|
Sawar Muhammad Hussain Stadium
Sowar (, also sawar or siwar meaning "the one who rides" or "rider", from Persian , from the Sasanid Persian Aswār, from the Achaemenid Persian Asabāra) was originally a rank during the Mughal Empire. Later, during the British Raj, it was the name in Anglo-Indian usage for a horse-soldier belonging to the cavalry troops of the native armies of British India and the feudal states. It is also used more specifically of a mounted orderly, escort or guard. It was also the rank held by ordinary cavalry troopers, equivalent to sepoy in the infantry — this rank has been inherited by the modern armies of India and Pakistan. The rank higher is Acting Lance Daffadar. History An image from the Carnatic Wars features a Sowar armed with a musket. ''Sowar'' has been used as the name of a line of wrist-watches by the Swiss West End Watch Co. See also * Suvari Suvari or Süvari (; , "cavalry", from Persian ''Sawār'') is a Turkish or Estonian surname. As a Turkish surname it means "ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
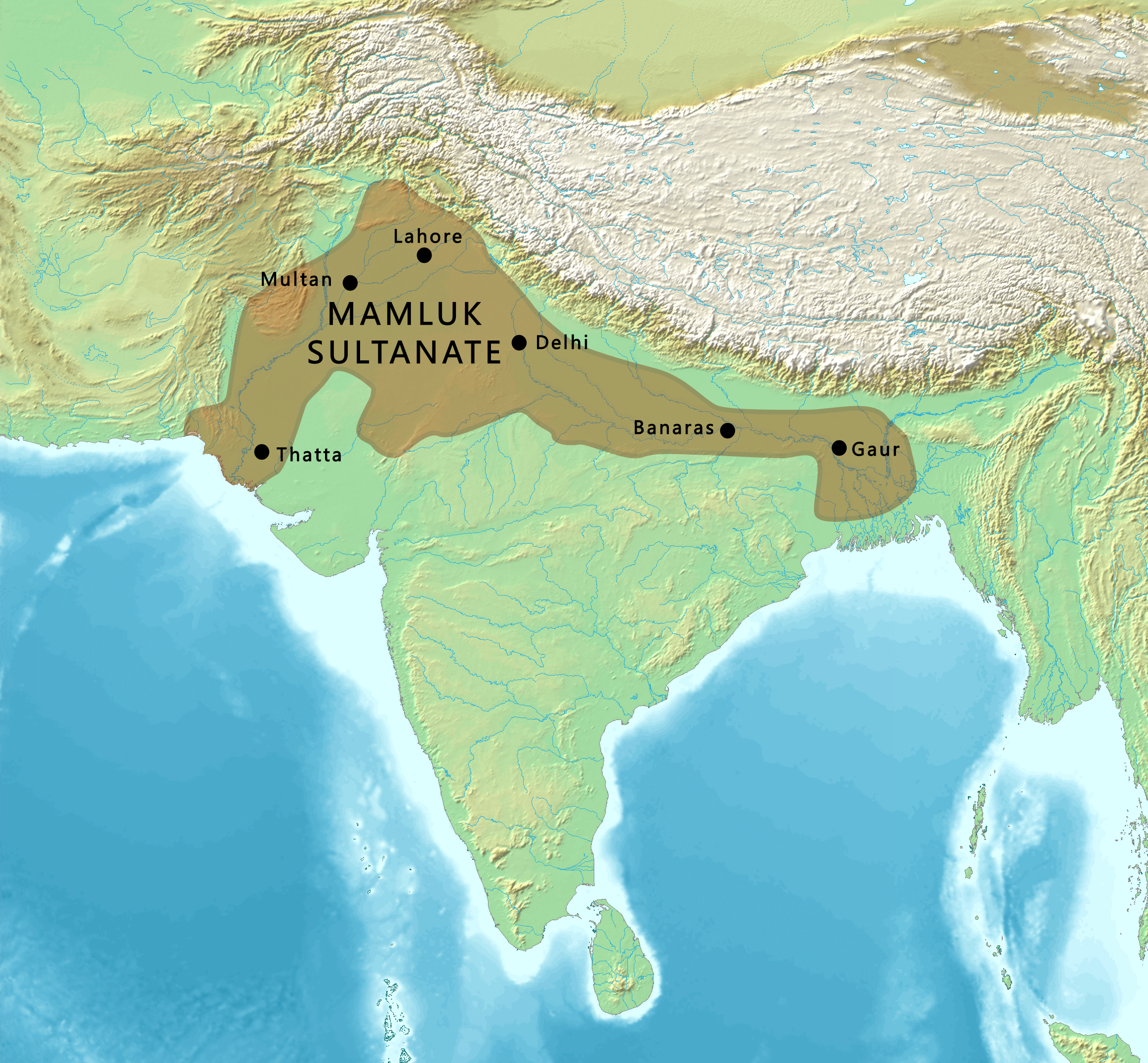
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aswaran
The Aswārān (singular aswār), also spelled Asbārān and Savaran, was a cavalry force that formed the backbone of the army of the Sasanian Empire. They were provided by the aristocracy, were heavily armored, and ranged from archers to cataphracts. Etymology The word comes from the Old Persian word ''asabāra'' (from ''asa''- and ''bar'', a frequently used Achaemenid military technical term). The various other renderings of the word are the following: Parthian ''asbār'' (spelt ''spbr'' or ''SWSYN''), Middle Persian ''aswār'' (spelt ''ʼswbʼl'' or ''SWSYA''), Classical Persian ''suwār'' (), ''uswār''/''iswār'' (), Modern Persian ''savār'' (). The Arabic word ''asāwira'' (), used to refer to a certain faction of the Sasanian cavalry after the Muslim conquest, is a broken plural form of the Middle Persian ''aswār''. However, the word ''aswār'' only means "horseman" in Middle Persian literature, and it is only the late Arabic term that has a more specialized meaning. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christ Church Mhow Plaque Malwa Contingent
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religion. Most Christians consider Jesus to be the incarnation of God the Son and awaited messiah, or Christ, a descendant from the Davidic line that is prophesied in the Old Testament. Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically. Accounts of Jesus's life are contained in the Gospels, especially the four canonical Gospels in the New Testament. Since the Enlightenment, academic research has yielded various views on the historical reliability of the Gospels and how closely they reflect the historical Jesus. According to Christian tradition, as preserved in the Gospels and the Acts of the Apostles, Jesus was circumcised at eight days old, was baptized by John the Baptist as a young adult, and after 40 day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suvari
Suvari or Süvari (; , "cavalry", from Persian ''Sawār'') is a Turkish or Estonian surname. As a Turkish surname it means "cavalry soldier". It may refer to: * Adnan Suvari (1926-1991), Turkish football coach * Mena Suvari, American actress See also * Sowar Sowar (, also sawar or siwar meaning "the one who rides" or "rider", from Persian language, Persian , from the Sasanian Empire, Sasanid Middle Persian, Persian Aswaran, Aswār, from the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Old Persian, Persian Asabār ... References {{surname Turkish-language surnames Estonian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West End Watch Co
West End Watch Company is a manufacturer of watches located at Leytron (Switzerland). It was established in 1886 and has been in business for more than 120 years. The company has produced and distributed more than 15 million watches worldwide since 1886. History The West End Watch Company was created in 1886. The West End of London, West End, a district of the centre of London, inspired its name to M. Arnold Charpié who was the Bombay representative of the Alcide Droz & Sons firm, a watch company established at Saint-Imier (Canton of Bern) in Switzerland. In 1886, MM. Amstutz and Droz, the owner of Alcide Droz & Sons firm, began the exploitation of the trademark West End Watch Company in the Indian market and developed the first waterproof pocket watch ever produced: L'impermeable, "L'Impermeable" (nowadays displayed at the International Watchmaking Museum of La Chaux-de-Fonds). During the First World War, a large force of British and Indian soldiers was sent from Bombay t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maratha Sowar And Sepoy
The Marathi people (; Marathi: , ''Marāṭhī lōk'') or Marathis (Marathi: मराठी, ''Marāṭhī'') are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are native to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a Marathi-speaking state of India on 1 May 1960, as part of a nationwide linguistic reorganisation of the Indian states. The term "Maratha" is generally used by historians to refer to all Marathi-speaking peoples, irrespective of their caste; However, it may refer to a Maharashtrian caste known as the Maratha which also includes farmer sub castes like the Kunbis. The Marathi community came into political prominence in the 17th century, when the Maratha Empire was established by Shivaji in 1674. Etymology According to R. G. Bhandarkar, the term Maratha is derived from Rattas, a tribe which held political supremacy in the Deccan from the remotest time. The Rattas called themselves ''Maha Rattas'' or Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acting Lance Daffadar
Acting lance daffadar (ALD) is a non-commissioned officer rank used in the armies of Pakistan and India, ranking between lance daffadar and sowar. It was also used in the British Indian Army. The rank is equivalent to the rank of lance corporal used in British Army The British Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of the United Kingdom. the British Army comprises 73,847 regular full-time personnel, 4,127 Brigade of Gurkhas, Gurkhas, 25,742 Army Reserve (United Kingdom), volunteer reserve perso .... Its infantry equivalent is lance naik. The rank is used in cavalry and armoured regiments of Indian Army and Pakistan Army and formerly in the British Indian Army. The rank insignia for an acting lance daffadar is a single chevron similar to lance naik. The role of an Acting Lance daffadar is to assist in the leadership of small teams or units. References {{reflist Pakistan Army ranks Military ranks of the Indian Army Military ranks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepoy
''Sepoy'' () is a term related to ''sipahi'', denoting professional Indian infantrymen, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire and the Maratha. In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its European counterparts employed locally recruited soldiers within India, mainly consisting of infantry designated as "sepoys". The largest sepoy force, trained along European lines, served the British East India Company. The term "sipahi" (or sometimes "sepoy") continues in use in the Indian, Pakistan and Nepalese armies, where it denotes the rank of private. Etymology In Persian (Aspa) means horse and Ispahai is also the word for cavalrymen. The term ''sepoy'' is the anglicised form of the Persian word (), meaning the traditional "infantry soldier" in the Mughal Empire. In the Ottoman Empire the term was used to refer to cavalrymen. Historical usage The term ''sepoy'' came into common use in the forces of the British East India Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757, the East India Company set up "factories" (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century three ''Presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India, 1757–1858, the Company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "Presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government oversight, in effect sharing sovereig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, Screening (tactical), screening, and skirmisher, skirmishing, or as heavy cavalry for decisive economy of force and shock attacks. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as a cavalryman, Equestrianism, horseman, trooper (rank), trooper, cataphract, knight, Drabant Corps of Charles XII, drabant, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, samurai or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any Military animal, military forces that used other animals or platforms for mounts, such as chariots, Camel cavalry, camels or War elephant, elephants. Infantry who m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |