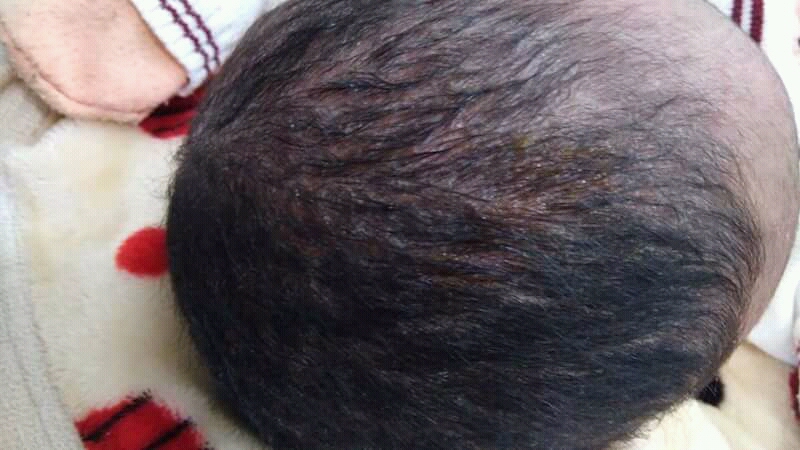
Seborrhoeic dermatitis (also spelled seborrheic dermatitis in American English) is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in sebum, oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Mild seborrhoeic dermatitis of the scalp may be described in lay terms as dandruff due to the dry, flaky character of the skin. However, as dandruff may refer to any dryness or scaling of the scalp, not all dandruff is seborrhoeic dermatitis. Seborrhoeic dermatitis is sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea. The cause is unclear but believed to involve a number of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors for seborrhoeic dermatitis include immunocompromised, poor immune function, Parkinson's disease, and alcoholic pancreatitis. The condition ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the Human skin, skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A List of dermatologists, dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Ancient Greek, Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία ''wikt:-logia, -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases (Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert, Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print around the same time.Freedber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gland
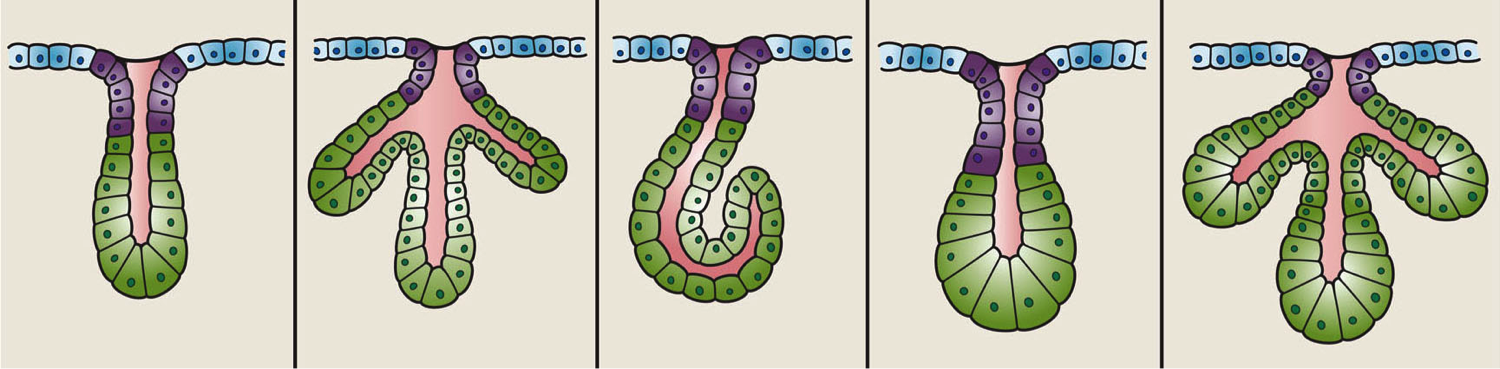
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also function to remove unwanted substances such as urine from the body. There are two types of gland, each with a different method of secretion. Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete their products, hormones, directly into interstitial spaces to be taken up into the bloodstream. Exocrine glands secrete their products through a duct into a body cavity or outer surface. Glands are mostly composed of epithelium, epithelial tissue, and typically have a supporting framework of connective tissue, and a capsule. Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelium, epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elemental state or as pure ore compounds in Earth's crust. Selenium ( ) was discovered in 1817 by , who noted the similarity of the new element to the previously discovered tellurium (named for the Earth). Selenium is found in :Sulfide minerals, metal sulfide ores, where it substitutes for sulfur. Commercially, selenium is produced as a byproduct in the refining of these ores. Minerals that are pure selenide or selenate compounds are rare. The chief commercial uses for selenium today are glassmaking and pigments. Selenium is a semiconductor and is used in photocells. Applications in electronics, once important, have been mostly replaced with silicon semiconductor devices. Selenium is still used in a few types of Direct current, DC power surge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione (or pyrithione zinc) is a coordination complex of zinc. It has fungistatic (inhibiting the division of fungal cells) and bacteriostatic (inhibiting bacterial cell division) properties and is used in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff. Structure of the compound The pyrithione ligands, which are formally monoanions, are chelated to Zn2+ via oxygen and sulfur centers. In the crystalline state, zinc pyrithione exists as a centrosymmetric dimer (see figure), where each zinc is bonded to two sulfur and three oxygen centers. In solution, however, the dimers dissociate via scission of one Zn-O bond. This compound was first described in the 1930s. Pyrithione is the conjugate base derived from 2-mercaptopyridine-''N''-oxide (CAS# 1121-31-9), a derivative of pyridine-''N''-oxide. Uses Medicine Zinc pyrithione can be used to treat dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis. It also has antibacterial properties and is effective against many pathoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciclopirox
Ciclopirox is a medication used for the treatment of moderate onychomycosis of fingernails and toenails, and for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. In 2022, it was the 247th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions. Medical uses Ciclopirox is indicated as topical treatment in immunocompetent people with mild to moderate onychomycosis of fingernails and toenails without lunula involvement, due to ''Trichophyton rubrum'',; and for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. Nail infections In addition to other formulations, ciclopirox is used in lacquers for topical treatment of onychomycosis (fungal infections of the nails). A meta-analysis of the six trials of nail infections available in 2009 concluded that they provided evidence that topical ciclopirox had poor cure rates, and that amorolfine might be substantially more effective, but more research was required. "Combining data from 2 trials of ciclopiroxolamine versu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral, among others, is an antiandrogen, antifungal drug, antifungal, and antiglucocorticoid medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous candidiasis, pityriasis versicolor, dandruff, and seborrhoeic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis. Taken oral administration, by mouth it is a less preferred option and recommended for only severe infections when other agents cannot be used. Other uses include treatment of hirsutism, excessive male-patterned hair growth in women and Cushing's syndrome. Common side effects when transdermal administration, applied to the skin include redness. Common side effects when taken by mouth include nausea, headache, and liver problems. Liver problems may result in death or the need for a liver transplantation. Other severe side effects when taken orally include QT prolongation, adrenocortical insufficiency, and anaphyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contagious Disease
A contagious disease is an infectious disease that can be spread rapidly in several ways, including direct contact, indirect contact, and droplet contact. These diseases are caused by organisms such as parasites, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. While many types of organisms live on the human body and are usually harmless, these organisms can sometimes cause disease. Some common infectious diseases are influenza, COVID-19, ebola, hepatitis, HIV/AIDS, Human papillomavirus infection, Polio, and Zika virus. A disease is often known to be contagious before medical science discovers its causative agent. Koch's postulates, which were published at the end of the 19th century, were the standard for the next 100 years or more, especially with diseases caused by bacteria. Microbial pathogenesis attempts to account for diseases caused by a virus. Historical meaning Originally, the term referred to a ''contagion'' or disease transmissible only by direct physical contact. In the mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
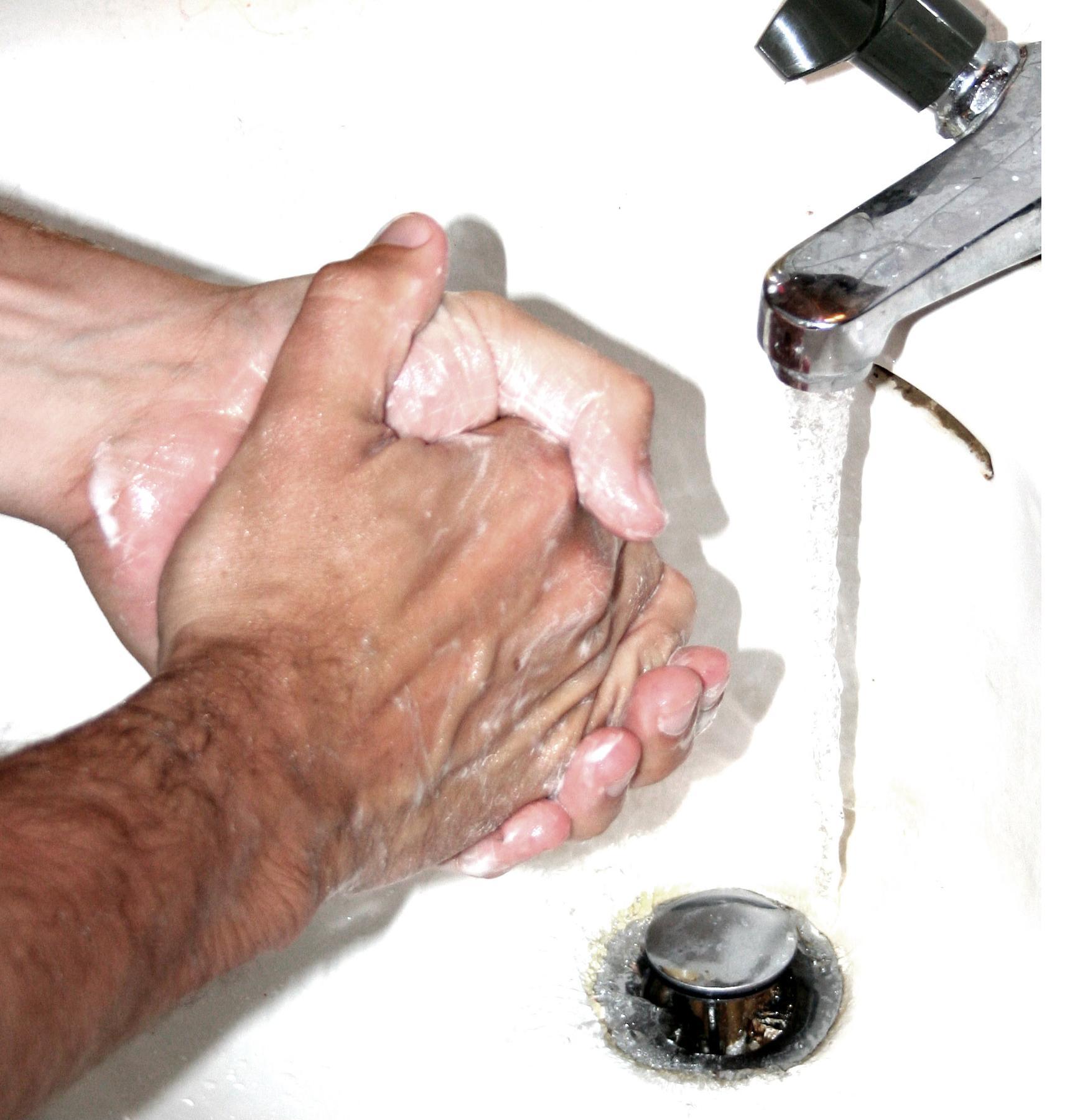
Hygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refers to maintaining the body's cleanliness. Hygiene activities can be grouped into the following: home and everyday hygiene, personal hygiene, medical hygiene, sleep hygiene, and Food safety, food hygiene. Home and every day hygiene includes hand washing, respiratory hygiene, food hygiene at home, hygiene in the kitchen, hygiene in the bathroom, laundry hygiene, and medical hygiene at home. And also environmental hygiene in the society to prevent all kinds of bacterias from penetrating into our homes. Many people equate hygiene with "cleanliness", but hygiene is a broad term. It includes such personal habit choices as how frequently to take a shower or bath, wash hands, trim Nail (anatomy), fingernails, and wash clothes. It also includes atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malassezia
''Malassezia'' is a genus of fungi (specifically, a yeast belonging to the division Basidiomycota). Some species of ''Malassezia'' are found on the skin of animals, including humans. Because malassezia requires fat to grow, it is most common in areas with many sebaceous glandson the scalp, face, and upper part of the body. Role in human diseases ''Malassezia'' infections of human skin can cause or aggravate a variety of conditions, including dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Dermatitis and dandruff When ''Malassezia'' grows too rapidly, the natural renewal of cells is disturbed, and dandruff can appear with itching (a similar process may also occur with other fungi or bacteria). Identification of ''Malassezia'' on skin has been aided by the application of molecular or DNA-based techniques. These investigations show that ''M. globosa'' is the species that causes most skin disease in humans, and that it is the most common cause of dandruff and seborrhoeic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholic Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormones. There are two main types, acute pancreatitis and chronic pancreatitis. Signs and symptoms of pancreatitis include pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and vomiting. The pain often goes into the back and is usually severe. In acute pancreatitis, a fever may occur; symptoms typically resolve in a few days. In chronic pancreatitis, weight loss, fatty stool, and diarrhea may occur. Complications may include infection, bleeding, diabetes mellitus, or problems with other organs. The two most common causes of acute pancreatitis are a gallstone blocking the common bile duct after the pancreatic duct has joined; and heavy alcohol use. Other causes include direct trauma, certain medications, infections such as mumps, and tumors. Chronic pancreatitis may develop as a result of acute pancreatitis. It is most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become more prevalent as the disease progresses. The motor symptoms are collectively called parkinsonism and include tremors, bradykinesia, spasticity, rigidity as well as postural instability (i.e., difficulty maintaining balance). Non-motor symptoms develop later in the disease and include behavior change (individual), behavioral changes or mental disorder, neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, anosmia, and mood swings. Most Parkinson's disease cases are idiopathic disease, idiopathic, though contributing factors have been identified. Pathophysiology involves progressive nerve cell death, degeneration of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a midbrain region that provides dopamine to the basal ganglia, a system invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seborrhoea
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location In humans, sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands: those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |