|
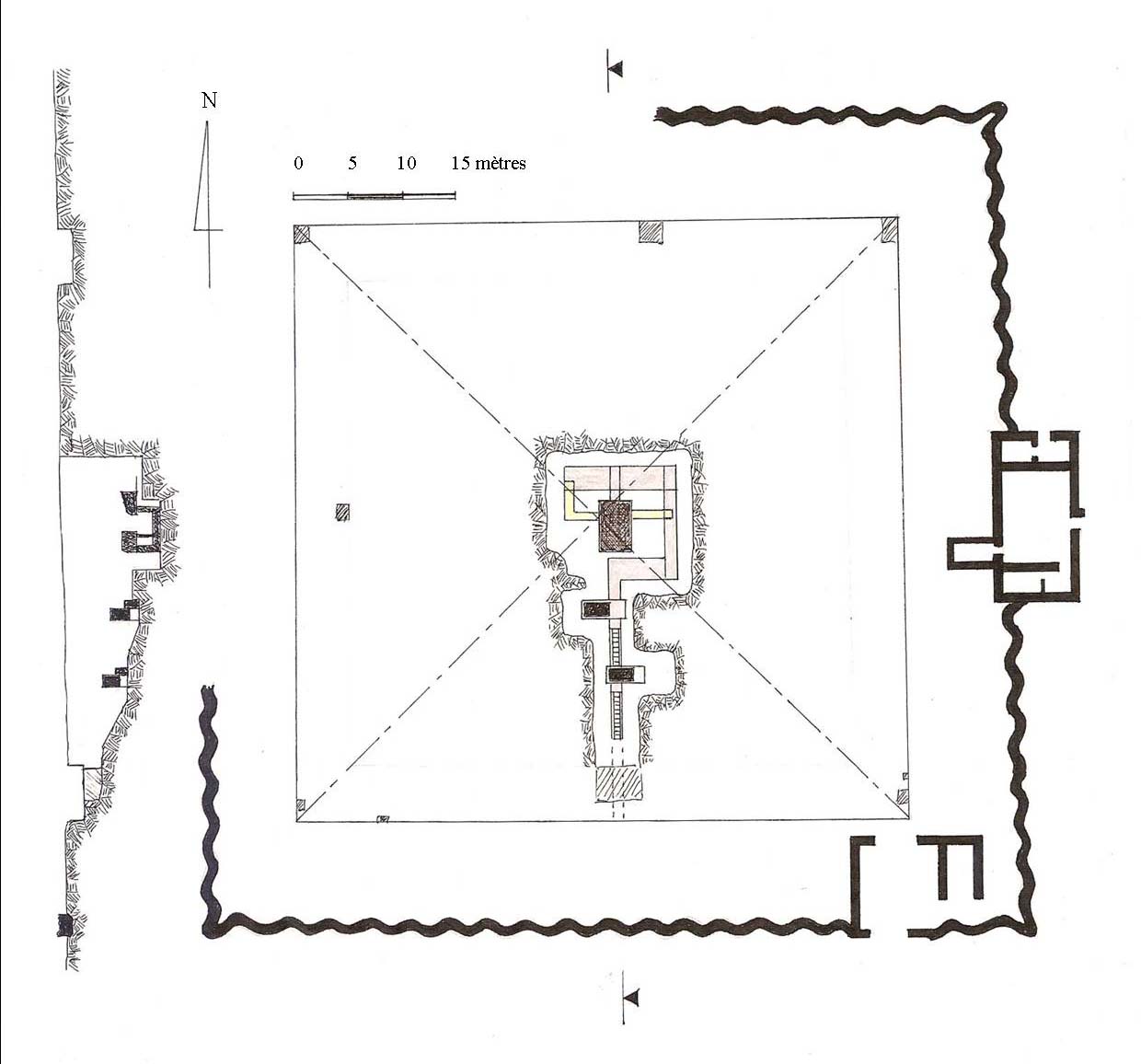
S 9 (Abydos)
S 9 (also Abydos-south S9) is the modern name given to a monumental ancient Egyptian tomb complex at Abydos, Egypt, Abydos in Egypt. The tomb is most likely royal and dates to the mid-Thirteenth dynasty of Egypt, 13th Dynasty, during the late Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom. Finds from the area of the tomb indicate that S9 suffered extensive, state-sanctioned stone and grave robbing during the Second Intermediate Period, only a few decades after its construction, as well as during the later Egypt (Roman province), Roman and Coptic periods. Although no direct evidence was found to determine the tomb owner, strong indirect evidence suggest that the neighbouring and slightly smaller tomb S 10 (Abydos), S10 belongs to pharaoh Sobekhotep IV (fl. c. 1725 BC). Consequently, S9 has been tentatively attributed by the Egyptologist Josef W. Wegner to Sobekhotep IV's predecessor and brother, Neferhotep I (fl. c. 1735 BC). According to Wegner, the tomb might originally have been capped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
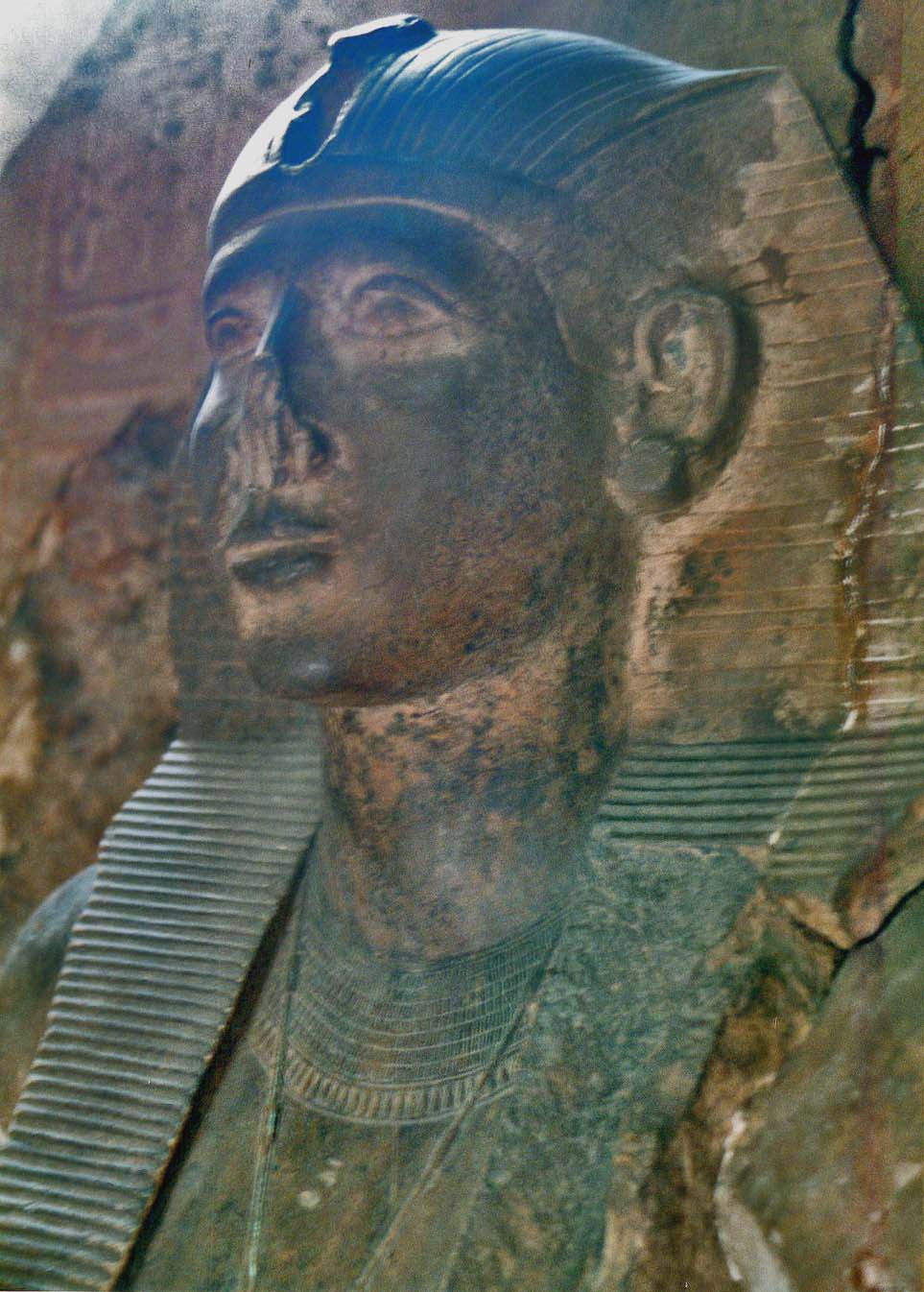
Neferhotep I
Khasekhemre Neferhotep I was an Ancient Egypt, Egyptian pharaoh of the mid Thirteenth dynasty of Egypt, Thirteenth Dynasty ruling in the second half of the 18th century BCKim Ryholt, Ryholt, K.S.B: The Political Situation in Egypt During the Second Intermediate Period, c.1800–1550 BC', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, (1997). . . . during a time referred to as the late Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom or early Second Intermediate Period, depending on the scholar. One of the best attested rulers of the 13th Dynasty, Neferhotep I reigned for 11 years according to the Turin King List. The grandson of a non-royal townsman from a Thebes, Egypt, Theban family with a military background, Neferhotep I's relation to his predecessor Sobekhotep III is unclear and he may have usurped the throne. Neferhotep I was likely contemporaneous with kings Zimri-Lim of Mari, Syria, Mari and Hammurabi of Babylon. Little is known of his activities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wah-Sut
Wah-Sut (, meaning ''Enduring are the places of Khakaure justified in Abydos'') is a town located south of Abydos in Middle Egypt. The name of the town indicates that it was originally built as an outlying part of Abydos, set up by the Egyptian state as housing for the people working in and around the funerary complex of pharaoh Senusret III (fl. c. 1850 BCE) of the Twelfth Dynasty, at the peak of the Middle Kingdom. This complex consists of the mortuary temple, the town of Wah-Sut, and a tomb dug into the bed-rock beneath the Mountain of Anubis, a nearby hill with a pyramidal shape. The town continued to exist for at least another 150 years, well into the Thirteenth Dynasty, when it was close to a royal necropolis of the tombs of Neferhotep I and Sobekhotep IV (fl. c. 1730 BCE). A document attests to its existence during the much later New Kingdom. Archaeology In 1901–1902, Charles Trick Currelly, Arthur E. P. Weigall, Ayrton and Flinders Petrie found Senusret III's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sobekhotep I
Sekhemre Khutawy Amenemhat Sobekhotep was an Egyptian pharaoh of the early 13th Dynasty in the late Middle Kingdom. His chronological position is much debated. In literature, Sekhemre Khutawy Sobekhotep is known as Sobekhotep II and Amenemhat Sobekhotep. Kim Ryholt (1997) makes a strong case for Sekhemre Khutawy Sobekhotep as the founder of the dynasty, a hypothesis that is now dominant in Egyptology.Darrell D. Baker: ''The Encyclopedia of the Pharaohs: Volume I – Predynastic to the Twentieth Dynasty 3300–1069 BC'', Stacey International, , 2008, p. 443 If so, he may be the first ruler with this name, making him Sobekhotep I. His double name may also be a filiation, Sobekhotep, son of Amenemhat. Reign We know almost nothing about his reign except what can be interpreted by archaeological finds. He ruled at a time of political turmoil during the early Thirteenth Dynasty, where the order of succession is unclear. At Lahun, a papyrus indicate that he ruled not long after Amene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
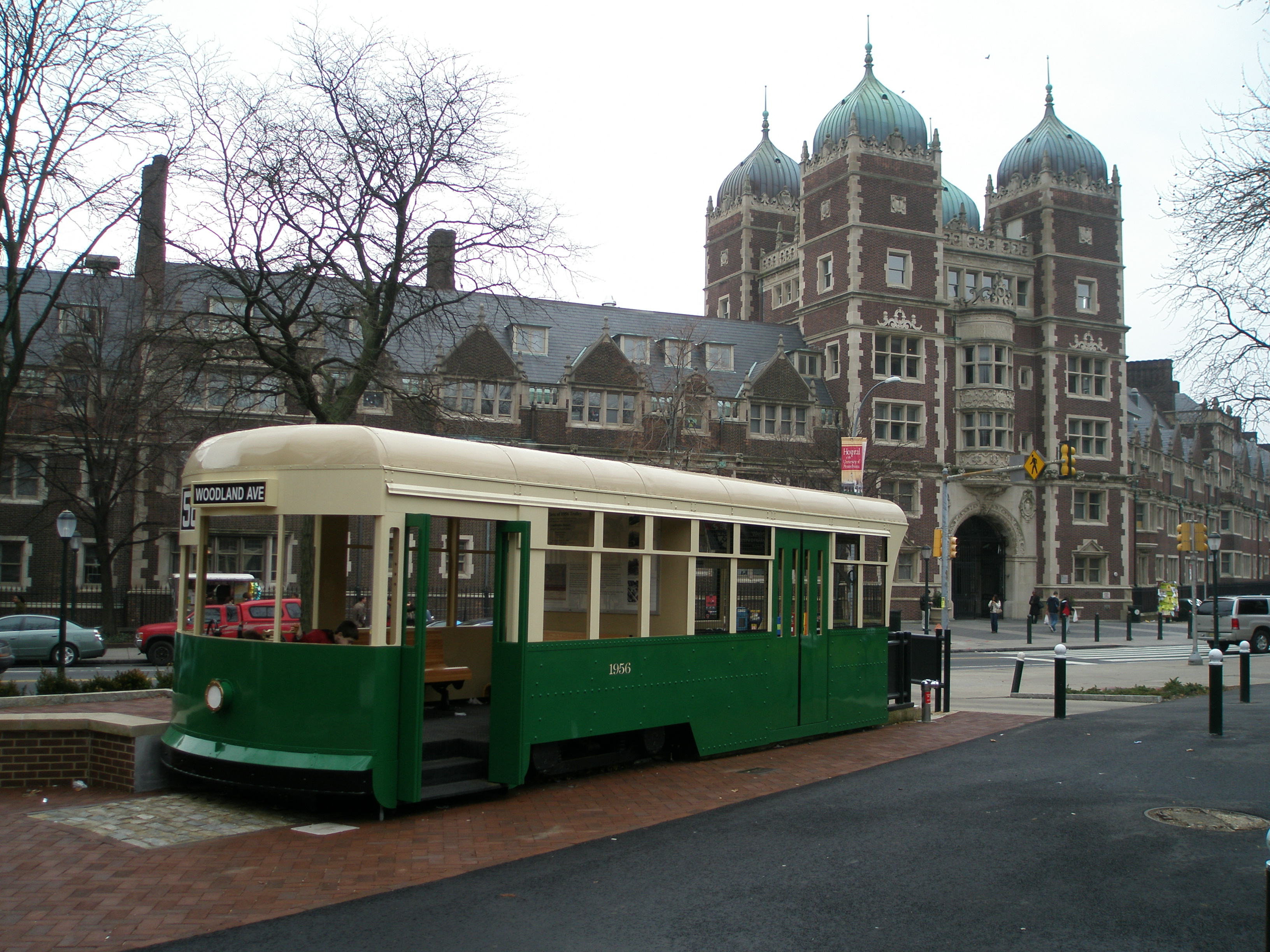
University Of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of founder and first president Benjamin Franklin, who had advocated for an educational institution that trained leaders in academia, commerce, and public service. The university has four undergraduate schools and 12 graduate and professional schools. Schools enrolling undergraduates include the College of Arts and Sciences, the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science, School of Engineering and Applied Science, the Wharton School, and the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, School of Nursing. Among its graduate schools are its University of Pennsylvania Law School, law school, whose first professor, James Wilson (Founding Father), James Wilson, helped write the Constitution of the United States, U.S. Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neferhotep I 2
Khasekhemre Neferhotep I was an Egyptian pharaoh of the mid Thirteenth Dynasty ruling in the second half of the 18th century BC Ryholt, K.S.B: The Political Situation in Egypt During the Second Intermediate Period, c.1800–1550 BC', Carsten Niebuhr Institute Publications, 20. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum Press, (1997). . . . during a time referred to as the late Middle Kingdom or early Second Intermediate Period, depending on the scholar. One of the best attested rulers of the 13th Dynasty, Neferhotep I reigned for 11 years according to the Turin King List. The grandson of a non-royal townsman from a Theban family with a military background, Neferhotep I's relation to his predecessor Sobekhotep III is unclear and he may have usurped the throne. Neferhotep I was likely contemporaneous with kings Zimri-Lim of Mari and Hammurabi of Babylon. Little is known of his activities during his decade-long reign and the most important document surviving from his rule is a stela from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aidan Dodson
Aidan Mark Dodson (born 1962) is an English Egyptologist and historian. He has been honorary professor of Egyptology at the University of Bristol since 1 August 2018. Academic career Dodson, born in London on 11 September 1962, studied at Langley Grammar School (1975–81), before moving to Collingwood College, Durham (1981-2). He completed a BA at the University of Liverpool (1985), and an MPhil (1986, museum practice and archaeology) and PhD (1995, Egyptology) at Christ's College, Cambridge. He began teaching at the University of Bristol in October 1996, also holding the post of Simpson Professor of Egyptology at the American University in Cairo from January to July 2013. His primary research interests concern Ancient Egypt, with a particular focus on dynastic history and chronology, tomb architecture, sarcophagus and coffin design, canopic equipment, and the history of Egyptology; he is also an historian of late 19th and early 20th century navies, and has written on the roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis (, ; Bohairic ; ), or Men-nefer, was the ancient capital of Inebu-hedj, the first Nome (Egypt), nome of Lower Egypt that was known as ''mḥw'' ("North"). Its ruins are located in the vicinity of the present-day village of Mit Rahina (), in markaz (county) Badrashin, Giza, Egypt. Along with the Memphite Necropolis, pyramid fields that stretch on a desert plateau for more than on its west, including the famous Giza pyramid complex, Pyramids of Giza, Memphis and its necropolis have been listed as a World Heritage Site. The site is open to the public as an open-air museum. According to legends related in the early third century BC by Manetho, a priest and historian who lived in the Ptolemaic Kingdom during the Hellenistic period of ancient Egypt, the city was founded by Pharaoh, King Menes. It was the List of Egyptian capitals, capital of ancient Egypt (''Kemet'' or ''Kumat'') during both the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom and remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid
A pyramid () is a structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon shape, such as triangular or quadrilateral, and its surface-lines either filled or stepped. A pyramid has the majority of its mass closer to the ground with less mass towards the pyramidion at the apex. This is due to the gradual decrease in the cross-sectional area along the vertical axis with increasing elevation. This offers a weight distribution that allowed early civilizations to create monumental structures.Ancient civilizations in many parts of the world pioneered the building of pyramids. The largest pyramid by volume is the Mesoamerican Great Pyramid of Cholula, in the Mexican state of Puebla. For millennia, the largest structures on Earth were pyramids—first the Red Pyramid in the Dashur Necropolis and then the Great Pyramid of Khufu, bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastaba
A mastaba ( , or ), also mastabah or mastabat) is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks or limestone. These edifices marked the burial sites of many eminent Egyptians during Egypt's Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom. Non-royal use of mastabas continued for over a thousand years. The word ''mastaba'' comes from the Arabic word (maṣṭaba) "stone bench". The Ancient Egyptian name was pr- Djt, meaning "house of stability", " house of eternity", or "eternal house". History The afterlife was centralized in the religion of ancient Egyptians. Their architecture reflects this, most prominently by the enormous amounts of time and labor involved in building tombs. Ancient Egyptians believed that the needs from the world of the living would be continued in the afterlife; it was therefore necessary to build tombs that would fulfill them, and be sturdy enough to last for an eter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Khendjer
The pyramid of Khendjer was a pyramid built for the burial of the 13th dynasty pharaoh Khendjer, who ruled Egypt c. 1760 BC during the Second Intermediate Period. The pyramid, which is part of larger complex comprising a mortuary temple, a chapel, two enclosure walls and a subsidiary pyramid, originally stood around high and is now completely ruined. The pyramidion was discovered during excavations under the direction of Gustave Jéquier in 1929, indicating that the pyramid was finished during Khendjer's lifetime. It is the only pyramid known to have been completed during the 13th Dynasty. Excavations The first investigations of the pyramid of Khendjer were undertaken in the mid 19th century by Karl Richard Lepsius, who included the pyramid in his list under the number XLIV. The pyramid was excavated by Gustave Jéquier from 1929 until 1931 with the excavation report published two years later in 1933.Gustave Jéquier: ''Deux pyramides du Moyen Empire'', Cairo 1933, pp. 3-3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts, and hence quartzite is a metasandstone. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Mazghuna Pyramid
The Southern Mazghuna Pyramid is an ancient Egyptian royal tomb which was built during the 12th or the 13th Dynasty in Mazghuna, 5 km south of Dahshur, Egypt. The building was never finished, and is still unknown which pharaoh was the owner, since no appropriate inscription have been found. The pyramid was rediscovered in 1910 by Ernest Mackay and excavated in the following year by Flinders Petrie. Dating The pyramid can be dated to either late 12th Dynasty or early 13th Dynasty. 12th Dynasty The pyramid might date to the 12th Dynasty, as the building shares some structural similarities to the Hawara pyramid of Amenemhat III. For this reason it is usually attributed to Amenemhat IV, while the northern Mazghuna pyramid is attributed to Sobekneferu. 13th Dynasty William C. Hayes (1953) believed that the southern pyramid was built during the 13th Dynasty, on the basis of some similarities with the pyramid of Khendjer.W.C. Hayes, ''The Scepter of Egypt. A Background for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |