|
Saturation Vapor Pressure
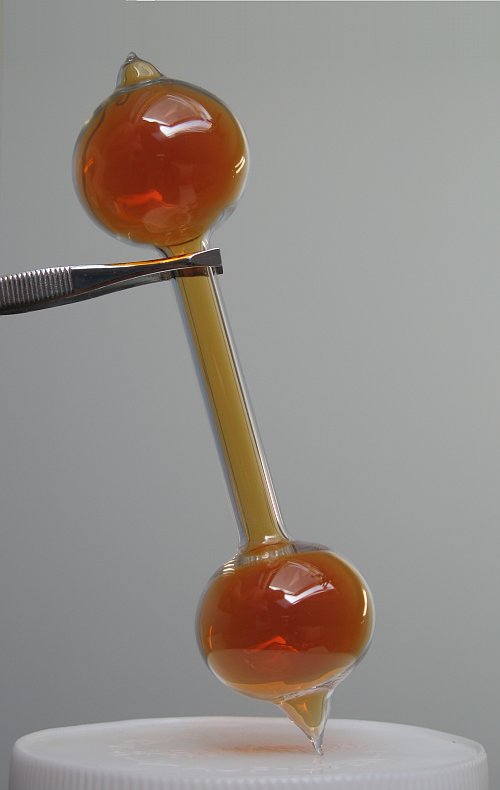
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's thermodynamic tendency to evaporate. It relates to the balance of particles escaping from the liquid (or solid) in equilibrium with those in a coexisting vapor phase. A substance with a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is often referred to as '' volatile''. The pressure exhibited by vapor present above a liquid surface is known as vapor pressure. As the temperature of a liquid increases, the attractive interactions between liquid molecules become less significant in comparison to the entropy of those molecules in the gas phase, increasing the vapor pressure. Thus, liquids with strong intermolecular interactions are likely to have smaller vapor pressures, with the reverse true for weaker interactions. The vapor p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (unit)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI). It is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is an SI coherent derived unit defined as one newton per square metre (N/m2). It is also equivalent to 10 barye (10 Ba) in the CGS system. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. The unit of measurement called '' standard atmosphere (atm)'' is defined as . Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
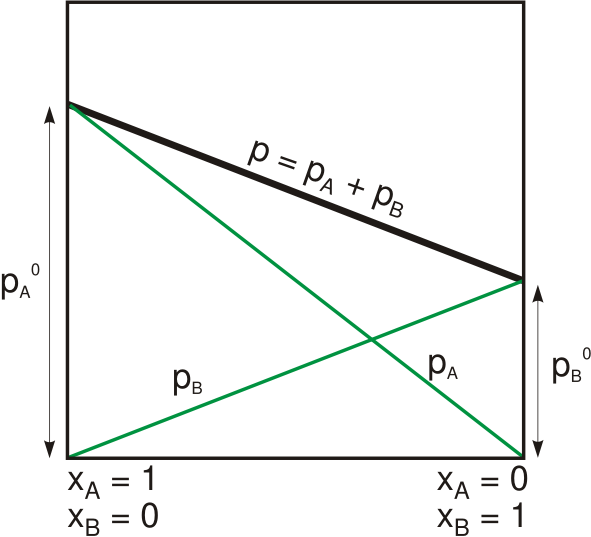
Raoult's Law
Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component (liquid or solid) multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. In consequence, the relative lowering of vapor pressure of a dilute solution of nonvolatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of solute in the solution. Mathematically, Raoult's law for a single component in an ideal solution is stated as : p_i = p_i^\star x_i where p_i is the partial pressure of the component i in the gaseous mixture above the solution, p_i^\star is the equilibrium vapor pressure of the pure component i, and x_i is the mole fraction of the component i in the liquid or solid solution. Where two volatile liquids A and B are mixed with each other to form a solution, the vapor phase consists of both compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as Pa. It is sometimes used as a ''reference pressure'' or ''standard pressure''. It is approximately equal to Earth's average atmospheric pressure at sea level. History The standard atmosphere was originally defined as the pressure exerted by a 760 mm column of mercury at and standard gravity (''g''n = ). It was used as a reference condition for physical and chemical properties, and the definition of the centigrade temperature scale set 100 °C as the boiling point of water at this pressure. In 1954, the 10th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) adopted ''standard atmosphere'' for general use and affirmed its definition of being precisely equal to dynes per square centimetre (). This defined pressure in a way that is independent of the properties of any particular substance. In addition, the CGPM noted that there had been some misapprehension that the previous definition (from the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Chloride
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula . One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, sweet-smelling, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in industrial chemistry, although it is rarely present in consumer products, and was formerly utilized as a refrigerant. Most chloromethane is Biogenic substance, biogenic. Occurrence Chloromethane is an abundant organohalogen, anthropogenic or natural, in the atmosphere. Natural sources produce an estimated 4,100,000,000 kg/yr. Marine Laboratory cultures of marine phytoplankton (''Phaeodactylum tricornutum'', ''Phaeocystis'' sp., ''Thalassiosira weissflogii'', ''Chaetoceros calcitrans'', ''Isochrysis'' sp., ''Porphyridium'' sp., ''Synechococcus'' sp., ''Tetraselmis'' sp., ''Prorocentrum'' sp., and ''Emiliana huxleyi'') produce CH3Cl, but in relatively insignificant amounts. An extensive study of 30 species of polar macroalgae revealed the relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Pressure Chart
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Herring, ''General Chemistry'', Prentice-Hall, 8th ed. 2002, p. 483–86. which means that the vapor can be condensed to a liquid by increasing the pressure on it without reducing the temperature of the vapor. A vapor is different from an aerosol. An aerosol is a suspension of tiny particles of liquid, solid, or both within a gas. For example, water has a critical temperature of , which is the highest temperature at which liquid water can exist at any pressure. In the atmosphere at ordinary temperatures gaseous water (known as water vapor) will condense into a liquid if its partial pressure is increased sufficiently. A vapor may co-exist with a liquid (or a solid). When this is true, the two phases will be in equilibrium, and the gas-partial pressure will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east, as well as with the Atlantic Ocean to its east, and the national capital and federal district of Washington, D.C. to the southwest. With a total area of , Maryland is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, ninth-smallest state by land area, and its population of 6,177,224 ranks it the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 18th-most populous state and the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, fifth-most densely populated. Maryland's capital city is Annapolis, Maryland, Annapolis, and the state's most populous city is Baltimore. Maryland's coastline was first explored by Europeans in the 16th century. Prior to that, it was inhabited by several Native Americans in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frostburg State University
Frostburg State University (FSU) is a public university in Frostburg, Maryland. The university is the only four-year institution of the University System of Maryland west of the Baltimore-Washington passageway in the state's Appalachian highlands. Founded in 1898 by Maryland State Senator, John Leake, Frostburg was selected because the site offered the best suitable location without a cost to the state. Today, the institution is a largely residential university. With an enrollment of approximately 4,858 students, the university offers 47 undergraduate majors, 16 graduate programs, and a doctorate in educational leadership. The university is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education and places primary emphasis on its role as a teaching and learning institution. History What was "Frostburg State Normal School No. 2" was founded by an act of the Maryland General Assembly, House Bill 742, from the General Appropriation Bill, on March 31, 1898. The bill was off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Equation
The Antoine equation is a class of semi-empirical correlations describing the relation between vapor pressure and temperature for pure substances. The Antoine equation is derived from the Clausius–Clapeyron relation. The equation was presented in 1888 by the French engineer (1825–1897). Equation The Antoine equation is \log_ p = A - \frac, where is the vapor pressure, is temperature (in °C or in K according to the value of ), and , and are component-specific constants. The simplified form with set to zero, \log_ p = A - \frac, is the August equation, after the German physicist Ernst Ferdinand August (1795–1870). The August equation describes a linear relation between the logarithm of the pressure and the reciprocal temperature. This assumes a temperature-independent heat of vaporization. The Antoine equation allows an improved, but still inexact description of the change of the heat of vaporization with the temperature. The Antoine equation can also be tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
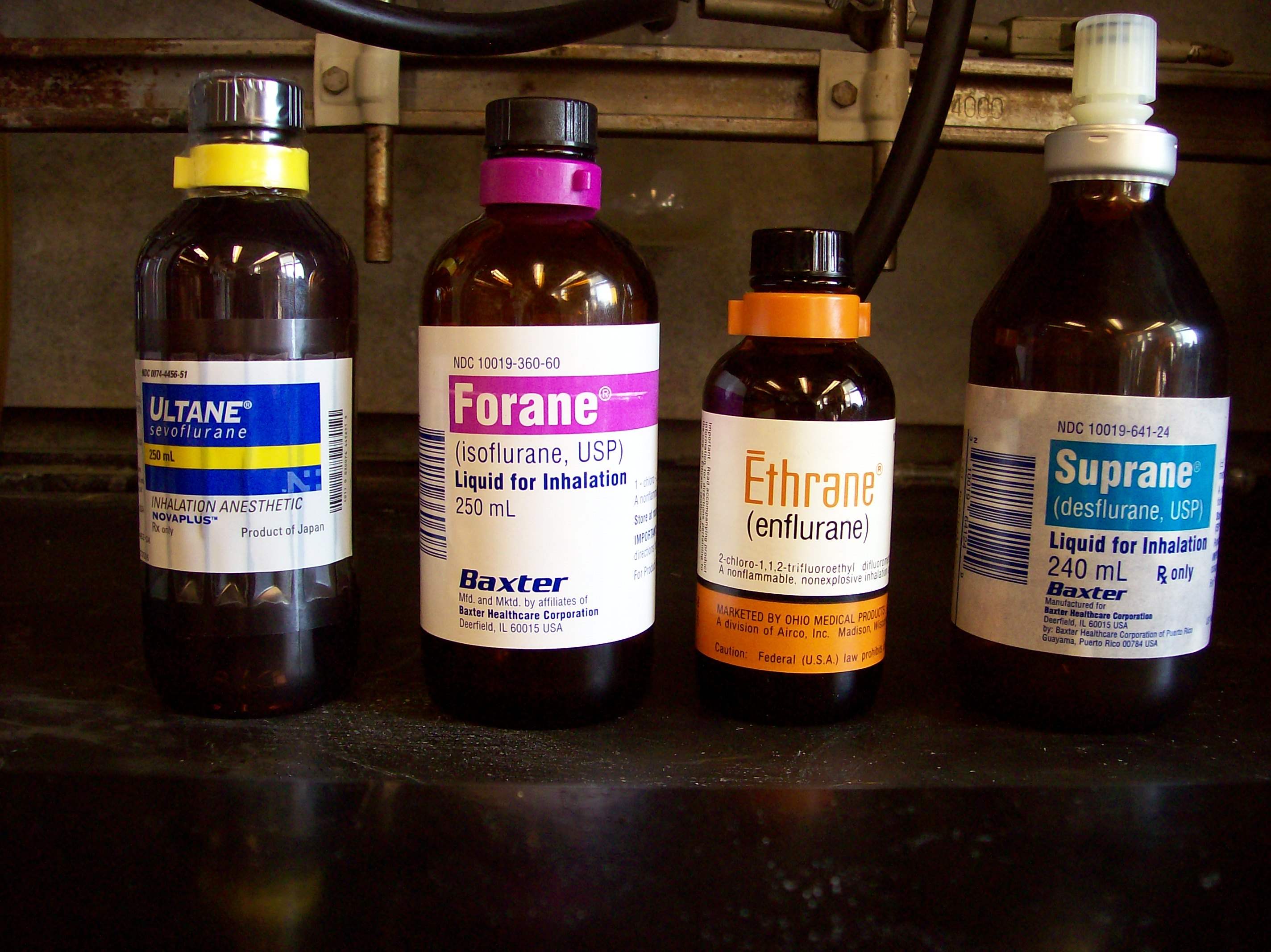
Inhalational Anesthetic
An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that is delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vaporiser and an anesthetic delivery system. Agents of significant contemporary clinical interest include volatile anesthetic agents such as isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane, as well as certain anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide and xenon. List of inhalational anaesthetic agents Currently-used agents * Desflurane * Isoflurane * Nitrous oxide * Sevoflurane * Xenon Previously-used agents Although some of these are still used in clinical practice and in research, the following anaesthetic agents are primarily of historical interest in developed countries: * Acetylene * Chloroethane (ethyl chloride) * Chloroform * Cryofluorane * Cyclopropane * Diethyl ether * Divinyl ether * Enflurane * Ethylene * Fluroxene * Halothane (still wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millimetre Of Mercury
A millimetre of mercury is a manometric unit of pressure, formerly defined as the extra pressure generated by a column of mercury one millimetre high. Currently, it is defined as exactly , or approximately 1 torr = atmosphere = pascals.Council Directive 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to units of measurement and on the repeal of Directive 71/354/EEC of the It is denoted mmHg or mm Hg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knudsen Effusion Cell
In crystal growth, a Knudsen cell is an effusion evaporator source for relatively low partial pressure elementary sources (e.g. Ga, Al, Hg, As). Because it is easy to control the temperature of the evaporating material in Knudsen cells, they are commonly used in molecular-beam epitaxy. Development The Knudsen effusion cell was developed by Martin Knudsen (1871–1949). A typical Knudsen cell contains a crucible (made of pyrolytic boron nitride, quartz, tungsten or graphite), heating filaments (often made of metal tantalum), water cooling system, heat shields, and an orifice shutter. Vapor pressure measurement The Knudsen cell is used to measure the vapor pressure Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indicat ...s of a solid with very low vapor pressure. Such a solid forms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |