|
SLCO1B1
Solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLCO1B1'' gene. Pharmacogenomic research indicates that genetic variations in this gene are associated with response to simvastatin. Clinical guidelines exist that can guide dosing of simvastatin based on ''SLCO1B1'' gene variant using genotyping or whole exome sequencing. See also * Solute carrier family The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family Thyroid hormone transporters {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simvastatin
Simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor among others, is a statin, a type of lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease hyperlipidemia, elevated lipid levels. It is also used to decrease the risk of Cardiovascular disease, heart problems in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include constipation, headaches, and nausea. Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, muscle breakdown, liver problems, and increased blood sugar levels. A lower dose may be needed in people with chronic kidney disease, kidney problems. There is evidence of harm to the developing baby when taken during pregnancy and it should not be used by those who are breastfeeding. It is in the statin class of medications and works by decreasing the manufacture of cholesterol by the liver. Simvastatin is made from the fungus ''Aspergillus terreus''. It was patented by Merck and Co., Merck in 1980, and came into medical use in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacogenomic
Pharmacogenomics, often abbreviated "PGx," is the study of the role of the genome in drug response. Its name ('' pharmaco-'' + ''genomics'') reflects its combining of pharmacology and genomics. Pharmacogenomics analyzes how the genetic makeup of a patient affects their response to drugs. It deals with the influence of acquired and inherited genetic variation on drug response, by correlating DNA mutations (including point mutations, copy number variations, and structural variations) with pharmacokinetic (drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination), pharmacodynamic (effects mediated through a drug's biological targets), and/or immunogenic endpoints. Pharmacogenomics aims to develop rational means to optimize drug therapy, with regard to the patients' genotype, to achieve maximum efficiency with minimal adverse effects. It is hoped that by using pharmacogenomics, pharmaceutical drug treatments can deviate from what is dubbed as the "one-dose-fits-all" approach. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solute Carrier Family
The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) and is the basis for the official HGNC names of the genes that encode these transporters. A more general transmembrane transporter classification can be found in TCDB, TCDB database. Solutes that are transported by the various SLC group members are extremely diverse and include both charged and uncharged organic molecules as well as inorganic ions and the gas Ammonia transporter, ammonia. As is typical of integral membrane proteins, SLCs contain a number of hydrophobic transmembrane Alpha helix, alpha helices connected to each other by hydrophilic intra- and extra-cellular loops. Depending on the SLC, these transporters are functional as either monomers or obligate homo- or hetero-oligomers. Many SLC fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotyping
Genotyping is the process of determining differences in the genetic make-up (genotype) of an individual by examining the individual's DNA sequence using bioassay, biological assays and comparing it to another individual's sequence or a reference sequence. It reveals the alleles an individual has inherited from their parents. Traditionally genotyping is the use of DNA sequences to define biological Population, populations by use of molecular tools. It does not usually involve defining the genes of an individual. Techniques Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms A restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a variation between different people at sites of the genome recognized by Restriction enzyme, restriction enzymes. DNA containing different restriction sites will be cut by bacterial restriction enzymes differently and this can be seen using gel electrophoresis. When running the sample through, a successfully cleaved sample will contain two bands, while the sample wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
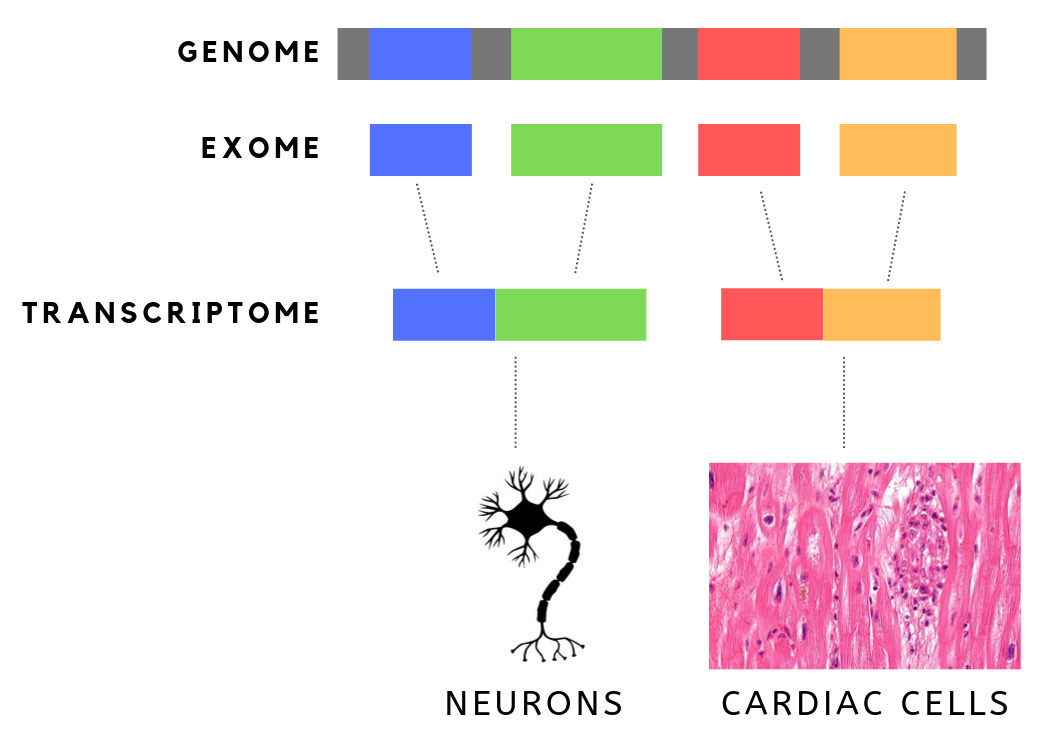
Exome
The exome is composed of all of the exons within the genome, the sequences which, when transcribed, remain within the mature RNA after introns are removed by RNA splicing. This includes untranslated regions of messenger RNA (mRNA), and coding regions. Exome sequencing has proven to be an efficient method of determining the genetic basis of more than two dozen Mendelian or single gene disorders. Statistics The human exome consists of roughly 233,785 exons, about 80% of which are less than 200 base pairs in length, constituting a total of about 1.1% of the total genome, or about 30 megabases of DNA. Though composing a very small fraction of the genome, mutations in the exome are thought to harbor 85% of mutations that have a large effect on disease. Definition It is important to note that the exome is distinct from the transcriptome, which is all of the transcribed RNA within a cell type. While the exome is constant from cell-type to cell-type, the transcriptome changes ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequencing
In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure (sometimes incorrectly called the primary sequence) of an unbranched biopolymer. Sequencing results in a symbolic linear depiction known as a sequence which succinctly summarizes much of the atomic-level structure of the sequenced molecule. DNA sequencing DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleotide order of a given DNA fragment. So far, most DNA sequencing has been performed using the chain termination method developed by Frederick Sanger. This technique uses sequence-specific termination of a DNA synthesis reaction using modified nucleotide substrates. However, new sequencing technologies such as pyrosequencing are gaining an increasing share of the sequencing market. More genome data are now being produced by pyrosequencing than Sanger DNA sequencing. Pyrosequencing has enabled rapid genome sequencing. Bacterial genomes can be sequenced in a single run with several times cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |