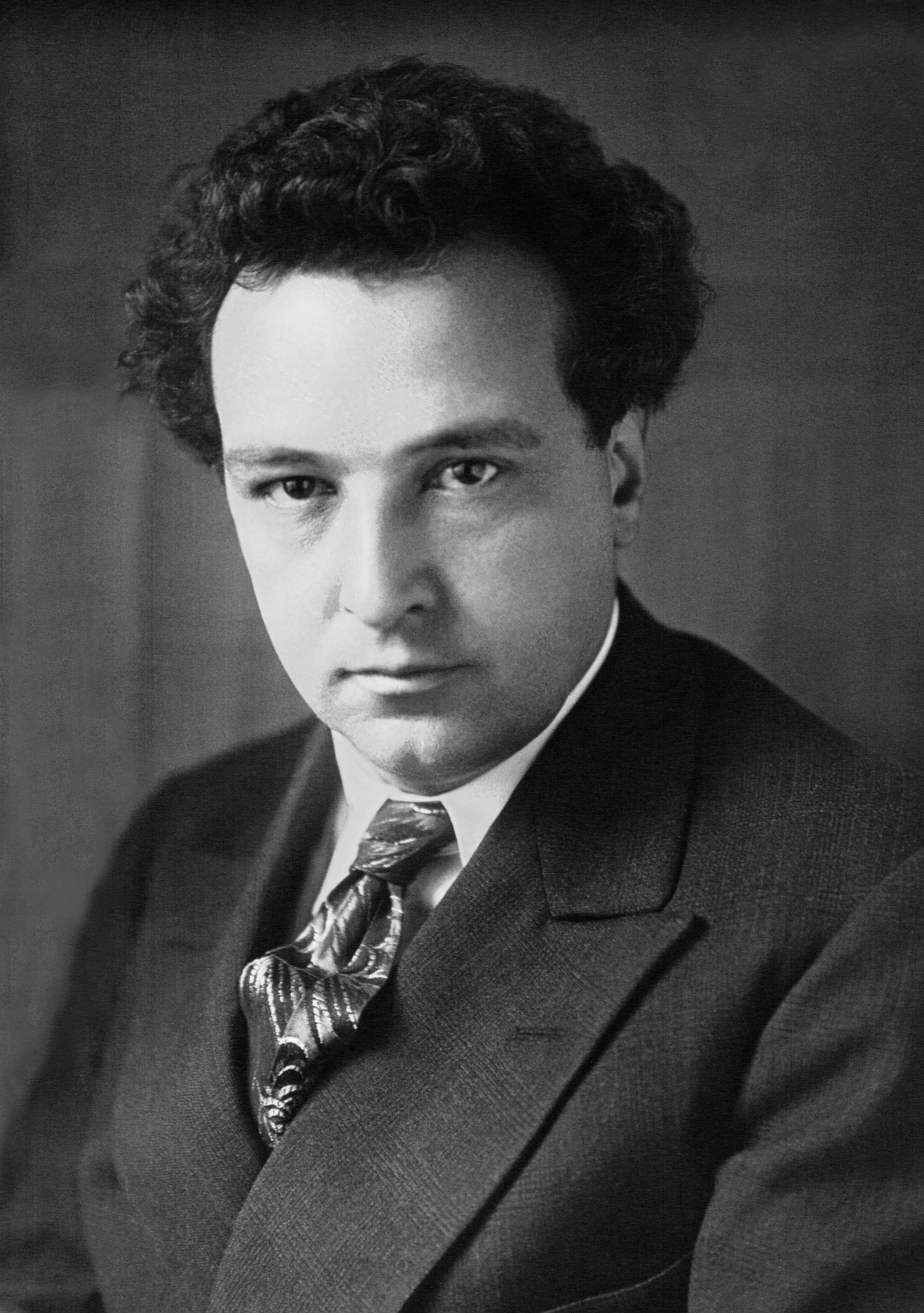|
Roger Bourdin
Roger Bourdin (14 June 1900 in Paris – 14 September 1973 in Paris) was a French baritone, particularly associated with the French repertory. His career was largely based in France. His daughter is Françoise Bourdin. Life and career Born in the 19th arrondissement of Paris, Bourdin studied at the Conservatoire de Paris, where he was a pupil of André Gresse and Jacques Isnardon. He made his professional debut at the Opéra-Comique in 1922, as Lescaut in ''Manon''. His debut at the Palais Garnier took place in 1942, in Henri Rabaud's '' Mârouf, savetier du Caire''. The major part of his career was to be spent between these two theatres, where he created some 30 roles, among them the title role in Milhaud's ''Bolivar''. Bourdin seldom performed outside France, but did a few guest appearances at the Royal Opera House in London (including Pelléas to the Mélisande of Maggie Teyte in 1930),Obituary - Roger Bourdin. ''Opera'', January 1974, Vol 25 No.1, p.74. La Scala in Mila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, Fashion capital, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called Caput Mundi#Paris, the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaucochard Et Fils Ier
is an unfinished by Emmanuel Chabrier of which only some numbers survive. The French libretto was by Paul Verlaine.Delage R. ''Emmanuel Chabrier''. Paris, Fayard, 1999 (Catalogue des Oeuvres). Background In the early 1860s Chabrier was a close friend of Verlaine and dined at the Verlaines' house, rue Lecluze every Saturday from 1860-1863. With Verlaine and Chabrier, the friends who met together there included Albert Mérat, Adolphe Racot, François Coppée, Louis-Xavier de Ricard and Édouard Lepelletier.Delage R. ''Chabrier, Iconographie musicale.'' Minkoff Lattès, 1982, p49. Although Roger Delage has dated Chabrier’s work on the score of ''Vaucochard et fils Ier'' to around 1864, Verlaine continued to mention work for the project for several years after. Only four complete numbers exist from this early comic piece where the cowardly but bawdy title role is a satire of Napoleon III. In this, one of the Chabrier's earliest works, Poulenc discerned elements of the compose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salle Gaveau
The Salle Gaveau, named after the French piano maker Gaveau, is a classical concert hall in Paris, located at 45-47 rue La Boétie, in the 8th arrondissement of Paris. It is particularly intended for chamber music. Construction The plans for the hall were drawn up by Jacques Hermant in 1905, the year the land was acquired. The construction of the Gaveau building took place from 1906 to 1907. The vocation of this hall was chamber music from the beginning, and its seating capacity was a thousand, just as it is today. The hall was home to a large organ built in 1900 by the Cavaillé-Coll, Mutin-Cavaillé-Coll firm. This instrument with 39 stops (8 on the positive, 12 on the recitative, 12 on the grand organ and 7 on the pedal) was subsequently installed in 1957 in the commune of Saint-Saëns in Normandy. The hall is a concert venue renowned for its exceptional acoustics. Beginnings The hall opened its doors on 3 October 1907 for the concert of the Lehrergesangverein (Teachers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Quichotte à Dulcinée
Don Quichotte à Dulcinée is a song cycle by Maurice Ravel based on the story of ''Don Quixote''. It was first composed for voice and piano but later orchestrated. The songs are traditionally performed by a baritone or bass(-baritone). The cycle is made up of three independent pieces: ''Chanson Romanesque, Chanson épique,'' and ''Chanson à boire.'' The text was written by the librettist Paul Morand. It was composed between the years of 1932 and 1933. Composition history This was the last of Maurice Ravel's compositions, commissioned by the celebrated film director G. W. Pabst for a cinema version of ''Don Quixote'' starring the legendary bass Fyodor Chaliapin. The score was to include four songs (one more than the final version) along with background music for several episodes. As Ravel worked on the project in 1932, however, he suffered the increasingly disabling effects of Pick’s disease, a cerebral-neurological condition that gradually robbed him of motor skills and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operetta
Operetta is a form of theatre and a genre of light opera. It includes spoken dialogue, songs, and dances. It is lighter than opera in terms of its music, orchestral size, length of the work, and at face value, subject matter. Apart from its shorter length, the operetta is usually of a light and amusing character. It sometimes also includes satirical commentaries. "Operetta" is the Italian diminutive of "opera" and was used originally to describe a shorter, perhaps less ambitious work than an opera. Operetta provides an alternative to operatic performances in an accessible form targeting a different audience. Operetta became a recognizable form in the mid-19th century in France, and its popularity led to the development of many national styles of operetta. Distinctive styles emerged across countries including Austria-Hungary, Germany, England, Spain, the Philippines, Mexico, Cuba, and the United States. Through the transfer of operetta among different countries, cultural cosmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius Milhaud
Darius Milhaud (; 4 September 1892 – 22 June 1974) was a French composer, conductor, and teacher. He was a member of Les Six—also known as ''The Group of Six''—and one of the most prolific composers of the 20th century. His compositions are influenced by jazz and Brazilian music and make extensive use of polytonality. Milhaud is considered one of the key modernist composers.Reinhold Brinkmann & Christoph Wolff, ''Driven into Paradise: The Musical Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madame Bovary (opera)
''Madame Bovary'' is an opera by Emmanuel Bondeville premiered at the Opéra-Comique on 1 June 1951 in a production by Louis Musy, conducted by Albert Wolff, with Jacqueline Brumaire in the title roleWolff S. ''Un demi-siècle d'Opéra-Comique (1900–1950).'' André Bonne, Paris, 1953. The opera is based upon the novel ''Madame Bovary'' by Gustave Flaubert Gustave Flaubert ( , , ; 12 December 1821 – 8 May 1880) was a French novelist. Highly influential, he has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country. According to the literary theorist Kornelije Kvas, "in Flauber .... Recordings *Andree Esposito, Julien Haas, Yves Bisson, Nadine Denize, Orchestre de la Radio Lyrique de Paris, Pierre-Michel Le Conte 1962 References External linksOpera chicJohn Adams on ''Madame Bovary'' Operas based on works by Gustave Flaubert Operas Operas based on novels French-language operas Opera world premieres at the Opéra-Comique 1951 operas { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmanuel Bondeville
Emmanuel Bondeville was a French composer and music administrator, born 29 October 1898 in Rouen, and died 26 November 1987 in Paris. He was a member of the Académie des Beaux-Arts. Biography As a young man he was organist at the church of Saint-Nicaise in Rouen and Notre-Dame in Caen. Bondeville lost both his parents when he was 16, and took on various jobs – organist, bank clerk, translator - to get by.Landormy P. ''La Musique Française après Debussy.'' Gallimard, Paris, 1943. He made his beginnings in music around 1923 writing works for piano, symphonic poems, opéras-comiques and opéras. During this time he also travelled around Europe and worked as an assistant in a music shop. He eventually had lessons in harmony and counterpoint from Jean Déré. In 1935 he became musical director of the radio stations Radio Tour Eiffel, Radio Paris, Radiodiffusion française then artistic director of Radio Monte-Carlo. From 1949 to 1951 Bondeville was director of the Opéra-Comique, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynaldo Hahn
Reynaldo Hahn (; 9 August 1874 – 28 January 1947) was a Venezuelan-born French composer, conductor, music critic, and singer. He is best known for his songs – '' mélodies'' – of which he wrote more than 100. Hahn was born in Caracas but his family moved to Paris when he was a child, and he lived most of his life there. Following the success of his song "''Si mes vers avaient des ailes''" (If my verses had wings), written when he was aged 14, he became a prominent member of ''fin de siècle'' French society. Among his closest friends were Sarah Bernhardt and Marcel Proust. After the First World War, in which he served in the army, Hahn adapted to new musical and theatrical trends and enjoyed successes with his first opérette, ''Ciboulette'' (1923) and a collaboration with Sacha Guitry, the musical comedy ''Mozart'' (1926). During the Second World War Hahn, who was of Jewish descent, took refuge in Monaco, returning to Paris in 1945 where he was appointed director of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Ibert
Jacques François Antoine Marie Ibert (15 August 1890 – 5 February 1962) was a French composer of classical music. Having studied music from an early age, he studied at the Paris Conservatoire and won its top prize, the Prix de Rome at his first attempt, despite studies interrupted by his service in World War I. Ibert pursued a successful composing career, writing (sometimes in collaboration with other composers) seven operas, five ballets, incidental music for plays and films, works for piano solo, choral works, and chamber music. He is probably best remembered for his orchestral works including ''Divertissement'' (1930) and ''Escales'' (1922). As a composer, Ibert did not attach himself to any of the prevalent genres of music of his time, and has been described as an eclectic. This is seen even in his best-known pieces: ''Divertissement'' for small orchestra is lighthearted, even frivolous, and ''Escales'' (1922) is a ripely romantic work for large orchestra. In tandem with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Honegger
Arthur Honegger (; 10 March 1892 – 27 November 1955) was a Swiss composer who was born in France and lived a large part of his life in Paris. A member of Les Six, his best known work is probably ''Antigone'', composed between 1924 and 1927 to the French libretto by Jean Cocteau based on the tragedy ''Antigone'' by Sophocles. It premiered on 28 December 1927 at the Théâtre Royal de la Monnaie with sets designed by Pablo Picasso and costumes by Coco Chanel. However, his most frequently performed work is probably the orchestral work ''Pacific 231'', which was inspired by the sound of a steam locomotive. Biography Born Oscar-Arthur Honegger (the first name was never used) to Swiss parents in Le Havre, France, he initially studied harmony with Robert-Charles Martin (to whom he dedicated his first published work and violin in Le Havre. After studying for two years at the Zurich Conservatory, he enrolled in the Paris Conservatoire from 1911 to 1918, studying with both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Messager
André Charles Prosper Messager (; 30 December 1853 – 24 February 1929) was a French composer, organist, pianist and conductor. His compositions include eight ballets and thirty opéra comique, opéras comiques, opérettes and other stage works, among which his ballet ''Les Deux Pigeons (ballet), Les Deux Pigeons'' (1886) and opéra comique ''Véronique (operetta), Véronique'' (1898) have had lasting success; ''Les p'tites Michu, Les P'tites Michu'' (1897) and ''Monsieur Beaucaire (opera), Monsieur Beaucaire'' (1919) were also popular internationally. Messager took up the piano as a small child and later studied composition with, among others, Camille Saint-Saëns and Gabriel Fauré. He became a major figure in the musical life of Paris and later London, both as a conductor and a composer. Many of his Parisian works were also produced in the West End theatre, West End and some on Broadway theatre, Broadway; the most successful had long runs and numerous international revival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)