|
STAR Voting
STAR voting is an electoral system for single-seat elections. The name (an allusion to Star (classification), star ratings) stands for "Score Then Automatic Runoff", referring to the fact that this system is a combination of score voting, to pick two finalists with the highest total scores, followed by an "automatic runoff" in which the finalist who is preferred on more ballots wins. It is a type of cardinal voting electoral system. Method In STAR, voters are given a score ballot (or ratings ballot) on which each voter scores candidates with a number from 0 up to 5, with 0 representing "worst" and 5 representing "best". The scores for each candidate are then summed, and the two highest-scored candidates are selected as finalists. In the automatic runoff round, the finalist who was given a higher score on a greater number of ballots is selected as the winner. Usage The concept was first proposed in October 2014 by Mark Frohnmayer, and was initially called score runoff voting ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAR Ballot, Blue, Standard, 11-13-23
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye—all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material largely comprising hydrogen, helium, and traces of heavier elements. Its stellar mass, total mass mainly determines it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multnomah County, Oregon
Multnomah County is one of the Oregon counties, 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the county's population was 815,428. Multnomah County is part of the Portland metropolitan area. The state's smallest and most populous county, its county seat, Portland, is the state's List of cities in Oregon, most populous city. History The area of the lower Willamette River has been inhabited for thousands of years, including by the Multnomah people, Multnomah band of Chinookan peoples long before European contact, as evidenced by the nearby Cathlapotle village, just downstream. Multnomah County (the 13th in Oregon Territory) was created on December 22, 1854, formed out of two other Oregon counties – the eastern part of Washington County, Oregon, Washington County and the northern part of Clackamas County, Oregon, Clackamas County. Its creation was a result of a petition earlier that year by businessmen in Portland complaining of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
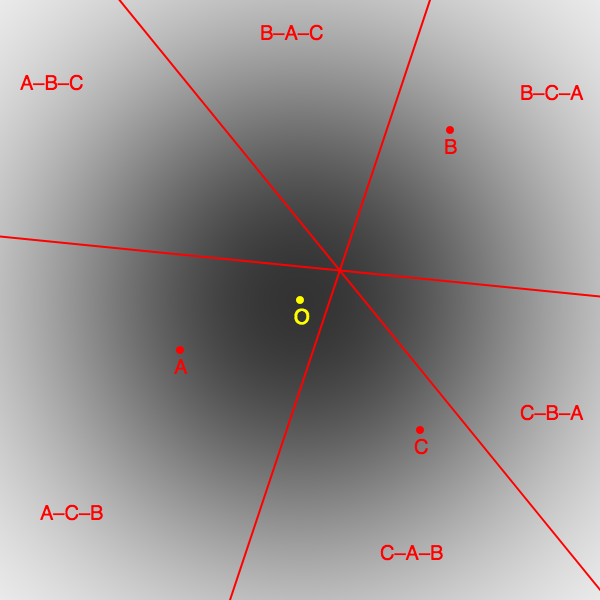
Voting System Criteria
This article discusses the methods and results of comparing different electoral systems. There are two broad methods to compare voting systems: # Metrics of voter satisfaction, either through simulation or survey. # Adherence to logical criteria. Evaluation by metrics Models of the electoral process Voting methods can be evaluated by measuring their accuracy under random simulated elections aiming to be faithful to the properties of elections in real life. The first such evaluation was conducted by Chamberlin and Cohen in 1978, who measured the frequency with which certain non-Condorcet systems elected Condorcet winners. Condorcet jury model The Marquis de Condorcet viewed elections as analogous to jury votes where each member expresses an independent judgement on the quality of candidates. Candidates differ in terms of their objective merit, but voters have imperfect information about the relative merits of the candidates. Such jury models are sometimes known as valence models. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resolvability Criterion
A voting system is called decisive, resolvable, or resolute if it ensures a low probability of tied elections. There are two different criterion that formalize this. * In Nicolaus Tideman's version of the criterion, adding one extra vote (with no tied ranks) should make the winner unique. * Douglas R. Woodall's version requires that the probability of a tied vote under an impartial culture model gives a tie approaches zero as the number of voters increases toward infinity. A non-resolvable social choice function is often only considered to be a ''partial'' electoral method, sometimes called a voting correspondence or set-valued voting rule. Such methods frequently require tiebreakers that can substantially affect the result. However, non-resolute methods can be used as a first stage to eliminate candidates before ties are broken with some other method. Methods that have been used this way include the Copeland set, the Smith set, and the Landau set. References {{voting syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Matters
''Voting matters'' was a peer-reviewed academic journal whose purpose is "To advance the understanding of preferential voting systems". Originally published by the Electoral Reform Society (1994–2003), ''Voting matters'' then became a publication of the McDougall Trust until April, 2013. The journal's founding editor-in-chief (1994–2010) was British mathematician and computer scientist Brian Wichmann, followed by Nicolaus Tideman. ''Voting matters'' papers dealt with the study of various electoral systems An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, nonprofit organizations and inf .... The journal has also republished several seminal papers on STV by Thomas Hare, Henry Richmond Droop, and Brian Meek. External links * McDougall Trust Single transferable vote Open access journals English-language jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonicity Criterion
Electoral system criteria In social choice, the negative response, perversity, or additional support paradox is a pathological behavior of some voting rules where a candidate loses as a result of having too much support (or wins because of increased opposition). In other words, increasing (decreasing) a candidate's ranking or rating causes that candidate to lose (win), respectively. Electoral systems that do not exhibit perversity are sometimes said to satisfy the monotonicity criterion.D R Woodall"Monotonicity and Single-Seat Election Rules" '' Voting matters'', Issue 6, 1996 Perversity is often described by social choice theorists as an exceptionally severe kind of electoral pathology, as such rules can have "backwards" responses to voters' opinions, where popularity causes defeat while unpopularity leads to a win. Similar rules treat the well-being of some voters as "less than worthless". These issues have led to constitutional prohibitions on such systems as violating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-round System
The two-round system (TRS or 2RS), sometimes called ballotage, top-two runoff, or two-round plurality, is a single-winner electoral system which aims to elect a member who has support of the majority of voters. The two-round system involves one or two rounds of choose-one voting, where the voter marks a single favorite candidate in each round. If no one has a majority of votes in the first round, the two candidates with the most votes in the first round move on to a second election (a second round of voting). The two-round system is in the family of plurality voting systems that also includes single-round plurality (FPP). Like instant-runoff (ranked-choice) voting and first past the post, it elects one winner. The two-round system first emerged in France and has since become the most common single-winner electoral system worldwide. Despite this, runoff-based rules like the two-round system and RCV have faced criticism from social choice theorists as a result of their suscep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approval Voting
Approval voting is a single-winner rated voting system where voters can approve of all the candidates as they like instead of Plurality voting, choosing one. The method is designed to eliminate vote-splitting while keeping election administration simple and Summability criterion, easy-to-count (requiring only a single score for each candidate). Approval voting has been used in both organizational and political elections to improve representativeness and voter satisfaction. Critics of approval voting have argued the simple ballot format is a disadvantage, as it forces a Dichotomous preferences, binary choice for each candidate (instead of the expressive grades of other rated voting rules). Effect on elections Research by Social choice theory, social choice theorists Steven Brams and Dudley R. Herschbach found that approval voting would increase voter participation, prevent minor-party candidates from being spoiler effect, spoilers, and reduce negative campaigning. Brams' researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instant-runoff Voting
Instant-runoff voting (IRV; ranked-choice voting (RCV), preferential voting, alternative vote) is a single-winner ranked voting election system where Sequential loser method, one or more eliminations are used to simulate Runoff (election), runoff elections. When no candidate has a majority of the votes in the first round of counting, each following round eliminates the candidate with the fewest First-preference votes, first-preferences (among the remaining candidates) and transfers their votes if possible. This continues until one candidate accumulates a majority of the votes still in play. Instant-runoff voting falls under the plurality-based voting-rule family, in that under certain conditions the candidate with the least votes is eliminated, making use of secondary rankings as contingency votes. Thus it is related to the Runoff election, two-round runoff system and the exhaustive ballot. IRV could also be seen as a single-winner equivalent of Single transferable vote, sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-past-the-post
First-past-the-post (FPTP)—also called choose-one, first-preference plurality (FPP), or simply plurality—is a single-winner voting rule. Voters mark one candidate as their favorite, or First-preference votes, first-preference, and the candidate with more first-preference votes than any other candidate (a Plurality (voting), ''plurality'') is elected, even if they do not have more than half of votes (a ''majority''). FPP has been used to elect part of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, British House of Commons since the Middle Ages before spreading throughout the British Empire. Throughout the 20th century, many countries that previously used FPP have abandoned it in favor of other electoral systems, including the former British colonies of Australia and New Zealand. FPP is still De jure, officially used in the majority of U.S. state, US states for most elections. However, the combination of Partisan primary, partisan primaries and a two-party system in these jurisd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oakridge, Oregon
Oakridge is a city in Lane County, Oregon, United States. The population was 3,205 as of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. It is located east of Westfir, Oregon, Westfir on Oregon Route 58, about east of Eugene, Oregon, Eugene and southeast of Portland, Oregon, Portland. Surrounded by the Willamette National Forest and the Cascade Range, Oakridge is popular with outdoor enthusiasts for its hiking, mountain biking, wildflowers, fly fishing, birding, watersports, and the nearby Willamette Pass Resort. The city was originally a community called "Hazeldell", and its post office was established on July 26, 1888. When a station on the Southern Pacific Transportation Company, Southern Pacific Railroad opened in May 1912, it was named "Oak Ridge" by a railroad executive for the surrounding topography, and on July 19 of that year the name was changed to be spelled as a single word. The economy of Oakridge and that of nearby Westfir is centered on recreation. Since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |