|
Samuel Rawle
Samuel Rawle (1771–1860) was an English topographical engraver and draughtsman. He practised in London. From 1798, he engraved many plates for the ''European Magazine'' and ''Gentleman's Magazine''. Later he was employed on some of the major topographical publications of the time. These included: James Cavanah Murphy's ''Arabian Antiquities of Spain'', 1816; Robert Surtees's ''History and Antiquities of the County Palatine of Durham'', 1816; Robert Wilkinson's ''Londina Illustrata'', 1819; James Hakewill, ''Picturesque Tour of Italy'', 1820; Thomas Frognall Dibdin's ''Bibliographical, Antiquarian and Picturesque Tour in France and Germany'', 1821; and Thomas Dunham Whitaker's ''Richmondshire'', 1823. Rawle exhibited landscapes at the Royal Academy in 1801 and 1806. External links * , an engraving of a view of the mines by Pennefather Esq. for Landscape Illustrations Of Moore’s Irish Melodies, 1835, with illustrative verse, ''The Golden Grave'', by Letitia Elizabeth Landon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rye House EM 1805
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe (Triticeae) and is closely related to both wheat (''Triticum'') and barley (genus ''Hordeum''). Rye grain is used for flour, bread, beer, crispbread, some whiskeys, some vodkas, and animal fodder. It can also be eaten whole, either as boiled rye berries or by being rolled, similar to rolled oats. Rye is a cereal grain and should not be confused with ryegrass, which is used for lawns, pasture, and as hay for livestock. Distribution and habitat Rye is one of a number of species that grow wild in the Levant, central and eastern Turkey and in adjacent areas. Evidence uncovered at the Epipalaeolithic site of Tell Abu Hureyra in the Euphrates valley of northern Syria suggests that rye was among the first cereal crops to be systematically cultivated, around 13,000 years ago. However, that claim remains controversial; critics point to inconsisten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Magazine
''The European Magazine'' (sometimes referred to as ''European Magazine'') was a monthly magazine published in London. Eighty-nine semi-annual volumes were published from 1782 until 1826. It was launched as the ''European Magazine, and London Review'' in January 1782, promising to offer "the Literature, History, Politics, Arts, Manners, and Amusements of the Age." It was in direct competition with ''The Gentleman's Magazine'', and in 1826 was absorbed into the ''Monthly Magazine''. Soon after launching the ''European Magazine'', its founding editor, James Perry, passed proprietorship to the Shakespearean scholar Isaac Reed and his partners John Sewell and Daniel Braithwaite, who guided the magazine during its first two decades. The articles and other contributions in the magazine appeared over initials or pseudonyms and have largely remained anonymous. Scholars believe that the contributions include the first published poem by William Wordsworth William Wordsworth (7 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentleman's Magazine
''The Gentleman's Magazine'' was a monthly magazine founded in London, England, by Edward Cave in January 1731. It ran uninterrupted for almost 200 years, until 1922. It was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (from the French ''magazine'', meaning "storehouse") for a periodical. Samuel Johnson's first regular employment as a writer was with ''The Gentleman's Magazine''. History The original complete title was ''The Gentleman's Magazine: or, Trader's monthly intelligencer''. Cave's innovation was to create a monthly digest of news and commentary on any topic the educated public might be interested in, from commodity prices to Latin poetry. It carried original content from a stable of regular contributors, as well as extensive quotations and extracts from other periodicals and books. Cave, who edited ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' under the pen name "Sylvanus Urban", was the first to use the term ''magazine'' (meaning "storehouse") for a periodical. Contributions to the maga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
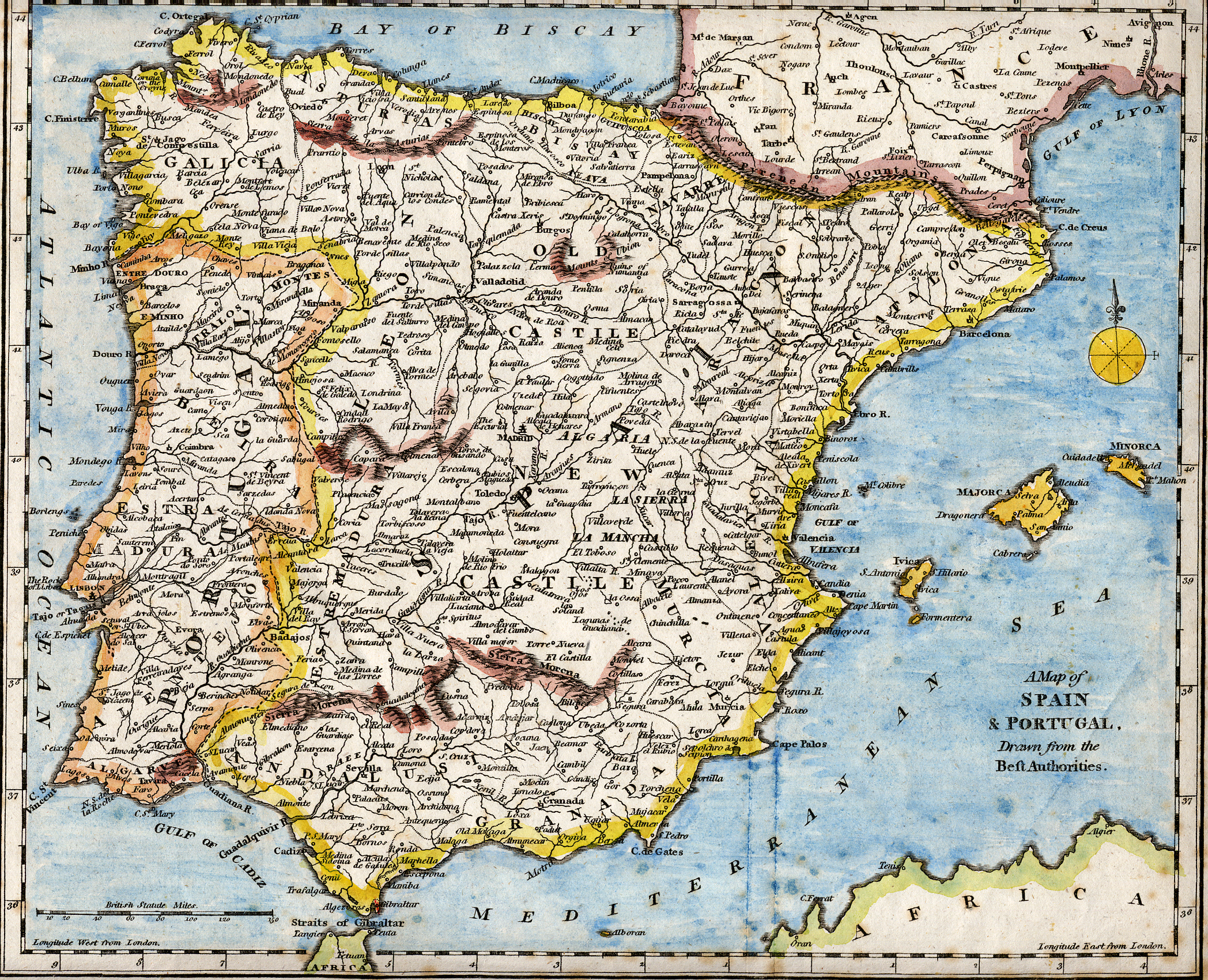
James Cavanah Murphy
James Cavanah Murphy (1760–1814) was an Irish architect and antiquary. Life Murphy was born at Blackrock, Cork, and was originally a bricklayer. He made his way to Dublin to study, and his name appeared in a list of the pupils of the drawing school of the Dublin Society about 1775, as working in miniature, chalk, and crayons. Later he practised in Dublin. In 1786 he was one of seven architects who were consulted on additions to the House of Commons, and he and another carried out the execution of James Gandon's design for the work. In December 1788, William Burton Conyngham commissioned Murphy to make drawings of Batalha Monastery in central Portugal. He was back in Dublin in 1790, and was in England at the end of the year. In 1802, he went to Cadiz, where he remained for seven years studying Moorish architecture, with some diplomatic duties. Settling again in England in 1809, Murphy took out a patent in 1813 for a method of preserving timber and other substances from decay. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Surtees (antiquarian)
Robert Surtees (1 April 1779 – 13 February 1834) was a celebrated English historian and antiquary of his native County Durham. Early life Surtees was born in South Bailey, Durham on 1 April 1779. He was the only surviving child of Dorothy Surtees (d. 1797) and Robert Surtees of Mainsforth (d. 1802), who were first cousins. His maternal grandparents were Robert Surtees of Redworth Hall, and the former Dorothy Lambton (second daughter of Thomas Lambton of Hardwick). His aunt, Jane Surtees (co-heiresses of their father Robert Surtees), also married a first cousin, Lt. Crosier Surtees, who died in 1803 when returning from a banquet with Lord Barnard at Raby Castle when he drunkenly fell into the moors and froze to death. They were grandparents of Henry Surtees, who inherited Redworth Hall, and Charles Surtees, who eventually inherited Mainsforth Hall. He was educated at Kepier School, Houghton-le-Spring, and later at Christ Church, Oxford, graduating with a B.A. degree i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Wilkinson (cartographer)
Wilkinson ( 1768 – 1825) was an English cartographer of maps and atlases, engraver, and book publisher. Career Most of Wilkinson's maps were derived from English map publisher John Bowles. Following Bowles' death in 1779, Wilkinson acquired the Bowles map plate library, after which he updated the plates until 1794, when he released ''The General Atlas of the World''. This atlas was reissued several times, in 1802 and 1809, before Wilkinson's death in 1825. Wilkinson's other works include ''Bowen and Kitchin's Large English Atlas'' (1785), ''Speer's West Indies'' (1796), ''Atlas Classica'' (1797), and independently issued maps of New Holland (1820) and North America (1823). He also published, initially together with William Herbert, groups of plates depicting historic scenes and buildings in London and the area surrounding it, under the title ''Scarce Topographical Prints No. II. ... of Londina Illustrata'' in 1808. These were issued serially until 1819, when they were publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Londina Illustrata
''Londina Illustrata. Graphic and Historic Memorials of Monasteries, Churches, Chapels, Schools, Charitable Foundations, Palaces, Halls, Courts, Processions, Places of Early Amusement and Modern & Present Theatres, In the Cities and Suburbs of London & Westminster'' was a book published in two volumes by Robert Wilkinson in 1819 & 1825, that had initially been released with William Herbert as groups of engravings between 1808 and 1819 which featured topographical illustrations by some of the foremost engravers and illustrators of the day, of the cities of London and Westminster, the county of Middlesex and some areas south of the River Thames, then in Surrey, such as Southwark. Most of the plates carry names of the draughtsman and engraver. A few early artists are included such as Wenceslaus Hollar. More recent draughtsmen included Robert Blemmell Schnebbelie, Frederick Nash, William Capon, George Jones, H. Gardner, George Shepherd, William Goodman, C.J.M. Whichelo, John C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hakewill
James Hakewill (1778–1843) was an English architect, best known for his illustrated publications. Life The second son of John Hakewill, he was brought up as an architect, and exhibited some designs at the Royal Academy. He was collecting materials for a work on the Rhine when he died in London, 28 May 1843. Works In 1813 he published a series of ''Views of the Neighbourhood of Windsor, &c., with engravings by others from his own drawings''. In 1816–17 he travelled in Italy, and on his return published in parts ''A Picturesque Tour of Italy'', in which some of his own drawings were finished into pictures for engraving by J. M. W. Turner. In 1820–1 he visited Jamaica, and subsequently published ''A Picturesque Tour in the Island of Jamaica, from his own drawings'' In 1828 he published ''Plans, Sections, and Elevations of the Abattoirs in Paris, with considerations for their adoption in London''. He also published a small tract on Elizabethan architecture. He was engaged i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Frognall Dibdin
Thomas Frognall Dibdin (177618 November 1847) was an English bibliographer, born in Calcutta to Thomas Dibdin, the sailor brother of the composer Charles Dibdin. Dibdin was orphaned at a young age. His father died in 1778 while returning to England, and his mother died one of the following two years, and an elderly maternal aunt eventually assumed responsibility for Dibdin.David A. Stoker, "Thomas Frognall Dibdin", ''Dictionary of Literary Biography, Volume 184: Nineteenth-Century British Book-Collectors and Bibliographers''. The Gale Group, 1997. He was educated at St John's College, Oxford, and studied for a time at Lincoln's Inn. After an unsuccessful attempt to obtain practice as a provincial counsel at Worcester, he was ordained a clergyman at the close of 1804, being appointed to a curacy at Kensington. It was not until 1823 that he received the living of Exning in Sussex. Soon afterwards he was appointed by Lord Liverpool Robert Banks Jenkinson, 2nd Earl o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Dunham Whitaker
Thomas Dunham Whitaker (1759–1821) was an English clergyman and topographer. Life Born at Raynham, Norfolk, on 8 June 1759, he was the son of William Whitaker (1730–1782), curate of Raynham, Norfolk, and his wife Lucy, daughter of Robert Dunham, and widow of Ambrose Allen. In 1760 his father moved to his ancestral house at Holme, in the township of Cliviger, Lancashire, and the boy was in November 1766 placed under the care of the Rev. John Shaw of Rochdale. In November 1774, after spending a short time with the Rev. William Sheepshanks of Grassington in Craven, he was admitted to St John's College, Cambridge, and went into residence in October 1775. He took the degree of LL.B. in November 1781. His intention to enter the legal profession changed on the death of his father in the following year, when he settled at Holme. He was ordained in 1785, but remained without pastoral charge until 1797, when he was licensed to the perpetual curacy of Holme Chapel, where he had rebu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its purpose is to promote the creation, enjoyment and appreciation of the visual arts through exhibitions, education and debate. History The origin of the Royal Academy of Arts lies in an attempt in 1755 by members of the Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce, principally the sculptor Henry Cheere, to found an autonomous academy of arts. Prior to this a number of artists were members of the Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce, including Cheere and William Hogarth, or were involved in small-scale private art academies, such as the St Martin's Lane Academy. Although Cheere's attempt failed, the eventual charter, called an 'Instrument', used to establish the Royal Academy of Arts over a dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Poem By Letitia Elizabeth Landon (L
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''a'' (pronounced ), plural English alphabet#Letter names, ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Greek alphabet#History, Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The Letter case, uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, "English articles, a", and its variant "English articles#Indefinite article, an", are Article (grammar)#Indefinite article, indefinite arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |