|
SR Merchant Navy Class 35018 British India Line
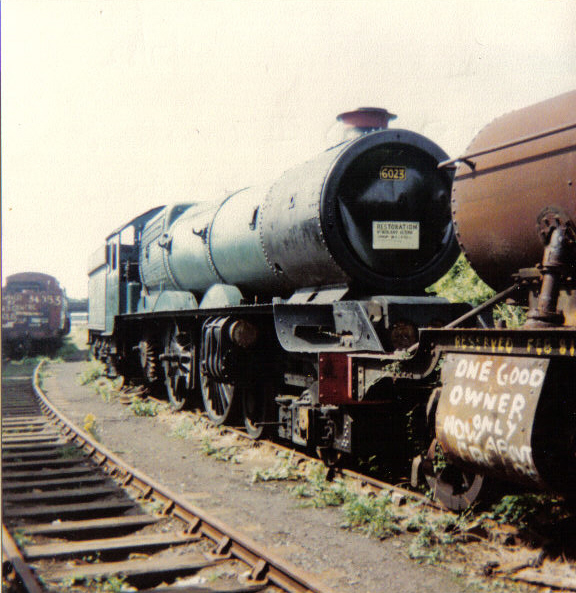
21C18 ''British India Line'' is a preserved SR Merchant Navy class steam locomotive built by the Southern Railway in 1945. ''British India Line'' was one of the first batch of twenty completed at Eastleigh Works in May 1945, and in that month was first shedded at Nine Elms shed, where it was to remain for most of its career, under both the Southern Railway and British Railways. On 24 November 1960 it was briefly re-allocated to Bournemouth's 71B shed, but in January of the following year it returned to Nine Elms 70A shed. 21C18 was withdrawn from service in August 1964 and sold on to Woodham Brothers scrapyard in Barry, South Wales where it arrived in December of the same year. It was rescued from the scrapyard in November 1979, but work to restore the locomotive began only in 2012 and ''British India Line'' ran again under its own steam on the main line in May 2017. Allocations and history The shed locations of 35018 on particular dates as well as where it has been stored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastleigh Works
Eastleigh Works is a locomotive, carriage and wagon building and repair facility in the town of Eastleigh, in the county of Hampshire in England. History LSWR The London and South Western Railway (LSWR) opened a carriage and wagon works at Eastleigh in 1891. In 1903, the Chief Mechanical Engineer, Dugald Drummond, oversaw the construction of a large motive power depot in the town; replacing the existing maintenance and repair shops at Northam, Southampton. In January 1910, locomotive building was likewise transferred to the new workshops at Eastleigh from Nine Elms in London. Among the locomotives produced by the LSWR under Drummond at Eastleigh, were the S14 0-4-0 and M7 0-4-4 tank engines, the P14 and T14 4-6-0, and D15 4-4-0, classes. Following the appointment of Robert Urie as Chief Mechanical Engineer in 1912, the works were responsible for the construction of the H15, S15, and N15 (King Arthur) 4-6-0 classes, and the G16 4-8-0, and H16 4-6-0 tank engines. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bournemouth
Bournemouth () is a coastal resort town in the Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole council area of Dorset, England. At the 2011 census, the town had a population of 183,491, making it the largest town in Dorset. It is situated on the English south coast, equidistant () from Dorchester and Southampton. Bournemouth is part of the South East Dorset conurbation, which has a population of 465,000. Before it was founded in 1810 by Lewis Tregonwell, the area was a deserted heathland occasionally visited by fishermen and smugglers. Initially marketed as a health resort, the town received a boost when it appeared in Augustus Granville's 1841 book, ''The Spas of England''. Bournemouth's growth accelerated with the arrival of the railway, and it became a town in 1870. Part of the historic county of Hampshire, Bournemouth joined Dorset for administrative purposes following the reorganisation of local government in 1974. Through local government changes in 1997, the town began to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Railways
West Coast Railways (WCR) is a railway spot-hire company and charter train operator based at Carnforth MPD in Lancashire. Using buildings and other facilities previously owned by the Carnforth MPD#Steamtown Carnforth, Steamtown Carnforth visitor attraction, in June 1998 the company became the first privately owned company to be given a licence as a train operating company. History Before 1998 After British Rail closed the Lakeside branch to passengers on 6 September 1965, a group of enthusiasts chaired by Peter Beet, Dr Peter Beet formed the Lakeside Railway Estates Company, with the idea of preserving both the line and Carnforth MPD, to provide a complete steam operating system. After agreeing to rent out part of the Carnforth MPD site, but with the counter the development of the A590 road meaning that the complete vision was unsuccessful, Beet developed the visitor attraction Steamtown Carnforth, which became a mecca for steam enthusiasts from 1967. In 1974, Sir William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a Historic counties of England, historic county, Ceremonial County, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, Lancashire, Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnforth
Carnforth is a market town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster in Lancashire, England, situated at the north-east end of Morecambe Bay. The parish of Carnforth had a population of 5,560 in the 2011 census, an increase from the 5,350 recorded in the 2001 census. The town is situated around 7 miles north of Lancaster, 17 miles south of Kendal, 40 miles east (bisected by Morecambe Bay) of Barrow-in-Furness and 28 miles northwest of Settle. The town is also close to the Cumbria/Lancashire border. Carnforth grew in the 19th century through the presence of the railway and ironworks. Due to the closeness of the coast and the hills, Carnforth is a popular base for walkers and cyclists exploring the area. The River Keer, the West Coast Main Line (WCML), the A6 and the Lancaster Canal pass through the town. The M6 motorway passes just to the east, linked to Carnforth by the A601(M). History The name "Carnforth" is thought to derive from its old function as a ford of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barry Scrapyard
Woodham Brothers Ltd is a trading business, based mainly around activities and premises located within Barry Docks, in Barry, South Wales. It is noted globally for its 1960s activity as a scrapyard (hence its colloquial name of Barry Scrapyard), where 297 withdrawn British Railways steam locomotives were sent, from which 213 were rescued for the developing railway preservation movement. History Established in 1892 as Woodham & Sons by Albert Woodham, the company was based at Thomson Street, Barry. The company bought old rope, dunnage wood and scrap metal from the ships, boats and marine businesses which used the newly created Barry Docks, which it then resold or scrapped. Albert retired in 1947, when his youngest son, Dai, was demobbed from the British Army after World War II. Dai renamed the business Woodham Brothers Ltd in 1953, creating four lines of business under four separate companies, which between them employed 200 people: Woodham Brothers, Woodham Transport, Woodha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SR West Country And Battle Of Britain Classes
The SR West Country and Battle of Britain classes, collectively known as ''Light Pacifics'' or informally as ''Spam Cans'', are streamliner, air-smoothed 4-6-2, 4-6-2 ''Pacific'' steam locomotives designed for the Southern Railway (UK), Southern Railway by its Chief Mechanical Engineer Oliver Bulleid. Incorporating a number of new developments in British steam locomotive technology, they were amongst the first British designs to use welding in the construction process, and to use steel Firebox (steam engine), fireboxes, which meant that components could be more easily constructed under wartime austerity and post-war economy.Arlett (1989), p. 29–30 They were designed to be lighter in weight than their sister locomotives, the SR Merchant Navy class, Merchant Navy class, to permit use on a wider variety of routes, including in the south-west of England and the Kent coast. They were a Mixed-traffic locomotive, mixed-traffic design, being equally adept at hauling passenger and frei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulleid Firth Brown Wheel
The Bulleid Firth Brown wheel (BFB) was a locomotive wheel developed for the Southern Railway in the late 1930s. It was a disc wheel, in contrast to the usual spoked wheels in general use on British railways. The wheel was designed by Oliver Bulleid and developed by the steel company Firth Brown of Sheffield. Design The BFB comprises a single disc, with teardrop-shaped indentations to give rigidity, and lightening holes to reduce weight. The advantage over a spoked wheel is that a disc wheel carries the tyre (the metal hoop shrunk onto the wheel to provide contact with the rail) more efficiently; spoked wheels are prone to shrink over time, causing the tyre to work loose, whilst in a disc wheel this is less pronounced. Disc wheels also distribute the weight more evenly, reducing the hammer effect on, and thus the damage to, the rail. The BFB weighed about ten per cent less than a spoked wheel of the same size.Day-Lewis p 146 Name The Bulleid Firth Brown, or BFB, is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walschaerts Valve Gear
The Walschaerts valve gear is a type of valve gear used to regulate the flow of steam to the pistons in steam locomotives, invented by Belgium, Belgian railway mechanical engineering, engineer Egide Walschaerts in 1844. The gear is sometimes named without the final "s", since it was incorrectly patented under that name. It was extensively used in steam locomotives from the late 19th century until the end of the steam era. History The Walschaerts valve gear was slow to gain popularity. The Stephenson valve gear remained the most commonly used valve gear on 19th-century locomotives. However, the Walschaerts valve gear had the advantage that it could be mounted entirely on the outside of the locomotives, leaving the space between the locomotive frame, frames clear and allowing easy access for service and adjustment, which resulted in it being adopted in some articulated locomotives. The first locomotive fitted with the Walschaerts valve gear was built at the Belgian Tubize worksh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
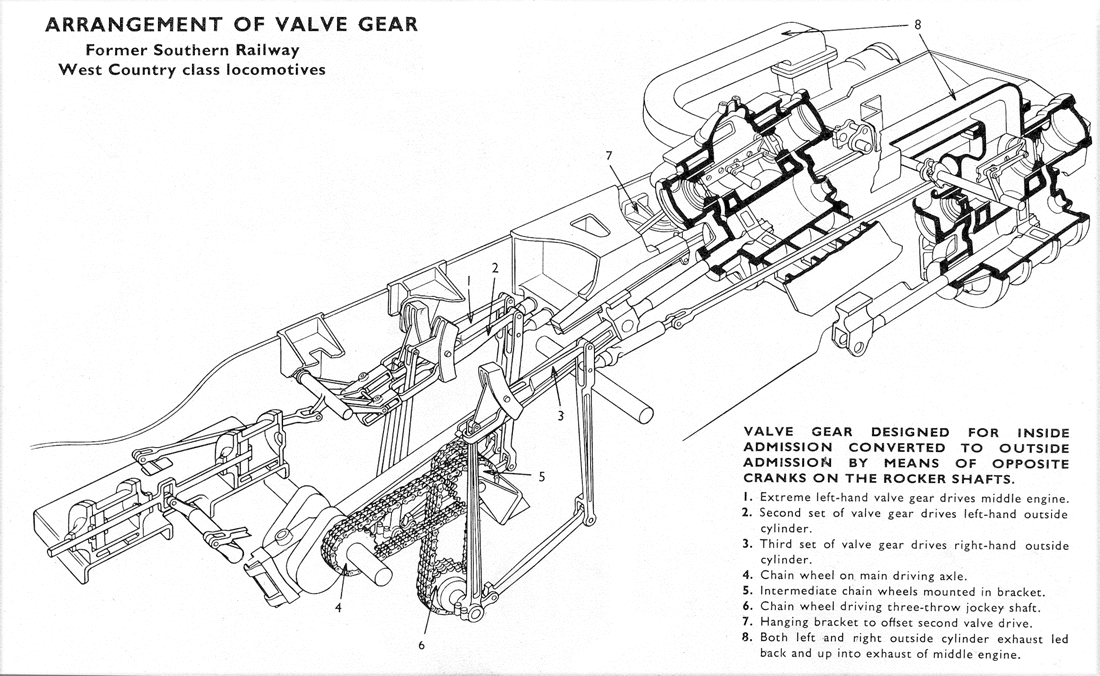
Bulleid Chain-driven Valve Gear
The Bulleid chain-driven valve gear is a type of steam locomotive valve gear designed by Oliver Bulleid during the Second World War for use on his Pacific (4-6-2) designs. It was peculiar to the Southern Railway in Britain, and borrowed from motor-vehicle practice in an attempt to create a compact and efficient design with a minimum of service requirements. Design principles Bulleid's decision to have three cylinders, all driving the middle coupled axle of his Merchant Navy and West Country / Battle of Britain classes, gave rise to several problems. As each cylinder was to have its own separate valve gear, this left very little space for the conventional inside set of motion. This prompted Bulleid to design a new miniaturised Walschaerts motion that was compact enough to enclose the whole system in a casing. All three sets of valve gear were worked from an auxiliary three-throw crankshaft. A Morse inverted-tooth drive chain ran horizontally from a triple sprocket on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnforth MPD
Carnforth MPD (Motive Power Depot) is a former London Midland and Scottish Railway railway depot located in the town of Carnforth, Lancashire, England. Completed in 1944 on the site of the former Furness Railway depot, its late construction in the steam locomotive age resulted in its long-term use and conservation by British Railways. Targeted as part of a preservation scheme, when this failed it was developed as major visitor attraction Steamtown Carnforth. Today, closed as a museum, it acts as the major national operational base of West Coast Railways. Importance of Carnforth Carnforth was not an important or well developed village before the Victorian era railway age, but was geographically strategically located to make it so. While supplies of limestone made it interesting, access into Westmorland, the Lake District and the coast of Cumberland beyond made it an ideal transport hub point. Carnforth railway station opened as a single platform wooden structure for access to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of , Dorset borders Devon to the west, Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north-east, and Hampshire to the east. The county town is Dorchester, in the south. After the reorganisation of local government in 1974, the county border was extended eastward to incorporate the Hampshire towns of Bournemouth and Christchurch. Around half of the population lives in the South East Dorset conurbation, while the rest of the county is largely rural with a low population density. The county has a long history of human settlement stretching back to the Neolithic era. The Romans conquered Dorset's indigenous Celtic tribe, and during the Early Middle Ages, the Saxons settled the area and made Dorset a shire in the 7th century. The first re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |