|
Rickarton House
Rickarton House is a 19th-century country house in Kincardineshire, Scotland. It lies approximately three-and-a-half miles northwest of Stonehaven in the former county of Kincardineshire. The house is situated on the north banks of the Cowie Water The Cowie Water ( gd, Uisge Chollaidh) is a river of Scotland. Geography The river rises in the Grampian Mountains in Kincardineshire, and discharges to the North Sea in the northern part of Stonehaven,United Kingdom Ordnance Survey Map Landra ... slightly upstream of the confluence with Cowton Burn. Rickarton is a category B listed building. Rickarton House was constructed in the first decade of the 19th century for William Rickart Hepburn. He commissioned the City Architect of Aberdeen, John Smith, to undertake the work. The house and the estate became the property of the Bairds in the mid 19th century. It is currently owned by the Baron of Rickarton, Ury, and Lochwood. References *Watt, Archibald, ''Highways and Byway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickarton House - Geograph
Rickarton is a settlement in Aberdeenshire. It is situated on the A957 to the northwest of Stonehaven. Rickarton was served by the 105 bus between Stonehaven and Banchory until its withdrawal in 2018. Rickarton was home to a Church of Scotland The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland. The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Reformation of 1560, when it split from the Catholic Church ... church until its closure in the late 1970s. References Villages in Aberdeenshire {{Aberdeenshire-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
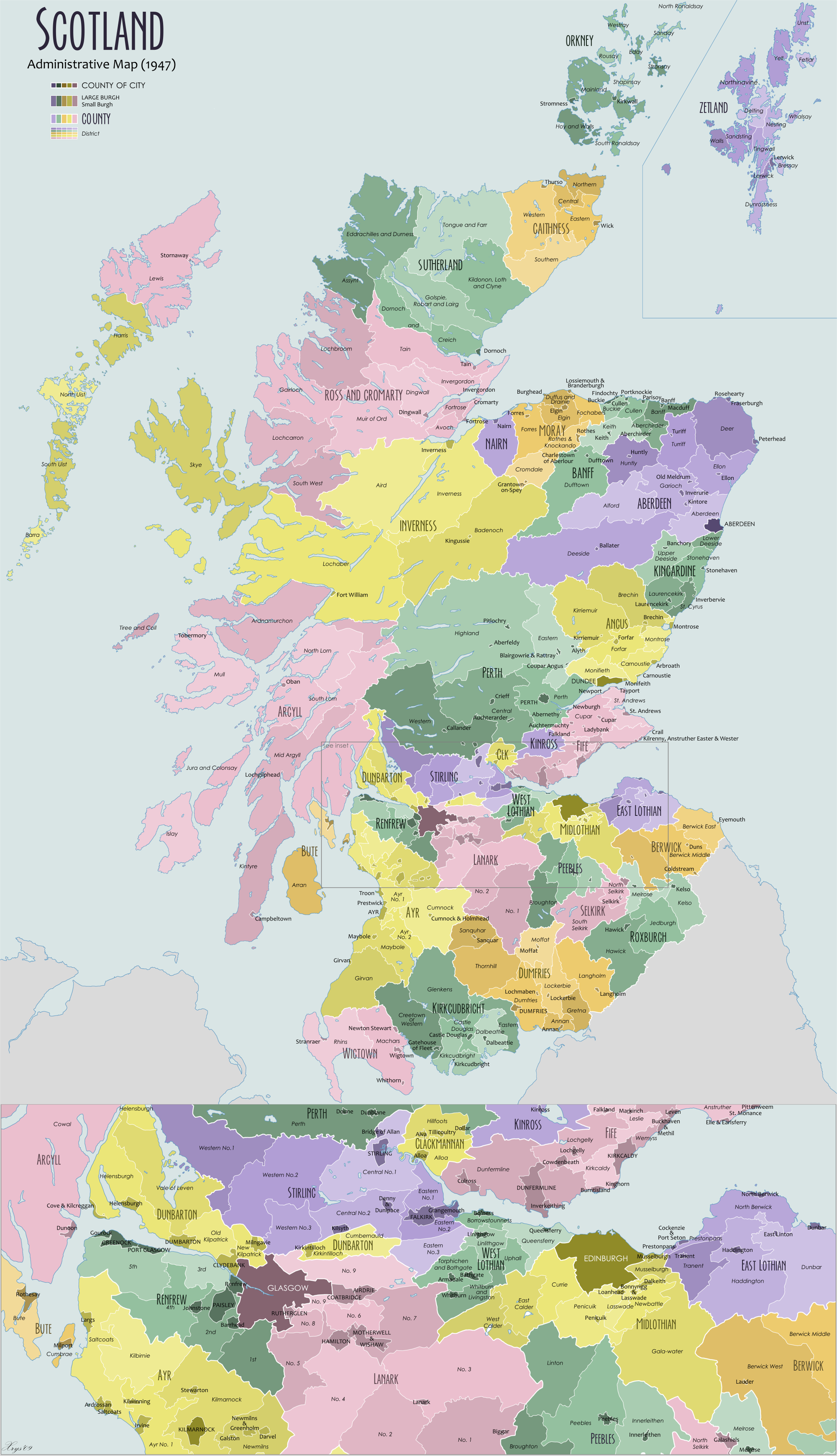
Kincardineshire
Kincardineshire, also known as the Mearns (from the Scottish Gaelic meaning "the Stewartry"), is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area on the coast of northeast Scotland. It is bounded by Aberdeenshire on the north and west, and by Angus on the south. The name "Kincardine" is also used in Kincardine and Mearns, a committee area of the Aberdeenshire Council, although this covers a smaller area than the county. History Anciently, the area was the Province of ''Mearns'', bordered on the north by Marr, and on the west by Angus. The name of the province simply refers to its status; the more important provinces were governed by a ''great steward'' ('' Mormaer''), while the less important ones were governed by a mere ''steward'' (''Maer''). It included the burghs of Stonehaven, Banchory, Inverbervie and Laurencekirk, and other settlements included Drumoak, Muchalls, Newtonhill and Portlethen. ''Mearns'' extended to Hill of Fare north of the Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stonehaven
Stonehaven ( , ) is a town in Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 11,602 at the 2011 Census. After the demise of the town of Kincardine, which was gradually abandoned after the destruction of its royal castle in the Wars of Independence, the Scottish Parliament made Stonehaven the successor county town of Kincardineshire. It is currently administered as part of the unitary authority of Aberdeenshire. Stonehaven had grown around an Iron Age fishing village, now the "Auld Toon" ("old town"), and expanded inland from the seaside. As late as the 16th century, old maps indicate the town was called ''Stonehyve'', ''Stonehive'', Timothy Pont also adding the alternative ''Duniness''. It is known informally to locals as ''Stoney''. Pre-history and archaeology Stonehaven is the site of prehistoric events evidenced by finds at Fetteresso Castle and Neolithic pottery excavations from the Spurryhillock area. In 2004, archaeological work by CFA Archa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shires Of Scotland
The shires of Scotland ( gd, Siorrachdan na h-Alba), or counties of Scotland, are historic subdivisions of Scotland established in the Middle Ages and used as administrative divisions until 1975. Originally established for judicial purposes (being the territory over which a sheriff had jurisdiction), from the 17th century they started to be used for local administration purposes as well. The areas used for judicial functions ( sheriffdoms) came to diverge from the shires, which ceased to be used for local government purposes after 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973. Today, local government in Scotland is based upon council areas, which sometimes incorporate county names, but frequently have vastly different boundaries. Counties continue to be used for land registration, and form the basis of the lieutenancy areas (although the latter are not entirely identical). History Sheriffdoms or shires Malcolm III (reigned 1058 to 1093) appears to have introduced s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowie Water
The Cowie Water ( gd, Uisge Chollaidh) is a river of Scotland. Geography The river rises in the Grampian Mountains in Kincardineshire, and discharges to the North Sea in the northern part of Stonehaven,United Kingdom Ordnance Survey Map Landranger 45, Stonehaven and Banchory, 1:50,000 scale, 2004 south of the ruined Cowie Castle. Tributaries of the Cowie Water include the Burn of Monboys, which drains the area to the north, in which the archaeological site Raedykes Roman Camp is situated; and Cowton Burn. Notable features in this vicinity include Dunnottar Castle, Fetteresso Castle and Muchalls Castle. Other nearby coastal waterways discharging to the North Sea include Burn of Muchalls to the north and Carron Water to the south. Hydrology and water quality Summer flow rates are typically in the range of at the river's mouth. July values for pH have been measured at 8.2 or slightly alkaline July water temperatures are about 11.9 degrees Celsius and electrical cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowton Burn
Cowton Burn is a stream that rises in the Mounth, or eastern range of the Grampian Mountains, on some of the northwest slopes of the Durris Forest west of Netherley, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The Grid Reference for the headwaters is NO 925 823); Cowton Burn is a tributary to the Cowie Water. The Cowton Burn is crossed by the A957 road slightly northwest of Rickarton House. Watershed characteristics The headwaters of the Cowton Burn rise in a coniferous forest area of the Durris Forest. The stream flows downslope on an easterly course as it makes its way to discharge to the Cowie Water. The stream generally has lush vegetation growing all the way to its margins throughout most of its course. The July flow rate is roughly six cubic feet per second in the headwaters reach. pH levels are slightly alkaline.C.M. Hogan, ''History of Muchalls Castle'', Natural History Section, Lumina Press, Aberdeen (2005) History The Roman Camp Raedykes occupied the northern higher ground of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Rickart Hepburn
William Rickart Hepburn (died 13 January 1807) was a Scottish politician and soldier who lived in Kincardineshire and was responsible for the construction of Rickarton House. He was the eldest son of Lieutenant-Colonel Robert Rickart Hepburn of Rickarton House, MP for Kincardineshire, and Magdalene Murray, and was born in Scotland during the latter part of the 19th century. He joined the British army and served with the 31st Regiment of Foot during the French revolutionary and Napoleonic wars. He rose to the rank of Lieutenant-Colonel and commanded the regiment during its time in the West Indies, 17974-97. In 1796 he married Janet Paul of Rathlodge, Fetteresso. The couple had two sons, Robert and William, and a daughter, Madeline. His great-great-grandsons were Canadian politicians, Brigadier-General Bernard Rickart Hepburn and James de Congalton Hepburn. He died in London on 13 January 1807.''The Scots Magazine,'' Volume 6/ref> See also *Fetteresso Castle *Muchalls Castle *U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smith (architect)
John Smith (1781 – 22 July 1852) was a Scottish architect. His career started in 1805 and he was appointed as the official city architect of Aberdeen in 1807, the first person to hold this post. Together with Archibald Simpson, he contributed significantly to the architecture of Aberdeen, and many of the granite buildings that gave the city the nickname 'The Granite City' or also 'The Silver City' are attributed to them. Smith was the son of a successful builder and architect and his own son, William, continued the family tradition by also becoming an architect. After completing his training in London, Smith quickly became established throughout the north-east of Scotland. He secured private commissions to design, renovate or alter numerous country houses, parish churches and castles; his official capacity as City Architect ensured he is also credited with several extensive public works. Towards the middle of his career around the 1830s, as his individuality developed, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron Of Rickarton, Ury, And Lochwood
Baron is a rank of nobility or title of honour, often hereditary, in various European countries, either current or historical. The female equivalent is baroness. Typically, the title denotes an aristocrat who ranks higher than a lord or knight, but lower than a viscount or count. Often, barons hold their fief – their lands and income – directly from the monarch. Barons are less often the vassals of other nobles. In many kingdoms, they were entitled to wear a smaller form of a crown called a ''coronet''. The term originates from the Latin term , via Old French. The use of the title ''baron'' came to England via the Norman Conquest of 1066, then the Normans brought the title to Scotland and Italy. It later spread to Scandinavia and Slavic lands. Etymology The word '' baron'' comes from the Old French , from a Late Latin "man; servant, soldier, mercenary" (so used in Salic law; Alemannic law has in the same sense). The scholar Isidore of Seville in the 7th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |