|
SAMV (algorithm)
SAMV (iterative sparse asymptotic minimum variance) is a parameter-free superresolution algorithm for the linear inverse problem in spectral estimation, direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation and tomographic reconstruction with applications in signal processing, medical imaging and remote sensing. The name was coined in 2013 to emphasize its basis on the asymptotically minimum variance (AMV) criterion. It is a powerful tool for the recovery of both the amplitude and frequency characteristics of multiple highly correlated sources in challenging environments (e.g., limited number of snapshots and low signal-to-noise ratio). Applications include synthetic-aperture radar, computed tomography scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Definition The formulation of the SAMV algorithm is given as an inverse problem in the context of DOA estimation. Suppose an M-element uniform linear array (ULA) receive K narrow band signals emitted from sources located at locations \mathbf = \, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super-resolution Imaging
Super-resolution imaging (SR) is a class of techniques that enhance (increase) the resolution of an imaging system. In optical SR the diffraction limit of systems is transcended, while in geometrical SR the resolution of digital imaging sensors is enhanced. In some radar and sonar imaging applications (e.g. magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), high-resolution computed tomography), subspace decomposition-based methods (e.g. MUSIC) and compressed sensing-based algorithms (e.g., SAMV) are employed to achieve SR over standard periodogram algorithm. Super-resolution imaging techniques are used in general image processing and in super-resolution microscopy. Basic concepts Because some of the ideas surrounding super-resolution raise fundamental issues, there is need at the outset to examine the relevant physical and information-theoretical principles: * Diffraction limit: The detail of a physical object that an optical instrument can reproduce in an image has limits that are mandated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vectorization (mathematics)
In mathematics, especially in linear algebra and matrix theory, the vectorization of a matrix is a linear transformation which converts the matrix into a column vector. Specifically, the vectorization of a matrix ''A'', denoted vec(''A''), is the column vector obtained by stacking the columns of the matrix ''A'' on top of one another: :\operatorname(A) = _, \ldots, a_, a_, \ldots, a_, \ldots, a_, \ldots, a_\mathrm Here, a_ represents A(i,j) and the superscript ^\mathrm denotes the transpose. Vectorization expresses, through coordinates, the isomorphism \mathbf^ := \mathbf^m \otimes \mathbf^n \cong \mathbf^ between these (i.e., of matrices and vectors) as vector spaces. For example, for the 2×2 matrix A = \begin a & b \\ c & d \end, the vectorization is \operatorname(A) = \begin a \\ c \\ b \\ d \end. The connection between the vectorization of ''A'' and the vectorization of its transpose is given by the commutation matrix. Compatibility with Kronecker products The ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Compression
Pulse compression is a signal processing technique commonly used by radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio. This is achieved by modulating the transmitted pulse and then correlating the received signal with the transmitted pulse. Simple pulse Signal description The simplest signal a pulse radar can transmit is a sinusoidal-amplitude pulse, A and carrier frequency, f_0, truncated by a rectangular function of width, T. The pulse is transmitted periodically, but that is not the main topic of this article; we will consider only a single pulse, s. If we assume the pulse to start at time t=0, the signal can be written the following way, using the complex notation: :s(t) = \begin A e^ &\text \; 0 \leq t where it reaches its maximum 1, and it decreases linearly on ,\frac{1}{2}/math> until it reaches 0 again. Figures at the end of this paragraph show the shape of the intercorrelation for a sample signal (in red) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Fourier Transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of sparse (mostly zero) factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the complexity of computing the DFT from O\left(N^2\right), which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to O(N \log N), where N is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where ''N'' may be in the thousands or millions. In the presence of round-off error, many FFT algorith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
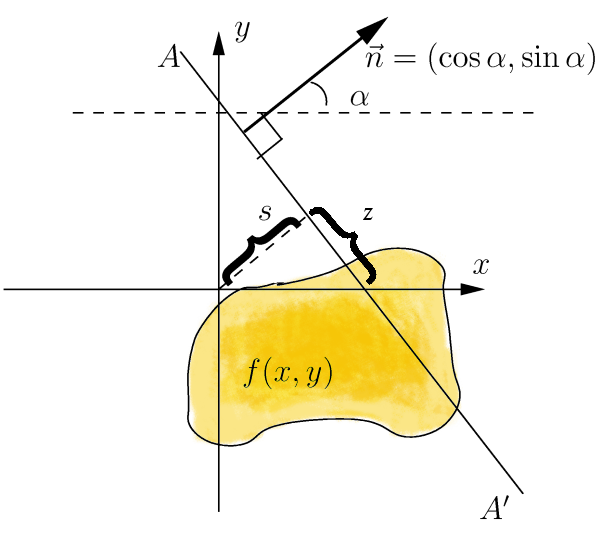
Radon Transform
In mathematics, the Radon transform is the integral transform which takes a function ''f'' defined on the plane to a function ''Rf'' defined on the (two-dimensional) space of lines in the plane, whose value at a particular line is equal to the line integral of the function over that line. The transform was introduced in 1917 by Johann Radon, who also provided a formula for the inverse transform. Radon further included formulas for the transform in three dimensions, in which the integral is taken over planes (integrating over lines is known as the X-ray transform). It was later generalized to higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, and more broadly in the context of integral geometry. The complex analogue of the Radon transform is known as the Penrose transform. The Radon transform is widely applicable to tomography, the creation of an image from the projection data associated with cross-sectional scans of an object. Explanation If a function f represents an unknown density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
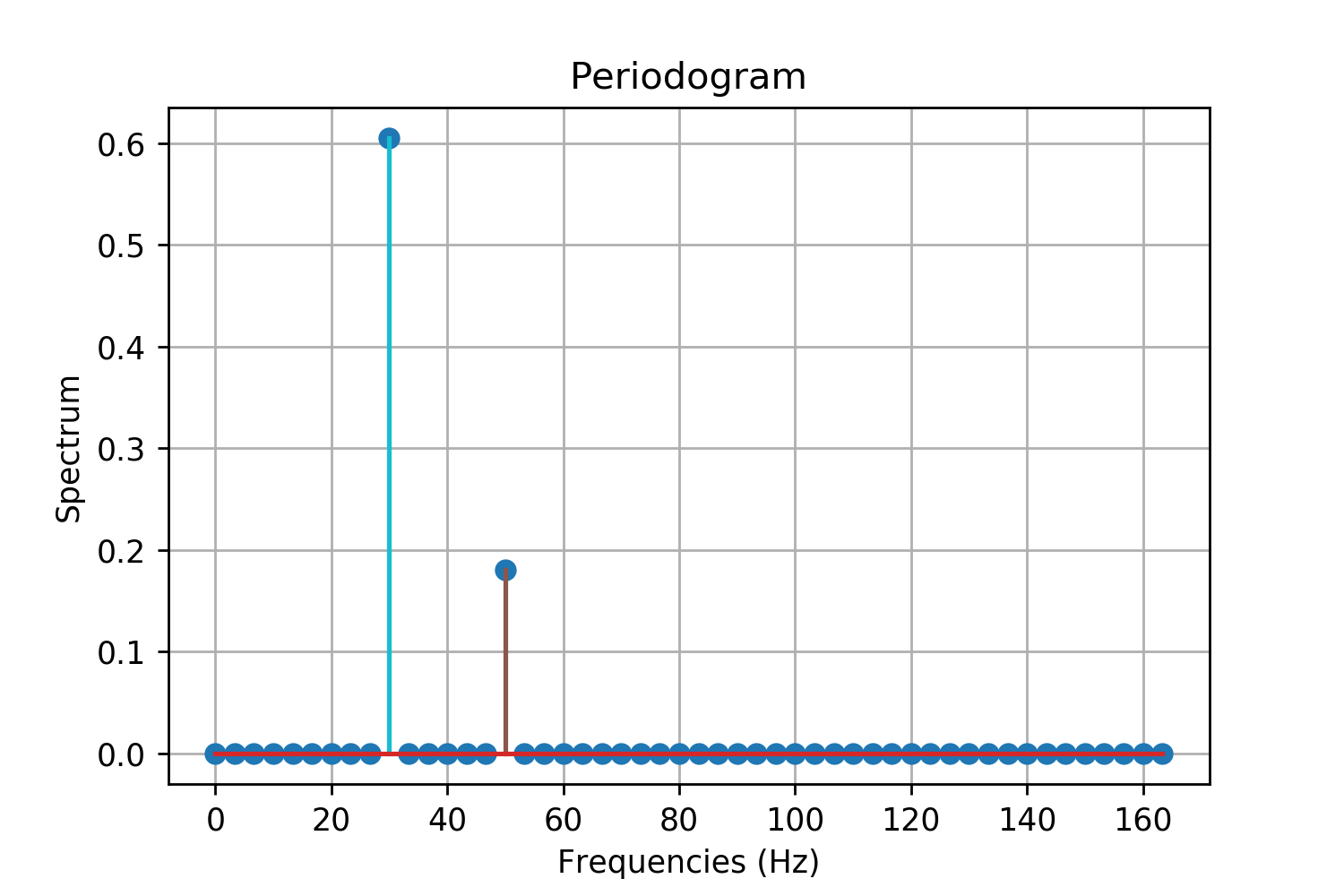
Periodogram
In signal processing, a periodogram is an estimate of the spectral density of a signal. The term was coined by Arthur Schuster in 1898. Today, the periodogram is a component of more sophisticated methods (see spectral estimation). It is the most common tool for examining the amplitude vs frequency characteristics of FIR filters and window functions. FFT spectrum analyzers are also implemented as a time-sequence of periodograms. Definition There are at least two different definitions in use today. One of them involves time-averaging, and one does not. Time-averaging is also the purview of other articles (Bartlett's method and Welch's method). This article is not about time-averaging. The definition of interest here is that the power spectral density of a continuous function, x(t), is the Fourier transform of its auto-correlation function (see Cross-correlation theorem, Spectral density#Power spectral density, and Wiener–Khinchin theorem): :\mathcal\ = X(f)\cdot X^ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matched Filter
In signal processing, a matched filter is obtained by correlating a known delayed signal, or ''template'', with an unknown signal to detect the presence of the template in the unknown signal. This is equivalent to convolving the unknown signal with a conjugated time-reversed version of the template. The matched filter is the optimal linear filter for maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the presence of additive stochastic noise. Matched filters are commonly used in radar, in which a known signal is sent out, and the reflected signal is examined for common elements of the out-going signal. Pulse compression is an example of matched filtering. It is so called because the impulse response is matched to input pulse signals. Two-dimensional matched filters are commonly used in image processing, e.g., to improve the SNR of X-ray observations. Matched filtering is a demodulation technique with LTI (linear time invariant) filters to maximize SNR. It was originally also known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-Doppler Radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational Pulse Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low ( infrasonic) to ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-input Single-output System
In control engineering, a single-input and single-output (SISO) system is a simple single variable control system with one input and one output. In radio it is the use of only one antenna both in the transmitter and receiver. Details SISO systems are typically less complex than multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. Usually, it is also easier to make order of magnitude or trending predictions "on the fly" or "back of the envelope". MIMO systems have too many interactions for most of us to trace through them quickly, thoroughly, and effectively in our heads. Frequency domain techniques for analysis and controller design dominate SISO control system theory. Bode plot, Nyquist stability criterion, Nichols plot, and root locus are the usual tools for SISO system analysis. Controllers can be designed through the polynomial design, root locus design methods to name just two of the more popular. Often SISO controllers will be PI, PID, or lead-lag. See also * Control theory * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Transaction On Signal Processing Paper Results Sample
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |