|
SOST
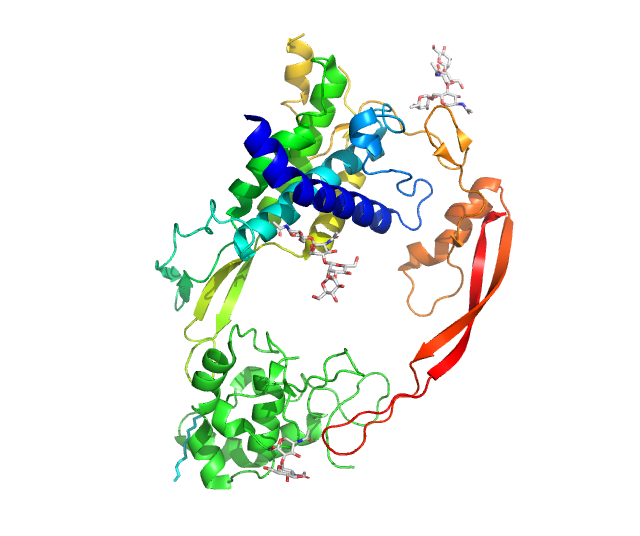
Sclerostin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SOST'' gene. It is a secreted glycoprotein with a C-terminus, C-terminal cysteine knot-like (CTCK) domain and sequence similarity to the PARN, DAN (differential screening-selected gene aberrative in neuroblastoma) family of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonists. Sclerostin is produced primarily by the osteocyte but is also expressed in other tissues, and has anti-anabolic effects on bone formation. Structure The sclerostin protein, with a length of 213 residues, has a secondary structure that has been determined by Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins, protein NMR to be 28% beta sheet (6 strands; 32 residues). Function Sclerostin, the product of the SOST gene, located on chromosome 17q12–q21 in humans, was originally believed to be a non-classical bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) antagonist. More recently, sclerostin has been identified as binding to LRP5/LRP6, 6 receptors and inhibiting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerosteosis
Sclerosteosis is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by bone overgrowth. It was first described in 1958 but given the current name in 1967. Excessive bone formation is most prominent in the skull, mandible and tubular bones. It can cause facial distortion and syndactyly. Increased intracranial pressure can cause sudden death in patients. It is a rare disorder that is most prominent in the Afrikaner population in South Africa (40 patients), but there have also been cases of American and Brazilian families. Cause Sclerosteosis is caused by mutations in the SOST gene that encodes the sclerostin protein. The sclerostin protein is necessary in inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway. Wnt signalling results in increased osteoblast activity and RANKL synthesis. Sclerostin therefore increases bone formation by indirectly inhibiting RANKL synthesis and thus osteoclast activation. See also * Van Buchem disease References External links "These Superhumans Are Real and Their DNA C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Buchem Disease
Van Buchem disease, or hyperostosis corticalis generalisata, is an autosomal recessive skeletal disease which is characterised by uninhibited bone growth, especially in the mandible, skull and ribs. The disease was first described in 1955 by Frans van Buchem, when describing two patients of the same family in Urk in the Netherlands. The cause, he found, was that the bone was produced faster than the body broke it down, making it much thicker as the patient got older. The first symptoms experienced by the affected were often deafness and paralysis of the face, caused by the growing bone pinching the nerves. This condition can be traced to a deletion on chromosome 17q. As the disease is recessive, a child will only be affected by the disease if both of the parents are carriers and the child is homozygous for the allele, meaning that they have the allele in duplicate. The gene involved is SOST, and by extension the protein involved is sclerostin. There have been attempts to relieve a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LRP6
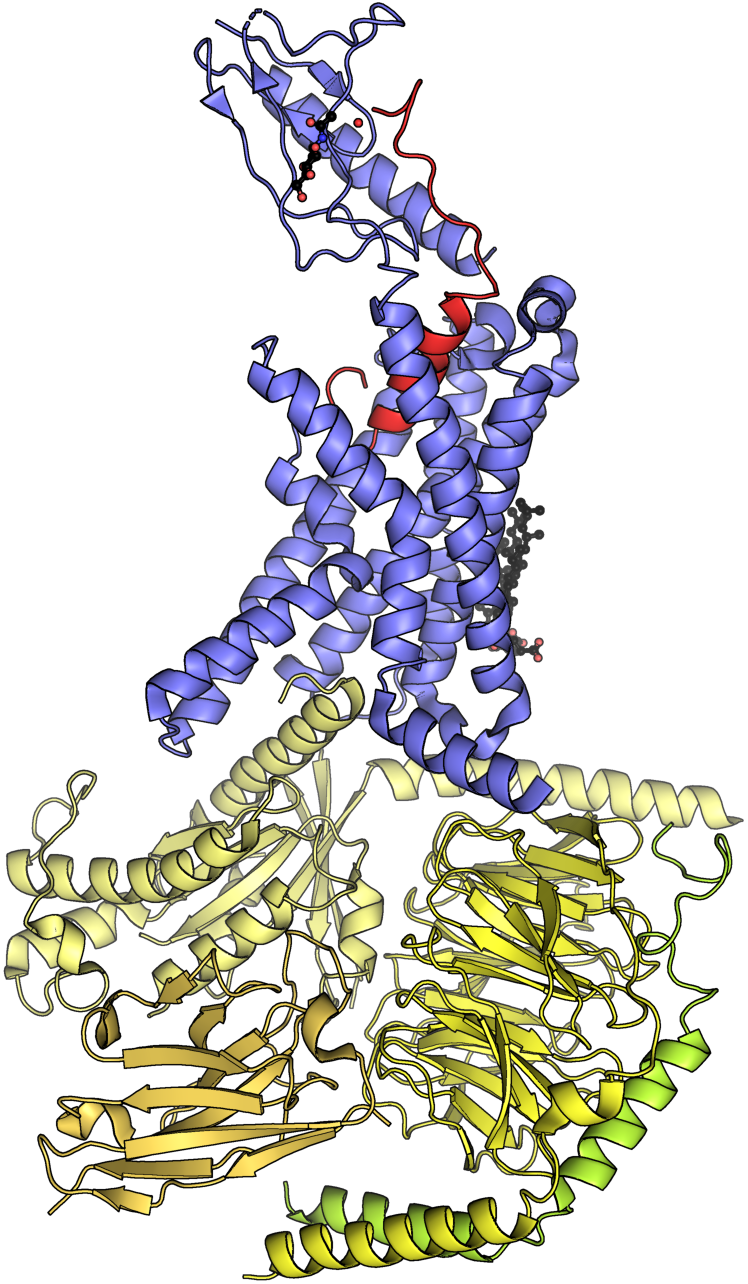
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LRP6'' gene. LRP6 is a key component of the LRP5/LRP6/Frizzled co-receptor group that is involved in canonical Wnt pathway. Structure LRP6 is a transmembrane low-density lipoprotein receptor that shares a similar structure with LRP5. In each protein, about 85% of its 1600- amino-acid length is extracellular. Each has four YWTD β-propeller motifs at the amino terminal end that alternate with four epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats, followed by three LDLR type A repeats. Most extracellular ligands bind to LRP5 and LRP6 at the β-propellers. Each protein has a single-pass, 22-amino-acid transmembrane helix followed by a 207-amino-acid segment that is internal to the cell. Function LRP6 acts as a co-receptor with LRP5 and the Frizzled protein family members for transducing signals by Wnt proteins through the canonical Wnt pathway. A LRP6 mutant lacking the intracel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteocyte
An osteocyte, an oblate-shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide and have an average half life of 25 years. They are derived from osteoprogenitor cells, some of which differentiate into active osteoblasts (which may further differentiate to osteocytes). Osteoblasts/osteocytes develop in mesenchyme. In mature bones, osteocytes and their processes reside inside spaces called lacunae (Latin for a ''pit'') and canaliculi, respectively. Osteocytes are simply osteoblasts trapped in the matrix that they secrete. They are networked to each other via long cytoplasmic extensions that occupy tiny canals called canaliculi, which are used for exchange of nutrients and waste through gap junctions. Although osteocytes have reduced synthetic activity and (like osteoblasts) are not capable of mitotic division, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiotrophin-1
Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) is a cytokine. It is a cardiac hypertrophic factor of 21.5 kDa and a protein member of the IL-6 cytokine family. Pathology CT-1 is associated with the pathophysiology of heart diseases, including hypertension, myocardial infarction, valvular heart disease, and congestive heart failure. Mode of action The protein exerts its cellular effects by interacting with the glycoprotein 130 (gp130)/leukemia inhibitory factor receptor beta (LIFR) heterodimer. In addition, CT-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3 kinase) in cardiac myocytes and enhances transcription factor NF-κB Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found i ... DNA -binding activities. CT-1 is highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle, prostate and ovary and to lower levels in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor
Leukemia inhibitory factor, or LIF, is an interleukin 6 class cytokine that affects cell growth by inhibiting differentiation. When LIF levels drop, the cells differentiate. Function LIF derives its name from its ability to induce the terminal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells, thus preventing their continued growth. Other properties attributed to the cytokine include: the growth promotion and cell differentiation of different types of target cells, influence on bone metabolism, cachexia, neural development, embryogenesis and inflammation. p53 regulated LIF has been shown to facilitate implantation in the mouse model and possibly in humans. It has been suggested that recombinant human LIF might help to improve the implantation rate in women with unexplained infertility. Binding/activation LIF binds to the specific LIF receptor ( LIFR-α) which forms a heterodimer with a specific subunit common to all members of that family of receptors, the GP130 signal transducin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin
Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Its importance in humans has not been as well established as its importance in other animals, as its function is usually not significant in the regulation of normal Calcium metabolism, calcium homeostasis. It belongs to the calcitonin-like protein family. Historically calcitonin has also been called thyrocalcitonin. Biosynthesis and regulation Calcitonin is formed by the proteolytic cleavage of a larger prepropeptide, which is the product of the CALC1 gene (). It is functionally an antagonist with PTH and Vitamin D3. The CALC1 gene belongs to a superfamily of related protein hormone precursors including islet amyloid precursor protein, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and the precursor of adrenomedul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphyses
The diaphysis (: diaphyses) is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat). It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavity which contains red or yellow marrow. In diaphysis, primary ossification occurs. Ewing sarcoma tends to occur at the diaphysis.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, Cuccurullo Additional images Illu long bone.jpg File:EpiMetaDiaphyse.jpg, Long bone See also *Epiphysis *Metaphysis The metaphysis (: metaphyses) is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the ep ... References Long bones {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytocic properties that is used as a medication. Dinoprostone is used in labor induction, bleeding after delivery, termination of pregnancy, and in newborn babies to keep the ductus arteriosus open. In babies it is used in those with congenital heart defects until surgery can be carried out. It is also used to manage gestational trophoblastic disease. It may be used within the vagina or by injection into a vein. PGE2 synthesis within the body begins with the activation of arachidonic acid (AA) by the enzyme phospholipase A2. Once activated, AA is oxygenated by cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes to form prostaglandin endoperoxides. Specifically, prostaglandin G2 (PGG2) is modified by the peroxidase moiety of the COX enzyme to produce prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) which is then converted to PGE2. Common side effects of PGE2 include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and excessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiroscience
Chiroscience Group Plc was a British-based biotech company, founded by Christopher Evans. The company was taken over by Celltech in 1999, which was acquired in 2004 by UCB. History Chiroscience was born from the demise of the company Enzymatix, which was ultimately acquired by Genzyme, when Andrew Richards joined the company and convinced Evans and Peter Keen to launch Chiros, which name was quickly revised to Chrioscience. Seed funding for the company of was provided by Schroder Ventures, Apax and 3i. Chiroscience became one of the first biotechnology Initial Public Offerings in the United Kingdom in 1994. In 1996, the company merged with the American biotech company ''Darwin Molecular Corporation'', based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, retaining Chiroscience as its name. By the time of its merger with Celltech in 1999, both Chris Evans and Peter Keen had left the company, leaving Andrew Richards as the sole remaining founder and member of the original management board. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |