|
Samson And Delilah (opera)
''Samson and Delilah'' (), Op. 47, is a grand opera in three acts and four scenes by Camille Saint-Saëns to a French libretto by Ferdinand Lemaire. It was first performed in Weimar at the (Grand Ducal) Theater (now the Staatskapelle Weimar) on 2 December 1877 in a German translation. The opera is based on the Biblical tale of Samson and Delilah found in Chapter 16 of the Book of Judges in the Old Testament. It is the only opera by Saint-Saëns that is regularly performed. The second act love scene in Delilah's tent is one of the set pieces that define French opera. Two of Delilah's arias are particularly well known: "" ("Spring begins") and "" ("My heart opens itself to your voice", also known as "Softly awakes my heart"), the latter of which is one of the most popular recital pieces in the mezzo-soprano/contralto repertoire. Composition history In the middle of the 19th century, a revival of interest in choral music swept France, and Saint-Saëns, an admirer of the ora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
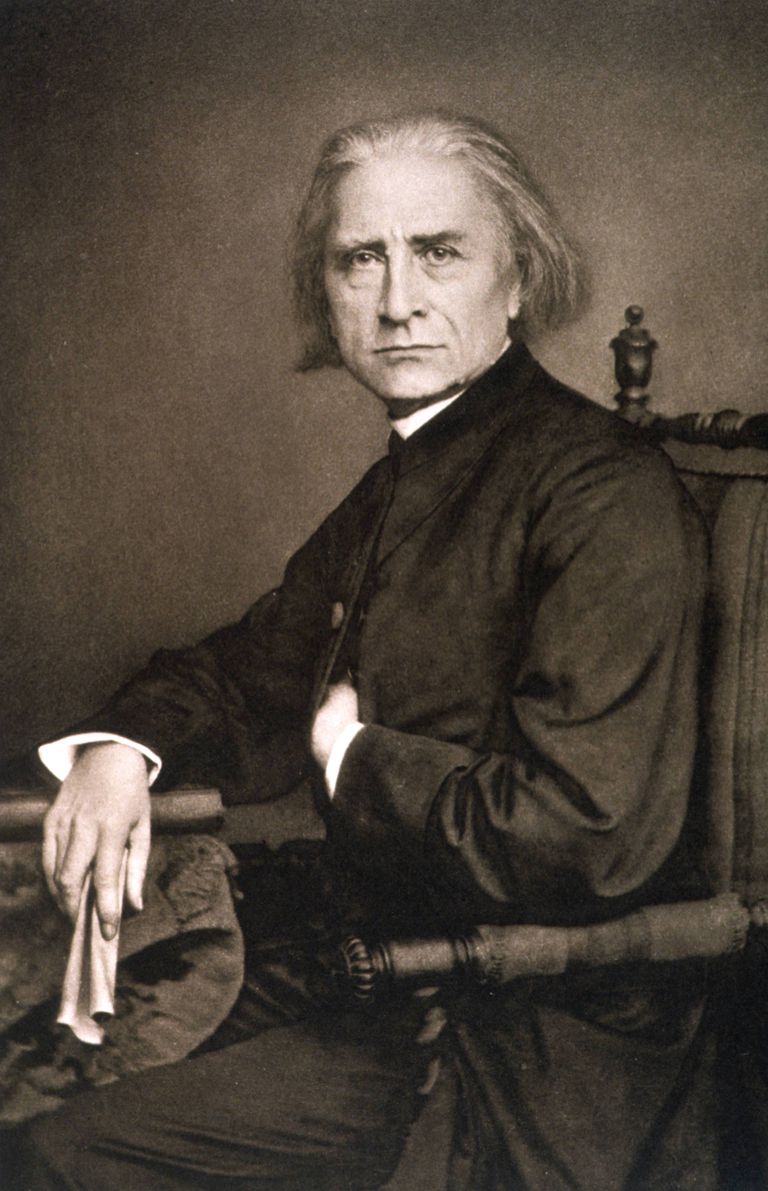
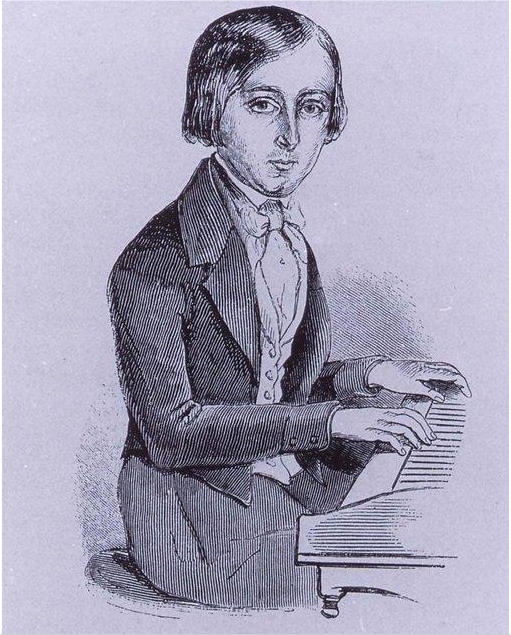
Camille Saint-Saëns
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (, , 9October 183516 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor and pianist of the Romantic music, Romantic era. His best-known works include Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso (1863), the Piano Concerto No. 2 (Saint-Saëns), Second Piano Concerto (1868), the Cello Concerto No. 1 (Saint-Saëns), First Cello Concerto (1872), ''Danse macabre (Saint-Saëns), Danse macabre'' (1874), the opera ''Samson and Delilah (opera), Samson and Delilah'' (1877), the Violin Concerto No. 3 (Saint-Saëns), Third Violin Concerto (1880), the Symphony No. 3 (Saint-Saëns), Third ("Organ") Symphony (1886) and ''The Carnival of the Animals'' (1886). Saint-Saëns was a musical prodigy; he made his concert debut at the age of ten. After studying at the Paris Conservatoire he followed a conventional career as a church organist, first at Saint-Merri, Paris and, from 1858, La Madeleine, Paris, La Madeleine, the official church of the Second French Empire, Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words is the music performed by the ensemble. Choirs may perform music from the classical music repertoire, which spans from the Medieval music, medieval era to the present, or popular music repertoire. Most choirs are led by a conducting, conductor, who leads the performances with arm, hand, and facial gestures. The term ''choir'' is very often applied to groups affiliated with a church (whether or not they actually occupy the Choir (architecture), quire), whereas a ''chorus'' performs in theatres or concert halls, but this distinction is not rigid. Choirs may sing without instruments, or accompanied by a piano, accordion, pipe organ, a small ensemble, or an orchestra. A choir can be a subset of an ensemble; thus one speaks of the "woodwind c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romain Bussine
Romain Bussine (4 November 1830 – 20 December 1899) was a French voice teacher, baritone singer, translator and poet active in the second half of the 19th century. Career He was born in Paris; and from the late 1860s until his death Bussine was professor of solfége (singing) at the city's Conservatoire. ''Le Monde artiste'' described him as teaching there for thirty years with undisputed authority. In 1871, together with Camille Saint-Saëns he founded the Société nationale de musique as a forum for promoting contemporary French chamber and orchestral music. In the 1880s a faction within the society successfully pressed for works by foreign composers to be accepted for performance by the society, as a result of which Bussine and Saint-Saëns resigned the joint presidency of the society in 1886.Cochard, Alain"150ème anniversaire de la naissance de la Société nationale de musique" Concertclassic.com. Retrieved 13 May 2021 Bussine translated the words of German and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Regnault
Alexandre Georges Henri Regnault (31 October 1843 – 19 January 1871) was a French painter. Biography Regnault was born in Paris, the son of Henri Victor Regnault. On leaving school he successively entered the studios of Antoine Montfort, Louis Lamothe and Alexandre Cabanel, was beaten for the ''Prix de Rome'' (1863) by Joseph Layraud and Xaiver Monchablon, and in 1864 exhibited two unremarkable portraits at the Paris Salon. In 1866, however, he carried off the ''Prix de Rome'' with a work of unusual force and distinction ''Thetis bringing the Arms forged by Vulcan to Achilles'' ( École de Beaux-Arts). The past in Italy did not touch him, but his illustrations to Wey's ''Rome'' show how observant he was of actual life and manners; even his ''Automedon'' (School of Fine Arts), executed in obedience to Academical regulations, was but a lively recollection of a carnival horse-race. At Rome, moreover, Regnault came into contact with the modern Hispano-Italian school, a schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta Holmès
Augusta Mary Anne Holmès (16 December 1847 – 28 January 1903) was a French composer of Ireland, Irish descent. In 1871, Holmès became a French nationality law, French national and added the accent to her last name.Rollo Myers: "Augusta Holmès: A Meteoric Career", in ''The Musical Quarterly'', vol. 53, no. 3 (July 1967), p. 365: "Her surname was Gallicized by the addition of a grave accent on its last syllable." She also published music under the name Hermann Zenta. She wrote the texts to almost all of her vocal music herself, including songs, oratorios, the libretto of her opera ''La Montagne noire'' and the programmatic poems for her symphonic poems including ''Irlande'' and ''Andromède''. Biography Holmès was born in Paris, the only child of Charles William Scott Dalkeith Holmes (17 July 1797 - 19 December 1869), originally from Youghal, Ireland, and Tryphina Anna Constance Augusta Shearer (1811–1858). The poet Alfred de Vigny, who was her godfather, was rumored to be h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. Lasting from 19 July 1870 to 28 January 1871, the conflict was caused primarily by France's determination to reassert its dominant position in continental Europe, which appeared in question following the decisive Austro-Prussian War, Prussian victory over Austria in 1866. According to some historians, Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck deliberately provoked the French into declaring war on Prussia in order to induce four independent southern German states—Grand Duchy of Baden, Baden, Kingdom of Württemberg, Württemberg, Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria and Grand Duchy of Hesse, Hesse-Darmstadt—to join the North German Confederation. Other historians contend that Bismarck exploited the circumstances as they unfolded. All agree that Bismarck recognized the potential for new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duet
A duet (italian language, Italian: ''duo'') is a musical composition for two Performing arts, performers in which the performers have equal importance to the piece, often a composition involving two singers or two pianists. It differs from a harmony, as the performers take turns performing a solo section rather than performing simultaneously. A piece performed by two pianists performing together on the same piano is a "piano duet" or "piano four hands". A piece for two pianists performing together on separate pianos is a "List of compositions for piano duo, piano duo". "Duet" is also used as a verb for the act of performing a musical duet, or colloquially as a noun to refer to the performers of a duet. A musical ensemble with more than two solo instruments or voices is called a Trio (music), trio, quartet, quintet, sextet, septet, octet (music), octet, etc. History When Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Mozart was young, he and his sister Maria Anna Mozart, Marianne played a duet of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
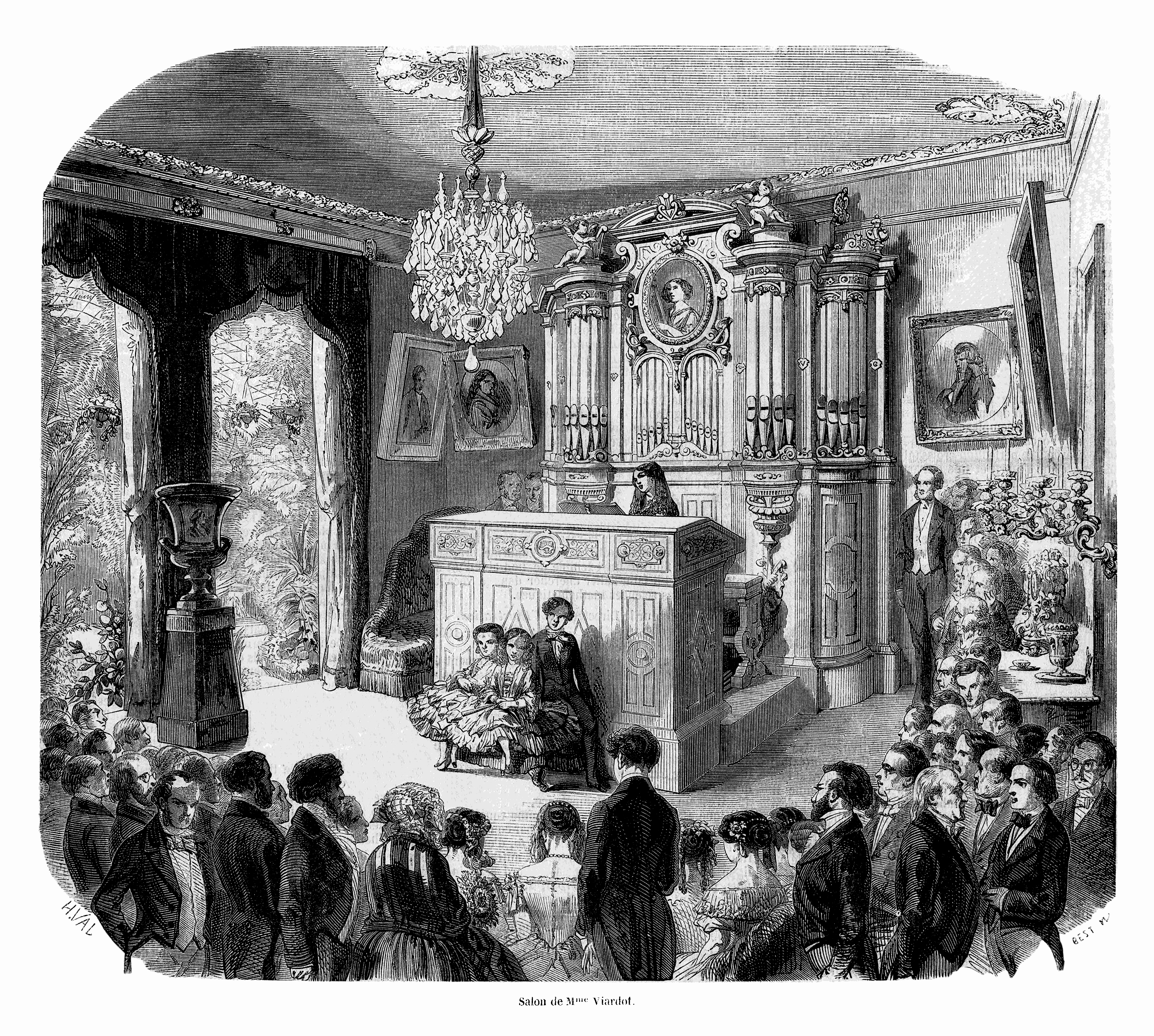
Pauline Viardot
Pauline Viardot (; 18 July 1821 – 18 May 1910) was a French dramatic mezzo-soprano, composer and pedagogue of Spanish descent. Born Michelle Ferdinande Pauline García,FitzLyon, p. 15, referring to the baptismal name. Thbirth recorddigitized at Paris's ''État civil reconstitué (XVIe-1859)'' reads instead: "Michelle Pauline Ferdinande Laurence Garcia". she came from a musical family and took up music at a young age. She began performing as a teenager and had a long and illustrious career as a star performer. Name Her name appears in various forms. When it is not simply "Pauline Viardot", it most commonly appears in association with her maiden name García or the unaccented form, Garcia. This name sometimes precedes Viardot and sometimes follows it. Sometimes the words are hyphenated; sometimes they are not. She achieved initial fame as "Pauline García"; the accent was dropped at some point, but exactly when is not clear. After her marriage, she referred to herself simply as " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Timbre D'argent
''Le timbre d'argent'' (, ''The Silver Bell'') is an in four acts by composer Camille Saint-Saëns to a French libretto by Jules Barbier and Michel Carré. Although completed in 1865, the opera did not receive its premiere performance until 23 February 1877, when it was presented by Albert Vizentini's Théâtre National Lyrique at the Théâtre de la Gaîté (rue Papin), Théâtre de la Gaîté in Paris.Saint-Saëns 1877, p. 3; Boston Public Library 1916p. 339 Langham-Smith 1992, p. 874; Harding 1980, p. 202. It includes the well-known aria "Le bonheur est chose légère". History ''Le timbre d'argent'' is the first opera that Saint-Saëns composed. The opera was commissioned by the Théâtre Lyrique and he began composing the music for it in 1864, finishing in 1865. The work's premiere was delayed, first by the financial difficulties of the opera house and then later by the Franco-Prussian War. Over the next 12 years Saint-Saëns recomposed the dialogue to form a Grand Opera vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Philippe Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; ; – ) was a French composer and music theory, music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of French opera and is also considered the leading French composer of his time for the harpsichord, alongside François Couperin. Little is known about Rameau's early years. It was not until the 1720s that he won fame as a major theorist of music with his ''Treatise on Harmony'' (1722) and also in the following years as a composer of masterpieces for the harpsichord, which circulated throughout Europe. He was almost 50 before he embarked on the operatic career on which his reputation chiefly rests today. His debut, ''Hippolyte et Aricie'' (1733), caused a great stir and was fiercely attacked by the supporters of Lully's style of music for its revolutionary use of harmony. Nevertheless, Rameau's pre-eminence in the field of French opera was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778), known by his ''Pen name, nom de plume'' Voltaire (, ; ), was a French Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment writer, philosopher (''philosophe''), satirist, and historian. Famous for his wit and his criticism of Christianity (especially Criticism of the Catholic Church, of the Roman Catholic Church) and of slavery, Voltaire was an advocate of freedom of speech, freedom of religion, and separation of church and state. Voltaire was a versatile and prolific writer, producing works in almost every literary form, including Stageplay, plays, poems, novels, essays, histories, and even scientific Exposition (narrative), expositions. He wrote more than 20,000 letters and 2,000 books and pamphlets. Voltaire was one of the first authors to become renowned and commercially successful internationally. He was an outspoken advocate of civil liberties and was at constant risk from the strict censorship laws of the Catholic French monarchy. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |