|
Rotary Actuator
A rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque. The simplest actuator is purely mechanical, where linear motion in one direction gives rise to rotation. The most common actuators are electrically powered; others may be powered pneumatically or hydraulically, or use energy stored in springs. The motion produced by an actuator may be either continuous rotation, as for an electric motor, or movement to a fixed angular position as for servomotors and stepper motors. A further form, the torque motor, does not necessarily produce any rotation but merely generates a precise torque which then either causes rotation or is balanced by some opposing torque. Actuator power sources Electric actuators Stepper motors Stepper motors are a form of electric motor that has the ability to move in discrete steps of a fixed size. This can be used either to produce continuous rotation at a controlled speed or to move by a controlled angular amount. If the stepper i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Servo
Micro may refer to: Measurement * micro- (μ), a metric prefix denoting a factor of 10−6 Places * Micro, North Carolina, town in U.S. People * DJ Micro, (born Michael Marsicano) an American trance DJ and producer *Chii Tomiya (都宮 ちい, born 1991), Japanese female professional wrestler, ring name Micro Arts, entertainment, and media * Micro (comics), often known as Micro, a character in Marvel Comics * ''Micro'' (novel), techno-thriller by Michael Crichton, published posthumously in 2011 * Micro (Thai band), a Thai rock band formed in 1983 * ''IEEE Micro'', a peer-reviewed scientific journal Brands and enterprises * Micro Cars, Sri Lankan automobile company, established 1995 * Micro Center, an American computer department store, established 1979 * Micro ISV (mISV or μISV), a term for a small independent software vendor * Micro Mobility Systems, Swiss company producing kickscooters Computing * ''Micro'', a mostly-obsolete term for a microcomputer, e.g.: **BBC Micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
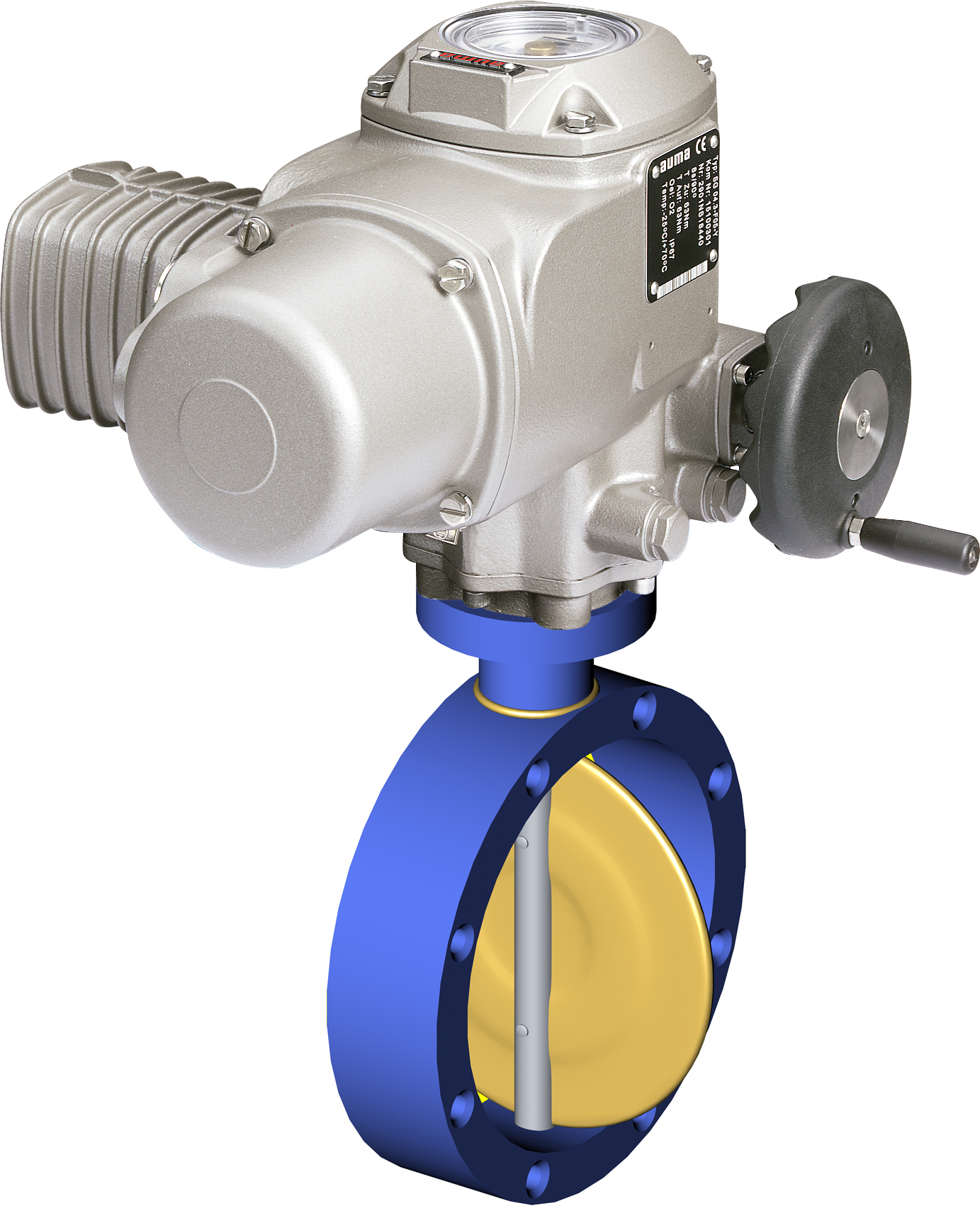
Valve Actuator
A valve actuator is the mechanism for opening and closing a valve. Manually operated valves require someone in attendance to adjust them using a direct or geared mechanism attached to the valve stem. Power-operated actuators, using gas pressure, hydraulic pressure or electricity, allow a valve to be adjusted remotely, or allow rapid operation of large valves. Power-operated valve actuators may be the final elements of an automatic control loop which automatically regulates some flow, level or other process. Actuators may be only to open and close the valve, or may allow intermediate positioning; some valve actuators include switches or other ways to remotely indicate the position of the valve. Used for the automation of industrial valves, actuators can be found in all kinds of process plants. They are used in waste water treatment plants, power plants, refineries, mining and nuclear processes, food factories, and pipelines. Valve actuators play a major part in automating proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Core Gauge
An air core gauge is a specific type of rotary actuator in an analog display gauge that allows an indicator to rotate a full 360 degrees. It is used in gauges and displays, most commonly automotive instrument clusters. A typical automotive application is shown at the right. The air core gauge is a type of "air-core motor". It may be considered a "gauge movement" or "pointer indication device". Background There are four common types of rotary actuators: * Physical gauges, in which the needle is attached directly to the value being measured; for example, a mechanical pressure gauge * Analog volt meters or d'Arsonval movements, which consist of a coil and a permanent magnet * Stepper motors, which move in one-notch increments or steps * Air-core motors, as described below. Construction and operation The air core gauge consists of two independent, perpendicular coils surrounding a hollow chamber. A needle shaft protrudes into the chamber, where a permanent magnet is affixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifold Vacuum
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in an internal combustion engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere. Manifold vacuum is an effect of a piston's movement on the induction stroke and the choked flow through a throttle in the intake manifold of an engine. It is a measure of the amount of restriction of airflow through the engine, and hence of the unused power capacity in the engine. In some engines, the manifold vacuum is also used as an auxiliary power source to drive engine accessories and for the crankcase ventilation system. Manifold vacuums should not be confused with Venturi vacuums, which are an effect exploited in carburetors to establish a pressure difference roughly proportional to mass airflow and to maintain a somewhat constant air/fuel ratio. It is also used in light airplanes to provide airflow for pneumatic gyroscopic instruments. Overview The rate of airflow through an internal combustion engine is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windscreen Wiper
A windscreen wiper, windshield wiper, wiper blade (American English), or simply wiper, is a device used to remove rain, snow, ice, washer fluid, water, or debris from a vehicle's front window. Almost all motor vehicles, including cars, trucks, buses, train locomotives, and watercraft with a cabin—and some aircraft—are equipped with one or more such wipers, which are usually a legal requirement. A wiper generally consists of a metal arm; one end pivots, and the other end has a long rubber blade attached to it. The arm is powered by a motor, often an electric motor, although pneumatic power is also used for some vehicles. The blade is swung back and forth over the glass, pushing water, other precipitation, or any other impediments to visibility from its surface. The speed is usually adjustable on vehicles made after 1969, with several continuous rates and often one or more ''intermittent'' settings. Most personal automobiles use two synchronized ''radial''-type arms, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressure by around 20%. But h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verin Rotatif Principe
Verin may refer to: *Vérin, a city in France *Verín, a city in Spain *Verín (comarca), a ''comarca'' in Spain *Verrine (demon), a demon in Christian mythology *Verin (Dungeons & Dragons) In the ''Dungeons & Dragons'' fantasy role-playing game, "monsters" are generally the antagonists which players must fight and defeat to progress in the game. Since the game's first edition in 1974, a bestiary was included along other game man ..., a demon lord in the ''Dungeons & Dragons'' roleplaying game * Verin Mathwin Sedai, a fictional character in Robert Jordan's ''The Wheel of Time'' fantasy series {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SparkFun Electronics
SparkFun Electronics (sometimes known by its abbreviation, ''SFE'') is an electronics retailer in Niwot, Colorado, United States. It manufactures and sells microcontroller development boards and breakout boards. All products designed and produced by SparkFun are released as open-source hardware. History SparkFun Electronics was founded in 2003 by Nathan Seidle when he was a Junior at University of Colorado Boulder. Its first products were Olimex printed circuit boards. The name 'SparkFun' came about because one of the founders of SparkFun was testing a development board, and sparks flew out; ''Fun'' was chosen because the company's self-stated aim is to educate people about electronics. In January 2011, an education department was formed to outreach to local schools, hackerspaces, and events. Open-source hardware During the Open Source Hardware summit in October 2010, SparkFun was one of the contributors in drafting the first OSHW definition. All products designed and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Wire
In metallurgy, a shape-memory alloy (SMA) is an alloy that can be deformed when cold but returns to its pre-deformed ("remembered") shape when heated. It may also be called memory metal, memory alloy, smart metal, smart alloy, or muscle wire. Parts made of shape-memory alloys can be lightweight, solid-state alternatives to conventional actuators such as hydraulic, pneumatic, and motor-based systems. They can also be used to make hermetic joints in metal tubing. Overview The two most prevalent shape-memory alloys are copper-aluminium-nickel and nickel-titanium (NiTi), but SMAs can also be created by alloying zinc, copper, gold and iron. Although iron-based and copper-based SMAs, such as Fe-Mn-Si, Cu-Zn-Al and Cu-Al-Ni, are commercially available and cheaper than NiTi, NiTi-based SMAs are preferable for most applications due to their stability and practicability as well as their superior thermo-mechanic performance. SMAs can exist in two different phases, with three differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio-controlled Model
A radio-controlled model (or RC model) is a model that is steerable with the use of radio control. All types of model vehicles have had RC systems installed in them, including ground vehicles, boats, planes, helicopters and even submarines and scale railway locomotives. History Radio control has been around since Nikola Tesla demonstrated a remote control boat in 1898. World War II saw increased development in radio control technology. The Luftwaffe used controllable winged bombs for targeting Allied ships. During the 1930s the Good brothers Bill and Walt pioneered vacuum tube based control units for R/C hobby use. Their "Guff" radio controlled plane is on display at the National Aerospace museum. Ed Lorenze published a design in Model Airplane News that was built by many hobbyists. Later, after WW2, in the late 1940s to mid 1950 many other R/C designs emerged and some were sold commercially, Berkeley's Super Aerotrol, was one such example. Originally simple 'on-off' syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servo (radio Control)
Servos (also RC servos) are small, cheap, mass-produced servomotors or other actuators used for radio control and small-scale robotics. Most servos are rotary actuators although other types are available. Linear actuators are sometimes used, although it is more common to use a rotary actuator with a bellcrank and pushrod. Some types, originally used as sail winches for model yachting, can rotate continuously. Construction A typical servo consists of a small electric motor driving a train of reduction gears. A potentiometer is connected to the output shaft. Some simple electronics provide a closed-loop servomechanism. Operation The position of the output, measured by the potentiometer, is continually compared to the commanded position from the control (i.e., the radio control). Any difference gives rise to an error signal in the appropriate direction, which drives the electric motor either forwards or backwards, and moving the output shaft to the commanded position. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |