|
SCR-784
The SCR-784 was a radar set used by the U.S. Army designed to be an amphibious version of the SCR-584, to control the fire of anti-aircraft batteries, and mounted on a searchlight trailer called a K-84. The set was used to guide the flare plane over the target. Statistics Frequency: 2,800 MHz Pulse Width: 0.8 µs Pulse Repetition Rate: 1707 pps Vertical Coverage: Indicator Type: display 7 inch PPI and, two 3 inch CRT's for range determination K-84 trailer * built by Fruehauf Trailer Corporation * Gross Weight is . * Tires are 9.00 X 20. 10 Ply. * Electric brakes, and parking brake. * Overall length 220-3/8" * Overall width 97-3/4" Surviving examples There are no known surviving examples of this array. See also * List of U.S. Signal Corps Vehicles * Signal Corps Radio * G-numbers This is the Group G series List of the United States military vehicles by (Ordnance) supply catalog designation, — ''one'' of the alpha-numeric "Standard Nomenclature Lists" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-84 Trailer
The SCR-784 was a radar set used by the U.S. Army designed to be an amphibious version of the SCR-584, to control the fire of anti-aircraft batteries, and mounted on a searchlight trailer called a K-84. The set was used to guide the flare plane over the target. Statistics Frequency: 2,800 MHz Pulse Width: 0.8 µs Pulse Repetition Rate: 1707 pps Vertical Coverage: Indicator Type: display 7 inch PPI and, two 3 inch CRT's for range determination K-84 trailer * built by Fruehauf Trailer Corporation * Gross Weight is . * Tires are 9.00 X 20. 10 Ply. * Electric brakes, and parking brake. * Overall length 220-3/8" * Overall width 97-3/4" Surviving examples There are no known surviving examples of this array. See also * List of U.S. Signal Corps Vehicles * Signal Corps Radio * G-numbers This is the Group G series List of the United States military vehicles by (Ordnance) supply catalog designation, — ''one'' of the alpha-numeric "Standard Nomenclature Lists" (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCR-584
The SCR-584 (short for '' Set, Complete, Radio # 584'') was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of the primary gun laying radars used worldwide well into the 1950s. A trailer-mounted mobile version was the SCR-784. In 1937, America's first fire-control radar, the SCR-268 radar, had proven to be insufficiently accurate due in part to its long wavelength. In 1940, Vannevar Bush, heading the National Defense Research Committee, established the "Microwave Committee" (section D-1) and the "Fire Control" division (D-2) to develop a more advanced radar anti-aircraft system in time to assist the British air-defense effort. In September of that year, a British delegation, the Tizard Mission, revealed to US and Canadian researchers that they had developed a magnetron oscillator operating at the top end of the UHF band (10 cm wavelength/3 GHz) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Corps Radio
Signal Corps Radios were U.S. Army military communications components that comprised "sets". Under the Army Nomenclature System, the abbreviation SCR initially designated "Set, Complete Radio", but was later misinterpreted as "Signal Corps Radio." Nomenclature The term SCR was part of a nomenclature system developed for the U.S. Signal Corps, used at least as far back as World War I. Three-letter designators beginning with "SC" were used to denote complete systems, while one and two-letter designators (such as "BC", for basic component, "FT" for mounting, etc.) were used for components. Only a few system designators were used: :::SCM Set, Complete, Meteorological :::SCR Set, Complete, Radio :::SCS Set, Complete, System SCR radio sets The U.S. Signal Corps used the term "sets" to denote specific groupings of individual components such as transmitters, receivers, power supplies, handsets, cases, and antennas. SCR radio sets ranged from the relatively small SCR-536 "handie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
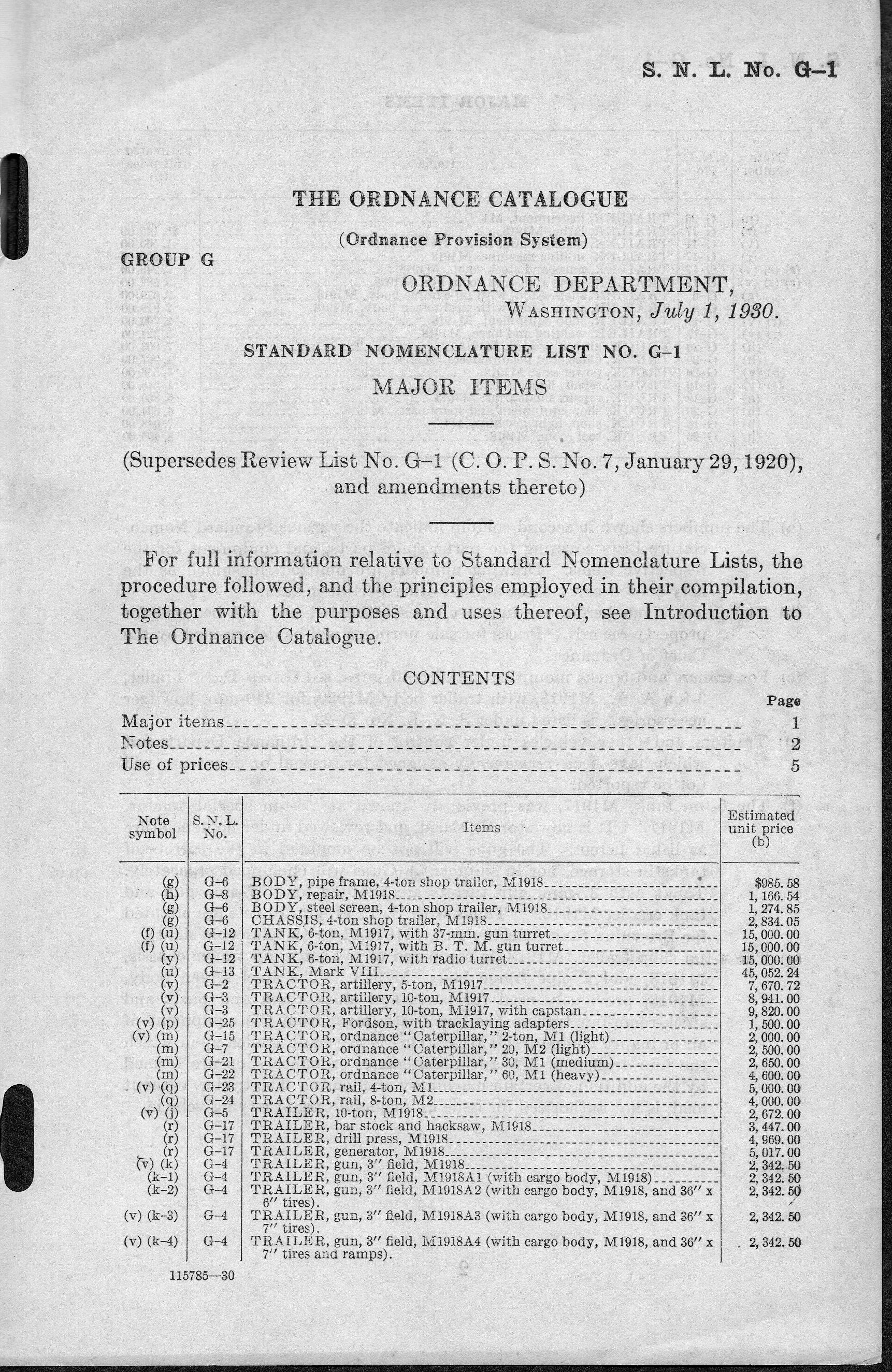
G-numbers
This is the Group G series List of the United States military vehicles by (Ordnance) supply catalog designation, — ''one'' of the alpha-numeric "Standard Nomenclature Lists" (SNL) that were part of the overall List of the United States Army weapons by supply catalog designation, a Supply Catalog that was used by the United States Army Ordnance Department / Ordnance Corps as part of the Ordnance Provision System, from about the mid-1920s to about 1958. In this, the ''Group G'' series numbers were designated to represent "Tank / Automotive materiel" – the various military vehicles and directly related materiel. These designations represent vehicles, modules, parts, and catalogs for supply and repair purposes. There can be numerous volumes, changes, and updates under each designation. The Group G list ''itself'' is also included, being numbered G-1. Generally, the G-series codes tended to group together "families" of vehicles that were similar in terms of their engine, tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products. At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames are produced. The ''flame'' is the visible portion of the fire. Flames consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce Plasma (physics), plasma. Depending on the substances alight, and any impurities outside, the color of the flame and the fire's Intensity (heat transfer), intensity will be different. Fire in its most common form can result in conflagration, which has the potential to cause physical damage through burning. Fire is an important process that affects ecological systems around the globe. The positive effects of fire include stimulating growth and maintaining various ecological systems. Its negative effects include hazard to life and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, subsurface ( submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO and the United States, ground-based air defence and air defence aircra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Battery
In military organizations, an artillery battery is a unit or multiple systems of artillery, mortar systems, rocket artillery, multiple rocket launchers, surface-to-surface missiles, ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, etc., so grouped to facilitate better battlefield communication and command and control, as well as to provide dispersion for its constituent gunnery crews and their systems. The term is also used in a naval context to describe groups of guns on warships. Land usage Historically the term "battery" referred to a cluster of cannon in action as a group, either in a temporary field position during a battle or at the siege of a fortress or a city. Such batteries could be a mixture of cannon, howitzer, or mortar types. A siege could involve many batteries at different sites around the besieged place. The term also came to be used for a group of cannon in a fixed fortification, for coastal or frontier defence. During the 18th century "battery" began to be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruehauf Trailer Corporation
Fruehauf Trailer Corporation, previously Fruehauf Trailer Company (1918–1963) and Fruehauf Corporation (1963–1989), was an American company engaged in the manufacture and sale of truck trailers, and other machinery and equipment, with headquarters located in Detroit, Michigan. It was founded in 1918 in Detroit, after August Fruehauf created the semi-trailer and launched a new industry. The Fruehauf trailer company introduced revolutionary inventions to trucking and transportation with hydraulic dump trailers, bulk tanker trailers, and automatic fifth-wheel couplings among their more than one thousand patents, including the shipping container in 1956. Expanding across the country, Fruehauf had 16 plants and more than 80 distributorships for parts and service. Globally, the company expanded into Europe, South America, and Asia. Following a proxy battle in the late 1980s the company filed for bankruptcy protection in 1997. International divisions became independent, U.S. subsidia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of U
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type) In computer science, a list or sequence is an abstract data type that represents a finite number of ordered values, where the same value may occur more than once. An instance of a list is a computer representation of the mathematical concept of ..., a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Radars Of The United States
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Laying Radars
A gun is a ranged weapon designed to use a shooting tube (gun barrel) to launch projectiles. The projectiles are typically solid, but can also be pressurized liquid (e.g. in water guns/cannons, spray guns for painting or pressure washing, projected water disruptors, and technically also flamethrowers), gas (e.g. light-gas gun) or even charged particles (e.g. plasma gun). Solid projectiles may be free-flying (as with bullets and artillery shells) or tethered (as with Taser guns, spearguns and harpoon guns). A large- caliber gun is also called a ''cannon''. The means of projectile propulsion vary according to designs, but are traditionally effected pneumatically by a high gas pressure contained within the barrel tube, produced either through the rapid exothermic combustion of propellants (as with firearms), or by mechanical compression (as with air guns). The high-pressure gas is introduced behind the projectile, pushing and accelerating it down the length of the tube, imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

