|
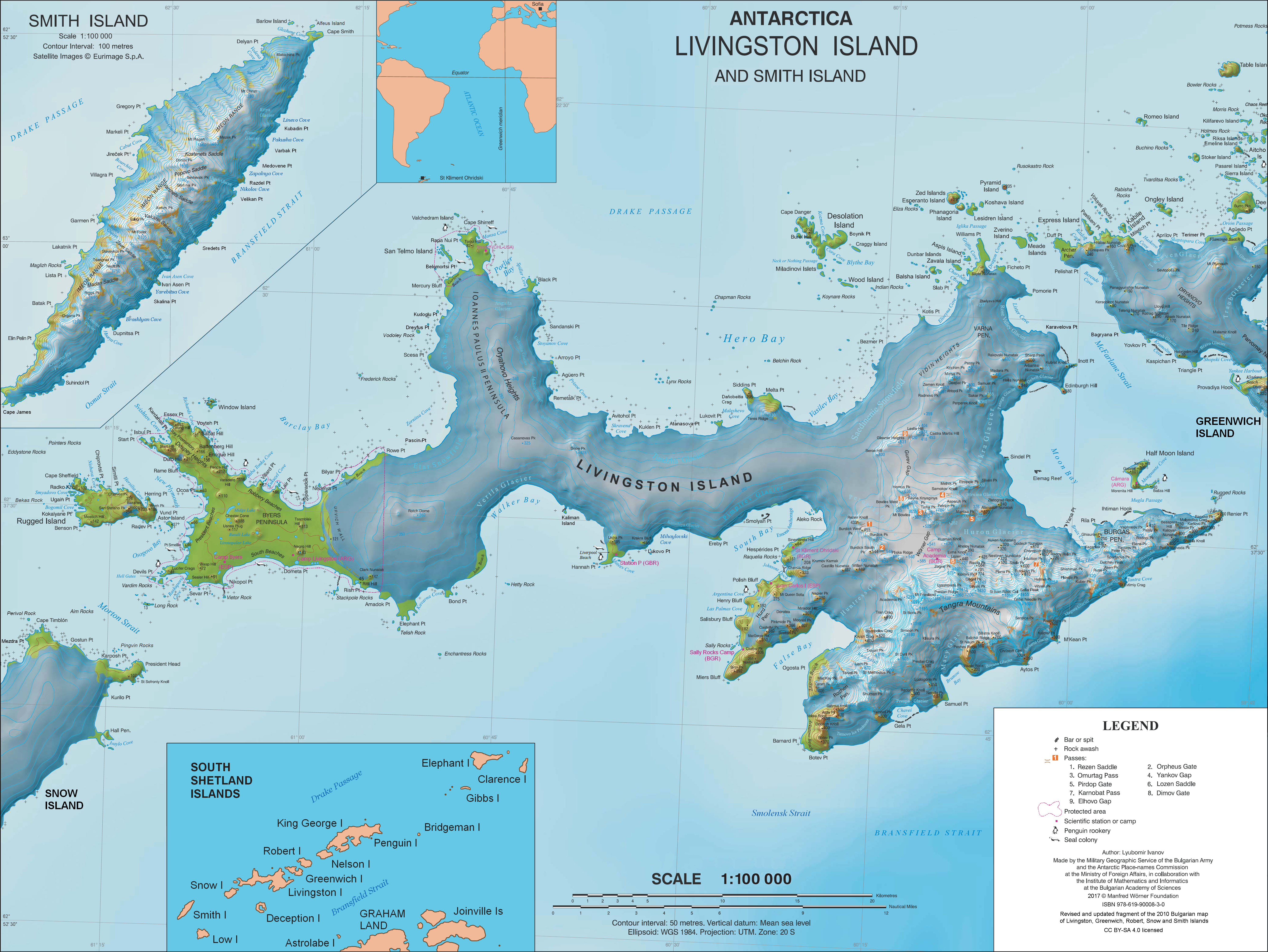
Sandanski Point
Sandanski Point (Nos Sandanski \'nos san-'dan-ski\) is the point forming the north side of the entrance to Stoyanov Cove on the east coast of Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, projecting 600 m into Hero Bay and formed by an offshoot of Oryahovo Heights. The point is named after the town of Sandanski in southwestern Bulgaria in connection with Yane Sandanski (1872–1915), a leader of the Bulgarian liberation movement in Macedonia.Ivanov, L. and N. Ivanova''Antarctic: Nature, History, Utilization, Geographic Names and Bulgarian Participation''.Sofia: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2014. pp. 338-339. (in Bulgarian) Location The point is located at which is 3.4 km north by west of Agüero Point, and 2.8 km south by east of Black Point. Maps * L.L. Ivanov et al. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands. Scale 1:100000 topographic map. Sofia: Antarctic Place-names Commission of Bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yane Sandanski
Yane Ivanov Sandanski (, ) (originally spelled in older Bulgarian orthography ) (18 May 1872 – 22 April 1915), was a Macedonian Bulgarian revolutionary.Per Julian Allan Brooks' thesis the term ‘Macedo-Bulgarian’ refers to the Exarchist population in Macedonia which is alternatively called ‘Bulgarian’ and ‘Macedonian’ in the documents. For more see: Managing Macedonia: British Statecraft, Intervention and 'Proto-peacekeeping' in Ottoman Macedonia, 1902-1905. Department of History, Simon Fraser University, 2013, p. 18. The designation ‘Macedo-Bulgarian’ is used also by M. Şükrü Hanioğlu and Ryan Gingeras. See: M. Şükrü Hanioğlu, Preparation for a Revolution: The Young Turks, 1902-1908 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001), 244; Ryan Gingeras, “A Break in the Storm: Reconsidering Sectarian, Violence in Ottoman Macedonia During the Young Turk Revolution” The MIT Electronic Journal of Middle East Studies 3 (Spring 2003): 1. Gingeras notes he uses the hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gaze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Point (Antarctica)
Black Point is a rocky promontory of L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands.Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. projecting 800 m northwards from the northeast coast of Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula into Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica to form the east side of the entrance to Porlier Bay. The area was visited by early 19th century sealers. The name of the point is a descriptive one. Fortín Rock is a sea stack lying off Black Point. Location The point is located at which is 4.8 km southeast of Cape Shirreff, 18.3 km west-southwest of Desolation Island, 15.88 km west-northwest of Siddins Point, 10 km north-northwest of Avitohol Point, 6.3 km north by west of Agüero Point and 3 km north by west of Sandanski Point. British mapping in 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, Spanish in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005 and 2009. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agüero Point
Agüero Point is the southeast extremity of a trapezoid-shaped and mostly ice-covered headland projecting 900 m from the east coast of Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula into Hero Bay, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The point forms the north side of the entrance to Prisoe Cove and, together with nearby Arroyo Point, separates the termini of Urdoviza Glacier to the north from Medven Glacier to the south. The feature is named after Clodomiro Agüero Soto, a crewman of the Chilean naval vessel ''Yelcho'' which rescued the Ernest Shackleton's expedition fellows members from Elephant Island in 1916. Location The point is located at which is 850 m south-southeast of Arroyo Point, 6.4 km south by east of Black Point and 4 km northwest of Avitohol Point (British mapping in 1968, Chilean in 1971, Argentine in 1980, Spanish in 1991, and Bulgarian in 2005, 2009 and 2017). See also * Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula * Livingston Island Maps * L. Iva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (region)
Macedonia () is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: larger parts in Greece, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria, and smaller parts in Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately and has a population of 4.76 million. Its oldest known settlements date back approximately to 7,000 BC. From the middle of the 4th century BC, the Kingdom of Macedon became the dominant power on the Balkan Peninsula; since then Macedonia has had a diverse history. Etymology Both proper nouns ''Makedṓn'' and ''Makednós'' are morphologically derived from the Ancient Greek adjective ''makednós'' meaning "tall, slim", and are related to the term Macedonia. Boundaries and definitions Ancient times The definition of Macedonia has chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandanski
Sandanski ( bg, Сандански ; el, Σαντάνσκι, formerly known as Sveti Vrach, bg, Свети Врач, until 1947) is a town and a recreation centre in south-western Bulgaria, part of Blagoevgrad Province. Named after the Bulgarian revolutionary Yane Sandanski, it is situated in Sandanski–Petrich Valley at the foot of Pirin Mountains, along the banks of Sandanska Bistritsa River. Sandanski is about 20 km away from Bulgaria-Greece border and 100 km away from Aegean sea. The town has a convenient location, a mild to warm climate (with the highest average annual temperature in the country, +16°C) and relatively high concentration of thermal water springs, which all make it a popular destination for relaxation and recreation. Geography Sandanski is located in the Sandanski–Petrich Valley, surrounded by the Pirin, Belasitsa and Ograzhden mountain ranges. The town is about 160 km south from Bulgaria's capital Sofia along the major European R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryahovo Heights
Oryahovo Heights (Oryahovski Vazvisheniya \o-'rya-hov-ski v&-zvi-'she-ni-ya\) are the ice-covered heights of elevation 340 m extending 6 km in north-south direction in central and eastern Ioannes Paulus II Peninsula, Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. They are linked to Snow Peak to the southeast by two saddles separated by the small ice dome of Casanovas Peak described by Àlex Simón i Casanovas from the Spanish Antarctic Programme in the 2000/01 austral summer. The heights were visited by a field party from the British base camp Station P during the summer season 1957/58.G.J. Hobbs. Map showing the physiography, geological station numbers and the survey routes on Livingston Island. In''The geology of Livingston Island ''.Scientific Report No. 47. British Antarctic Survey, 1963. Figure 1 They are named after the town of Oryahovo in northwestern Bulgaria. Location The heights are centered at (British mapping in 1963 and 1968, Bulgarian in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |