|
Sallustii
Gaius Sallustius Crispus, usually anglicisation, anglicised as Sallust (, ; –35 BC), was a historian and politician of the Roman Republic from a plebeian family. Probably born at Amiternum in the country of the Sabines, Sallust became a partisan of Julius Caesar (100 to 44 BC), circa 50s BC. He is the earliest known Latin-language Roman historian with surviving works to his name, of which ''Conspiracy of Catiline'' on Catilinarian conspiracy, the eponymous conspiracy, ''The Jugurthine War'' on the Jugurthine War, eponymous war, and the ''Histories'' (of which only fragments survive) remain extant. As a writer, Sallust was primarily influenced by the works of the 5th century BCE, 5th-century BC Greek historian Thucydides. During his political career he amassed great and ill-gotten wealth from his governorship of Africa. Life and career Sallust was probably born in Amiternum in Central Italy,.. though Eduard Schwartz takes the view that Sallust's birthplace was Rome. His birt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Sallustius Passienus Crispus
Gaius Sallustius Passienus Crispus was a prominent figure in the Roman Empire during the first century. He held the consulship twice, and was stepfather of the future emperor Nero. Background Suetonius reports that Passienus was born at Visellium, an obscure town whose location has been lost.Suetonius, "The Life of Passienus Crispus". He was the grandson of Lucius Passienus Rufus, consul in 4 BC. His father, who died in AD 21, was a grandnephew of the historian Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), who had no children of his own, and therefore adopted his sister's grandson as his heir. The elder Passienus assumed his uncle's names, in accordance with Roman custom, and in turn these names were passed to his son.Tacitus, ''Annales'', iii. 30. Early career Passienus was a regular pleader in the court of the Centumviri, which met in the Basilica Julia. Suetonius mentions a statue of Passienus, which had been set up in the Basilica. He made his first speech in the senate during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
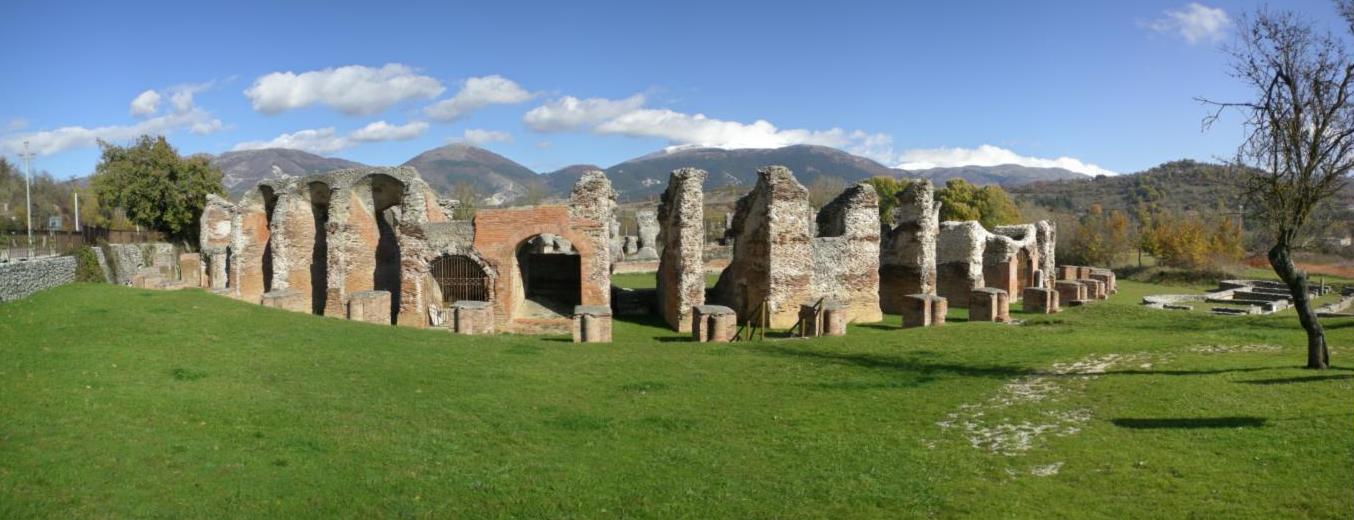
Amiternum
Amiternum was an ancient Sabine city, then Roman city and later bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see in the central Abruzzo region of modern Italy, located from L'Aquila. Amiternum was the birthplace of the historian Sallust (86 BC). History The site, in the upper Aterno valley, was one of the most important of Sabinum. Amiternum was defeated by the Romans in 293 BC. It lay at the point of junction of four roads: the Via Caecilia, the Via Claudia Nova and two branches of the Via Salaria. There are considerable remains of an amphitheatre and a theatre, all of which belong to the imperial period, while on the hill of the surrounding village of San Vittorino there are some Christian catacombs. A well known Roman funerary relief of the first century BC depicts the Roman funeral procession or ''pompa''. File:Amiternum 2015 by-RaBoe 097.jpg, Amphitheatre of Amiternum File:Amiternum 2015 by-RaBoe 064.jpg, Amiternum Theatre Ecclesiastical history The modern name of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Schwartz
Eduard Schwartz (22 August 1858 – 13 February 1940) was a German classical philologist. Born in Kiel, he studied under Hermann Sauppe in Göttingen, under Hermann Usener and Franz Bücheler in Bonn, under Theodor Mommsen in Berlin and under Ulrich von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff in Greifswald. In 1880 he obtained his doctorate from the University of Bonn.Saint Cyril, Patriarch of Alexandria. With Introduction and Notes by E. Schwartz, 1927 publications References External links Deutsche Wikisource extensive bibliography. {{DEFAULTSORT:Schwartz, Eduard [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebeian Tribune
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune () was the first office of the Roman state that was open to the plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate and magistrates. These tribunes had the power to convene and preside over the '' Concilium Plebis'' (people's assembly); to summon the senate; to propose legislation; and to intervene on behalf of plebeians in legal matters; but the most significant power was to veto the actions of the consuls and other magistrates, thus protecting the interests of the plebeians as a class. The tribunes of the plebs were typically found seated on special benches set up for them in the Roman Forum. The tribunes were sacrosanct, meaning that any assault on their person was punishable by death. In imperial times, the powers of the tribunate were granted to the emperor as a matter of course, and the office itself lost its independence and most of its fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaestor
A quaestor ( , ; ; "investigator") was a public official in ancient Rome. There were various types of quaestors, with the title used to describe greatly different offices at different times. In the Roman Republic, quaestors were elected officials who supervised the state treasury and conducted audits. When assigned to provincial governors, the duties were mainly administrative and logistical, but also could expand to encompass military leadership and command. It was the lowest ranking position in the ' (course of offices); by the first century BC, one had to have been quaestor to be eligible for any other posts. In the Roman Empire, the position initially remained as assistants to the magistrates with financial duties in the provinces, but over time, it faded away in the face of the expanding imperial bureaucracy. A position with a similar name (the ') emerged during the Constantinian period with judicial responsibilities. Etymology ''Quaestor'' derives from the Latin verb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cursus Honorum
The , or more colloquially 'ladder of offices'; ) was the sequential order of public offices held by aspiring politicians in the Roman Republic and the early Roman Empire. It was designed for men of senatorial rank. The comprised a mixture of military and political administration posts; the ultimate prize for winning election to each "rung" in the sequence was to become one of the two consuls in a given year. These rules were altered and flagrantly ignored in the course of the last century of the Republic. For example, Gaius Marius held consulships for five years in a row between 104 and 100 BC. He was consul seven times in all, also serving in 107 and 86. Officially presented as opportunities for public service, the offices often became mere opportunities for self-aggrandizement. The constitutional reforms of Sulla between 82 and 79 BC required a ten-year interval before holding the same office again for another term. To have held each office at the youngest pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social War (91–88 BC)
Social War may refer to: * Social War (357–355 BC), or the War of the Allies, fought between the Second Athenian Empire and the allies of Chios, Rhodes, and Cos as well as Byzantium * Social War (220–217 BC), fought among the southern Greek states * Social War (91–87 BC) The Social War (from Latin , "war of the allies"), also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought largely from 91 to 88 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies () in Roman Italy, Italy. Some of the ..., or the Italian or Marsic War, fought between the Roman Republic and several Italian cities * '' The Social War'', an 1872 novel by Simon Mohler Landis {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equestrian Order
The (; , though sometimes referred to as " knights" in English) constituted the second of the property/social-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an (). Description During the Roman Kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six (hundreds) of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians (plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 . These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly organisation, and were not granted the same privileges. By the time of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabines
The Sabines (, , , ; ) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains (see Sabina) of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome. The Sabines divided into two populations just after the founding of Rome, which is described by Roman legend. The division, however it came about, is not legendary. The population closer to Rome transplanted itself to the new city and united with the preexisting citizenry, beginning a new heritage that descended from the Sabines but was also Latinized. The second population remained a mountain tribal state, coming finally to war against Rome for its independence along with all the other Italic tribes. Afterwards, it became assimilated into the Roman Republic. Etymology The Sabines derived directly from the ancient Umbrians and belonged to the same ethnic group as the Samnites and the Sabelli, as attested by the common ethnonyms of ''Safineis'' (in ancient Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals (Tacitus)
The ''Annals'' () by Roman historian and senator Tacitus is a history of the Roman Empire from the reign of Tiberius to that of Nero, the years AD 14–68. The ''Annals'' are an important source for modern understanding of the history of the Roman Empire during the 1st century AD. Tacitus' final work, modern historians generally consider it his magnum opus which historian Ronald Mellor says represents the "pinnacle of Roman historical writing". Tacitus' ''Histories'' and ''Annals'' together amounted to 30 books, although some scholars disagree about which work to assign some books to, traditionally 14 are assigned to ''Histories'' and 16 to ''Annals''. Of the 30 books referred to by Jerome about half have survived. Modern scholars believe that as a Roman senator, Tacitus had access to '' Acta Senatus''—the Roman senate's records—which provided a solid basis for his work. Although Tacitus refers to part of his work as "my annals", the title of the work ''Annals'' used tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' (Latin: ) and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ), originally formed a continuous narrative of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the end of Domitian’s reign (96 AD). The surviving portions of the Annals focus on the reigns of Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see ), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''). Tacitus's ''Histories'' offers insights into Roman attitudes towards Jews, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Grant (classicist)
Michael Grant (21 November 1914 – 4 October 2004) was an English classicist, Professor of Humanity at the University of Edinburgh, numismatist, and author of numerous books on ancient history. His 1956 translation of Tacitus's '' Annals of Imperial Rome'' remains a standard of the work. Having studied and held a number of academic posts in the United Kingdom and the Middle East, he retired early to write full-time. He once described himself as "one of the very few freelancers in the field of ancient history: a rare phenomenon". As a populariser, his hallmarks were his prolific output and his unwillingness to oversimplify or talk down to his readership. He published over 70 works. Biography Grant was born in London, the son of Col. Maurice Grant who served in the Boer War and later wrote part of its official history. Young Grant attended Harrow School and read classics (1933–37) at Trinity College, Cambridge. His speciality was academic numismatics. His research fellowship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |