|
SOLAR-C
SOLAR-C (official name "High-sensitivity Solar Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Satellite") is a planned Solar observation, Sun-observing satellite being developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ), and international collaborators. It will be the follow-up to the Hinode (satellite), Hinode (SOLAR-B) and Yohkoh (SOLAR-A) missions and will carry the EUV High-throughput Spectroscopic Telescope (EUVST) and the Solar Spectral Irradiance Monitor (SoSpIM). It is scheduled to launch in fiscal year 2028. Objectives The mission aims to study the sun, its effects on Earth and the Solar System, and the mechanisms behind hot plasma formation. The satellite will also analyse the Sun's UV radiation spectrum. References External linkOfficial website (in Japanese) {{Japanese space program Satellites of Japan Space telescopes 2028 in spaceflight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
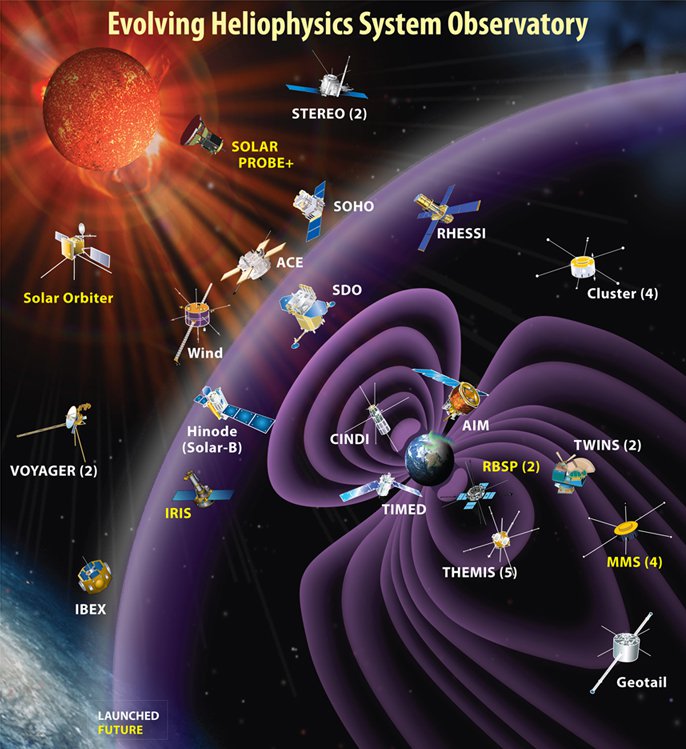
Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. NASA defines heliophysics as "(1) the comprehensive new term for the science of the Sun - Solar System Connection, (2) the exploration, discovery, and understanding of Earth's space environment, and (3) the system science that unites all of the linked phenomena in the region of the cosmos influenced by a star like our Sun." Heliophysics concentrates on the Sun's effects on Earth and other bodies within the Solar System, as well as the changing conditions in space. It is primarily concerned with the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, mesosphere, and upper atmosphere of the Earth and other planets. Heliophysics combines the science of the Sun, corona, heliosphere and geospace, and encompasses a wide variety of astronomical phenomena, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Astronomical Observatory Of Japan
The (NAOJ) is an astronomy, astronomical research organisation comprising several facilities in Japan, as well as an observatory in Hawaii and Chile. It was established in 1988 as an amalgamation of three existing research organizations - the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory of the University of Tokyo, International Latitude Observatory of Mizusawa, and a part of Research Institute of Atmospherics of Nagoya University. In the 2004 reform of national research organizations, NAOJ became a division of the National Institutes of Natural Sciences, Japan, National Institutes of Natural Sciences. Facilities ;Mitaka Campus (Mitaka, Tokyo. ) :The Headquarters, Astronomy Data Center, Advanced Technology Center, Public Relations Center :Solar Flare Telescope, Sunspot Telescope, TAMA 300 gravitational wave detector :Tokyo Photoelectric Meridian Circle :Historical instruments: Solar Tower Telescope, 65cm refractor dome, 20cm refractor dome ;Nobeyama Radio Observatory (Minamimaki, Nagano, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon (rocket)
The Epsilon Launch Vehicle, or (formerly ''Advanced Solid Rocket''), is a Japanese solid-fuel rocket designed to launch scientific satellites. It is a follow-on project to the larger and more expensive M-V rocket which was retired in 2006. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) began developing the Epsilon in 2007. It is capable of placing a 590 kg payload into Sun-synchronous orbit. Vehicle description The development aim is to reduce the US$70 million launch cost of an M-V; the Epsilon costs US$38 million per launch. Development expenditures by JAXA exceeded US$200 million. To reduce the cost per launch the Epsilon uses the existing SRB-A3, a solid rocket booster on the H-IIA rocket, as its first stage. Existing M-V upper stages will be used for the second and third stages, with an optional fourth stage available for launches to higher orbits. The J-I rocket, which was developed during the 1990s but abandoned after just one launch, used a similar design concept, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun-synchronous Orbit
A Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO), also called a heliosynchronous orbit, is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given point of the planet's surface at the same local mean solar time. More technically, it is an orbit arranged so that it precesses through one complete revolution each year, so it always maintains the same relationship with the Sun. Applications A Sun-synchronous orbit is useful for imaging, reconnaissance, and weather satellites, because every time that the satellite is overhead, the surface illumination angle on the planet underneath it is nearly the same. This consistent lighting is a useful characteristic for satellites that image the Earth's surface in visible or infrared wavelengths, such as weather and spy satellites, and for other remote-sensing satellites, such as those carrying ocean and atmospheric remote-sensing instruments that require sunlight. For example, a satellite in Sun-synchronous orbit might ascend ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Observation
Solar observation is the scientific endeavor of studying the Sun and its behavior and relation to the Earth and the remainder of the Solar System. Deliberate solar observation began thousands of years ago. That initial era of direct observation gave way to telescopes in the 1600s followed by satellites in the twentieth century. Prehistory Stratigraphic data suggest that solar cycles have occurred for hundreds of millions of years, if not longer; measuring varves in precambrian sedimentary rock has revealed repeating peaks in layer thickness corresponding to the cycle. It is possible that the early atmosphere on Earth was more sensitive to solar irradiation than today, so that greater glacial melting (and thicker sediment deposits) could have occurred during years with greater sunspot activity. This would presume annual layering; however, alternative explanations (diurnal) have also been proposed. Analysis of tree rings revealed a detailed picture of past solar cycles: Dendroch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
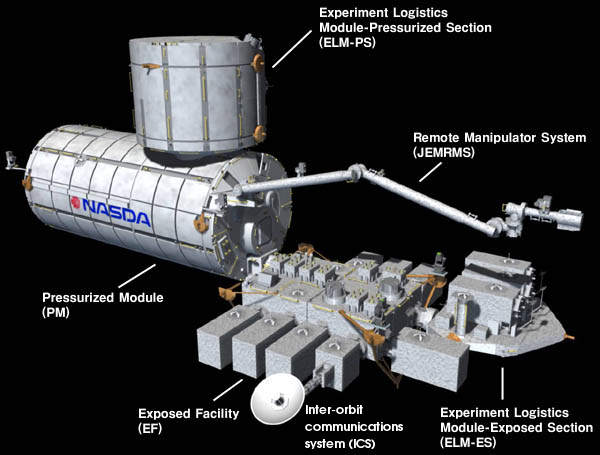
Hinode (satellite)
Hinode (; ja, ひので, , Sunrise), formerly Solar-B, is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Sun, Solar mission with United States and United Kingdom collaboration. It is the follow-up to the Yohkoh (Solar-A) mission and it was launched on the final flight of the M-V, M-V rocket from Uchinoura Space Center, Japan on 22 September 2006 at 21:36 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC (23 September, 06:36 Japan Standard Time, JST). Initial orbit was perigee height 280 km, apogee height 686 km, inclination 98.3 degrees. Then the satellite maneuvered to the quasi-circular sun-synchronous orbit over the day/night terminator (solar), terminator, which allows near-continuous observation of the Sun. On 28 October 2006, the probe's instruments captured their first images. The data from Hinode are being downloaded to the Norway, Norwegian, terrestrial Svalsat station, operated by ''Kongsberg Gruppen, Kongsberg'' a few kilometres west of Longyearbyen, Svalbard. From there, data is tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yohkoh
Yohkoh (, ''Sunbeam'' in Japanese), known before launch as Solar-A, was a Solar observatory spacecraft of the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (Japan), in collaboration with space agencies in the United States and the United Kingdom. It was launched into Earth orbit on August 30, 1991 by the M-3SII rocket from Kagoshima Space Center. It took its first soft X-ray image on September 13, 1991, 21:53:40, and movie representations of the X-ray corona over 1991-2001 are available at thYohkoh Legacy site Description The satellite was three-axis stabilized and in a near-circular orbit. It carried four instruments: a Soft X-ray Telescope (SXT), a Hard X-ray Telescope (HXT), a Bragg Crystal Spectrometer (BCS), and a Wide Band Spectrometer (WBS). About 50 MB were generated each day and stored on board by a 10.5 MB bubble memory recorder. Because SXT utilized a charge-coupled device (CCD) as its readout device, perhaps being the first X-ray astronomical telescope to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The SPIE
''Proceedings of SPIE'' is the conference record of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE). SPIE The first proceedings were published in 1963. Indexing and abstracting ''Proceedings of SPIE'' is indexed and abstracted in:References External links * Optics journals Publications established in 1963 Conference proceedings published in serials SPIE academic journals[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute For Solar System Research
The Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (abbreviation: MPS; german: Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung) is a research institute in astronomy and astrophysics located in Göttingen, Germany, where it relocated in February 2014 from the nearby village of Lindau. The exploration of the Solar System is the central theme for research done at this institute. MPS is a part of the Max Planck Society, which operates 80 research facilities in Germany. Research MPS is organised in three departments: Sun and Heliosphere, Planets and Comets, and Solar and Stellar Interiors. In addition, since 2002 there is also an International Max Planck Research School. Subjects of research at the institute are the various objects within the solar system. A major area of study concerns the Sun, its atmosphere, the interplanetary medium as influenced by the solar wind, as well as the impact of solar particles and radiation on the planets. The second area of research involves the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |