|
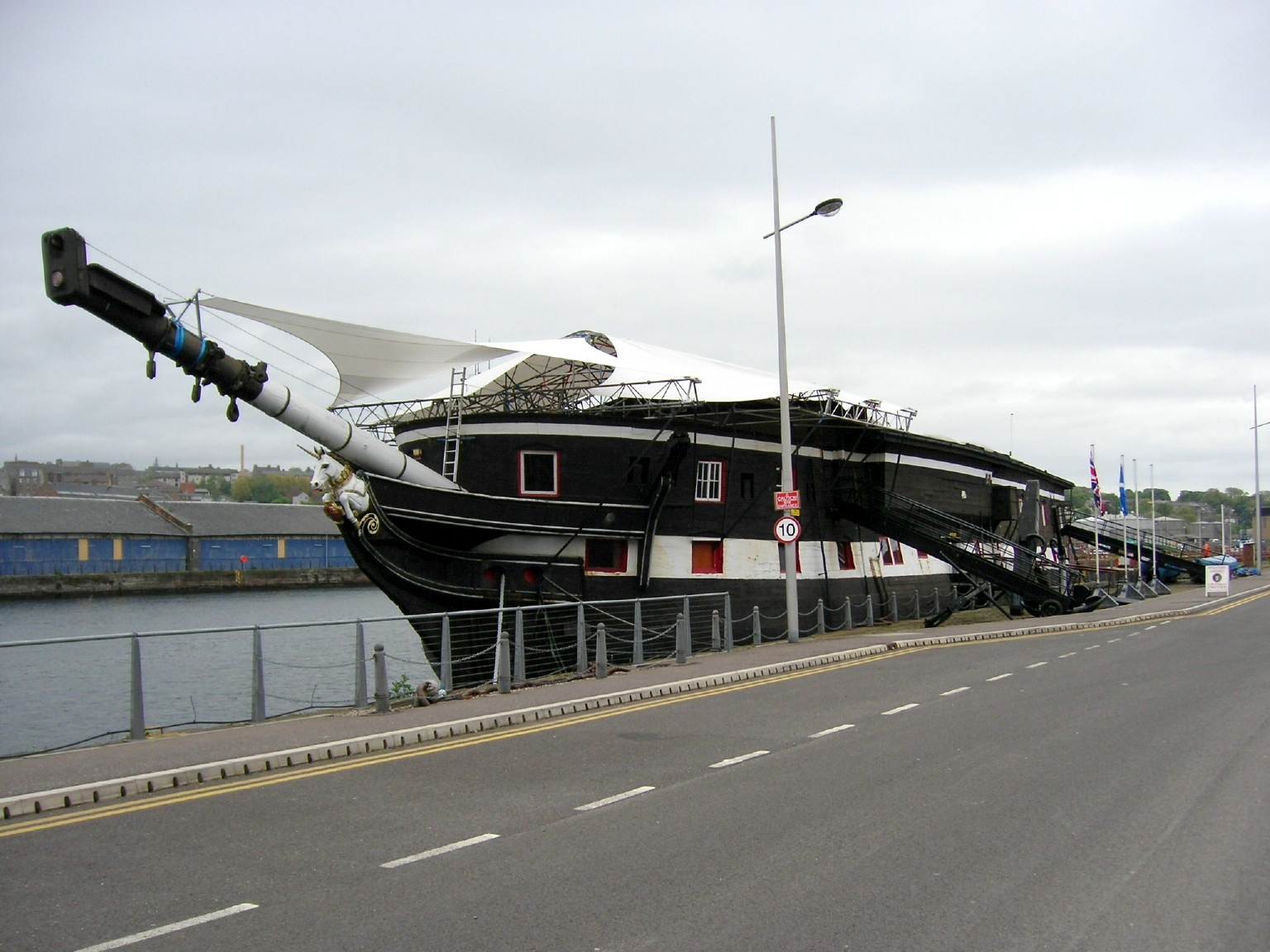
SATS General Botha
HMS ''Thames'' was a protected cruiser built for the Royal Navy (RN) in the 1880s. The ship was placed in reserve upon her completion in 1888 and was converted into a submarine depot ship in 1903. She was sold out of the navy in 1920 and was purchased by a South African businessman to serve as a training ship for naval cadets under the name SATS ''General Botha''. The ship arrived in South Africa in 1921 and began training her first class of cadets in Simon's Town the following year. ''General Botha'' continued to train cadets for the first several years of World War II, but the RN took over the ship in 1942 for use as an accommodation ship under her original name. She was scuttled by gunfire in 1947 and is now a diveable wreck. Design and description The ''Mersey''-class cruisers were improved versions of the ''Leander'' class with more armour and no sailing rig on a smaller displacement. Like their predecessors, they were intended to protect British shipping. The cruise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
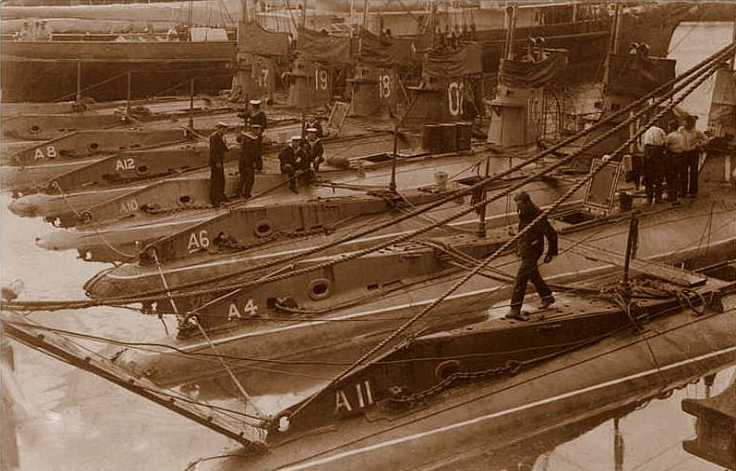
A-class Submarine (1903)
The A-class was the Royal Navy's first Ship class, class of British-designed submarines. Thirteen were built by Vickers at Barrow-in-Furness between 1902 and 1905 as an improvement on the US . Design and construction While there was considerable variation amongst the boats of the class, they were around long and displaced around 200 tons when submerged. The first, ''A1'' (ordered as ''Holland No. 6''), was launched in July 1902, the last, ''A13'', in April 1905. Propulsion All were propelled underwater by battery-powered electric motors and on the surface by shaft-drive Wolseley Motors, Wolseley petrol engines of (''A1''), (''A2-A4'') or (''A5''-''A12''). ''A13'' had an experimental Vickers diesel engine, which proved to be unreliable. Armaments Armament was two British 18 inch torpedo, torpedo tubes with four torpedoes except for ''A1'', which had 1 tube and 3 torpedoes. Service history This submarine class was plagued by numerous accidents and failures; al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
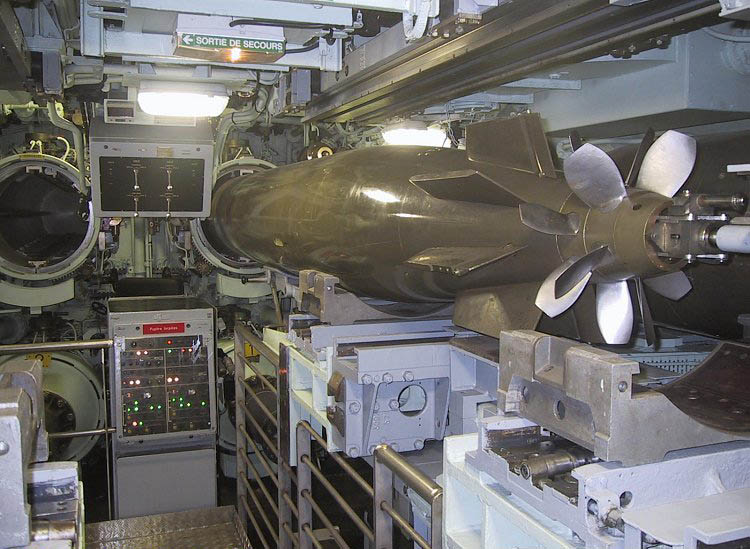
Torpedo Tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes. There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboard surface vessels. Deck-mounted torpedo launchers are usually designed for a specific type of torpedo, while submarine torpedo tubes are general-purpose launchers, and are often also capable of deploying naval mine, mines and cruise missiles. Most modern launchers are standardized on a diameter for light torpedoes (deck mounted aboard ship) or a diameter for heavy torpedoes (underwater tubes), although Torpedo#Classes and diameters, torpedoes of other classes and diameters have been used. Submarine torpedo tube A submarine torpedo tube is a more complex mechanism than a torpedo tube on a surface ship, because the tube has to accomplish the function of moving the torpedo from the normal atmospheric pressure within the submarine into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Between Perpendiculars
Length between perpendiculars (often abbreviated as p/p, p.p., pp, LPP, LBP or Length BPP) is the length of a ship along the summer load line from the forward surface of the stem, or main bow perpendicular member, to the after surface of the sternpost, or main stern perpendicular member. When there is no sternpost, the centerline axis of the rudder stock is used as the aft end of the length between perpendiculars. Measuring to the stern post or rudder stock was believed to give a reasonable idea of the ship’s carrying capacity, as it excluded the small, often unusable volume contained in its overhanging ends. On some types of vessels this is, for all practical purposes, a waterline measurement. In a ship with raked stems, naturally that length changes as the draught of the ship changes, therefore it is measured from a defined loaded condition. See also * Length overall Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p. 5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks". A merchant vessel has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leander-class Cruiser (1882)
The ''Leander'' class was a four-ship cruiser programme ordered by the Admiralty in 1880. The class comprised , , , and . Genesis "A new and better policy of unarmoured construction was inaugurated by the Admiralty of 1874-80. They began by building the two despatch vessels, and , with a speed not approached up to that date by any in naval service. In the ''Mercury'' and the ''Iris'', the speed was obtained by an enormous development of horse-power… The cost per ton was equal to that of the most powerful ironclad, while the fighting power was inconsiderable."Lord Brassey, ''The Naval Annual, 1886'', page 68 In 1880, the Admiralty Board were divided about next design of cruising ship to lay down. The First Naval Lord, Sir Astley Cooper Key, favoured an enlarged . Some of the other members of the board preferred an improved . The First Lord of the Admiralty, William H. Smith, backed the latter.Brown, ''Warrior to Dreadnought, Warship Development 1860–1905'', page 111 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuttling
Scuttling is the act of deliberately sinking a ship by allowing water to flow into the hull, typically by its crew opening holes in its hull. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self destruct, self-destruction to prevent the ship from being captured by an enemy force; as a blockship to restrict navigation through a Channel (geography), channel or within a harbor; to provide an artificial reef for divers and marine life; or to alter the flow of rivers. Notable historical examples Skuldelev ships (around 1070) The Skuldelev ships, five Viking ships, were sunk to prevent attacks from the sea on the Danish city of Roskilde. The scuttling blocked a major waterway, redirecting ships to a smaller one that required considerable local knowledge. Cog near Kampen (early 15th century) In 2012, a Cog (ship), cog preserved from the keel up to the decks in the silt was dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accommodation Ship
A barracks ship or barracks barge or berthing barge, or in civilian use accommodation vessel or accommodation ship, is a ship or a non-self-propelled barge containing a superstructure of a type suitable for use as a temporary barracks for sailors or other military personnel. A barracks ship, a military form of a dormitory ship, may also be used as a receiving unit for sailors who need temporary residence prior to being assigned to their ship. The United States Navy used to call them Yard Repair Berthing and Messing with designations YRBM and YRBM(L) and now classes them as either Auxiliary Personnel Barracks (APB) or Auxiliary Personnel Lighter (aka barge) (APL). Early use Barrack ships were common during the era of sailing ships when shore facilities were scarce or non-existent. Barrack ships were usually hulks. At times, barrack ships were also used as prison ships for convicts, prisoners of war or civilian internees. Use in World War II ''Barracks ships'' in the comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Cadet
Officer cadet is a rank held by military personnel during their training to become commissioned officers. In the United Kingdom, the rank is also used by personnel of University Service Units such as the University Officers' Training Corps. The term officer trainee is used interchangeably in some countries. Australia The Australian Defence Force follows the same usage as the British military system, using the rank of officer cadet (for the Australian Army (OCDT) and the Royal Australian Air Force (OFFCDT)), for personnel undergoing initial officer training. Unlike midshipmen in the Royal Australian Navy and officer cadets in the Royal Australian Air Force who hold a commission, officer cadets in the Australian Army do not yet hold a permanent commission, and are not saluted or referred to as "sir" or "ma'am". They do however hold probationary commissions. Officer cadets in the Australian Army are subordinate to warrant officers and officers and address them as "sir" or "ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini; and it encloses Lesotho. Covering an area of , the country has Demographics of South Africa, a population of over 64 million people. Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, as the seat of Parliament of South Africa, Parliament, is the legislative capital, and Bloemfontein is regarded as the judicial capital. The largest, most populous city is Johannesburg, followed by Cape Town and Durban. Cradle of Humankind, Archaeological findings suggest that various hominid species existed in South Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and modern humans inhabited the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully Ship decommissioning, decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". A reserve fleet may be colloquially referred to as a "ghost fleet". In the 21st century, ghost fleet may also refer to an active shadow fleet of aged reserve fleet Oil tanker, oil tankers returned to an active service in order to circumvent commodities sanctions. Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |