|
Richard E. Bellman
Richard Ernest Bellman (August 26, 1920 – March 19, 1984) was an American applied mathematician, who introduced dynamic programming in 1953, and made important contributions in other fields of mathematics, such as biomathematics. He founded the leading biomathematical journal Mathematical Biosciences. Biography Bellman was born in 1920 in New York City to non-practising Jewish parents of Polish and Russian descent, Pearl (née Saffian) and John James Bellman, who ran a small grocery store on Bergen Street near Prospect Park, Brooklyn. On his religious views, he was an atheist. He attended Abraham Lincoln High School, Brooklyn in 1937,Salvador SanabriaRichard Bellman profile at http://www-math.cudenver.edu retrieved October 3, 2008. and studied mathematics at Brooklyn College where he earned a BA in 1941. He later earned an MA from the University of Wisconsin. During World War II he worked for a Theoretical Physics Division group in Los Alamos. In 1946 he received h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Engineering is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), the National Academy of Medicine, and the National Research Council (now the program units of NASEM). The NAE operates engineering programs aimed at meeting national needs, encourages education and research, and recognizes the superior achievements of engineers. New members are annually elected by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. The NAE is autonomous in its administration and in the selection of its members, sharing with the rest of the National Academies the role of advising the federal government. History The National Academy of Sciences was created by an Act of Incorporation dated March 3, 1863, which was signed by then President of the United States A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Programming
Dynamic programming is both a mathematical optimization method and a computer programming method. The method was developed by Richard Bellman in the 1950s and has found applications in numerous fields, from aerospace engineering to economics. In both contexts it refers to simplifying a complicated problem by breaking it down into simpler sub-problems in a recursive manner. While some decision problems cannot be taken apart this way, decisions that span several points in time do often break apart recursively. Likewise, in computer science, if a problem can be solved optimally by breaking it into sub-problems and then recursively finding the optimal solutions to the sub-problems, then it is said to have '' optimal substructure''. If sub-problems can be nested recursively inside larger problems, so that dynamic programming methods are applicable, then there is a relation between the value of the larger problem and the values of the sub-problems.Cormen, T. H.; Leiserson, C. E.; R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Mathematics
Applied mathematics is the application of mathematical methods by different fields such as physics, engineering, medicine, biology, finance, business, computer science, and industry. Thus, applied mathematics is a combination of mathematical science and specialized knowledge. The term "applied mathematics" also describes the professional specialty in which mathematicians work on practical problems by formulating and studying mathematical models. In the past, practical applications have motivated the development of mathematical theories, which then became the subject of study in pure mathematics where abstract concepts are studied for their own sake. The activity of applied mathematics is thus intimately connected with research in pure mathematics. History Historically, applied mathematics consisted principally of applied analysis, most notably differential equations; approximation theory (broadly construed, to include representations, asymptotic methods, variati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard E
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick", "Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", "Rick", " Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * Richard Anderson (other) * Richard Cartwright (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Medal Of Honor
The IEEE Medal of Honor is the highest recognition of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). It has been awarded since 1917, when its first recipient was Major Edwin H. Armstrong. It is given for an exceptional contribution or an extraordinary career in the IEEE fields of interest. The award consists of a gold medal, bronze replica, certificate, and honorarium. The Medal of Honor may only be awarded to an individual. The medal was created by the Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE) as the ''IRE Medal of Honor''. It became the IEEE Medal of Honor when IRE merged with the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) to form the IEEE in 1963. It was decided that IRE's Medal of Honor would be presented as IEEE's highest award, while the Edison Medal would become IEEE's principal medal. Edward Field Sanford, Jr. designed the medal in 1917. Eleven persons with an exceptional career in electrical engineering received both the IEEE Edison Medal and the IEEE Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Von Neumann Theory Prize
The John von Neumann Theory Prize of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) is awarded annually to an individual (or sometimes a group) who has made fundamental and sustained contributions to theory in operations research and the management sciences. The Prize named after mathematician John von Neumann is awarded for a body of work, rather than a single piece. The Prize was intended to reflect contributions that have stood the test of time. The criteria include significance, innovation, depth, and scientific excellence. The award is $5,000, a medallion and a citation. The Prize has been awarded since 1975. The first recipient was George B. Dantzig for his work on linear programming. List of recipients * 2022 Vijay Vazirani * 2021 Alexander Shapiro * 2020 Adrian Lewis * 2019 Dimitris Bertsimas and Jong-Shi Pang * 2018 Dimitri Bertsekas and John Tsitsiklis ** ''for contributions to Parallel and Distributed Computation as well as Neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman Equation
In optimal control theory, the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equation gives a necessary and sufficient condition for optimality of a control with respect to a loss function. It is, in general, a nonlinear partial differential equation in the value function, which means its solution the value function itself. Once this solution is known, it can be used to obtain the optimal control by taking the maximizer (or minimizer) of the Hamiltonian involved in the HJB equation. The equation is a result of the theory of dynamic programming which was pioneered in the 1950s by Richard Bellman and coworkers. The connection to the Hamilton–Jacobi equation from classical physics was first drawn by Rudolf Kálmán. In discrete-time problems, the corresponding difference equation is usually referred to as the Bellman equation. While classical variational problems, such as the brachistochrone problem, can be solved using the Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation, the method can be applied to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grönwall's Inequality
In mathematics, Grönwall's inequality (also called Grönwall's lemma or the Grönwall–Bellman inequality) allows one to bound a function that is known to satisfy a certain differential inequality, differential or integral inequality by the solution of the corresponding differential or integral equation. There are two forms of the lemma, a differential form and an integral form. For the latter there are several variants. Grönwall's inequality is an important tool to obtain various estimates in the theory of ordinary differential equation, ordinary and stochastic differential equations. In particular, it provides a comparison theorem that can be used to prove uniqueness quantification, uniqueness of a solution to the initial value problem; see the Picard–Lindelöf theorem. It is named for Thomas Hakon Grönwall (1877–1932). Grönwall is the Swedish spelling of his name, but he spelled his name as Gronwall in his scientific publications after emigrating to the United States. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellman's Lost In A Forest Problem
Bellman's lost-in-a-forest problem is an unsolved minimization problem in geometry, originating in 1955 by the American applied mathematician Richard E. Bellman Richard Ernest Bellman (August 26, 1920 – March 19, 1984) was an American applied mathematician, who introduced dynamic programming in 1953, and made important contributions in other fields of mathematics, such as biomathematics. He founde .... The problem is often stated as follows: ''"A hiker is lost in a forest whose shape and dimensions are precisely known to him. What is the best path for him to follow to escape from the forest?"'' It is usually assumed that the hiker does not know the starting point or direction he is facing. The best path is taken to be the one that minimizes the worst-case distance to travel before reaching the edge of the forest. Other variations of the problem have been studied. Although real world applications are not apparent, the problem falls into a class of geometric optimization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellman–Ford Algorithm
The Bellman–Ford algorithm is an algorithm that computes shortest paths from a single source vertex to all of the other vertices in a weighted digraph. It is slower than Dijkstra's algorithm for the same problem, but more versatile, as it is capable of handling graphs in which some of the edge weights are negative numbers. The algorithm was first proposed by , but is instead named after Richard Bellman and Lester Ford Jr., who published it in 1958 and 1956, respectively. Edward F. Moore also published a variation of the algorithm in 1959, and for this reason it is also sometimes called the Bellman–Ford–Moore algorithm. Negative edge weights are found in various applications of graphs, hence the usefulness of this algorithm. If a graph contains a "negative cycle" (i.e. a cycle whose edges sum to a negative value) that is reachable from the source, then there is no ''cheapest'' path: any path that has a point on the negative cycle can be made cheaper by one more walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
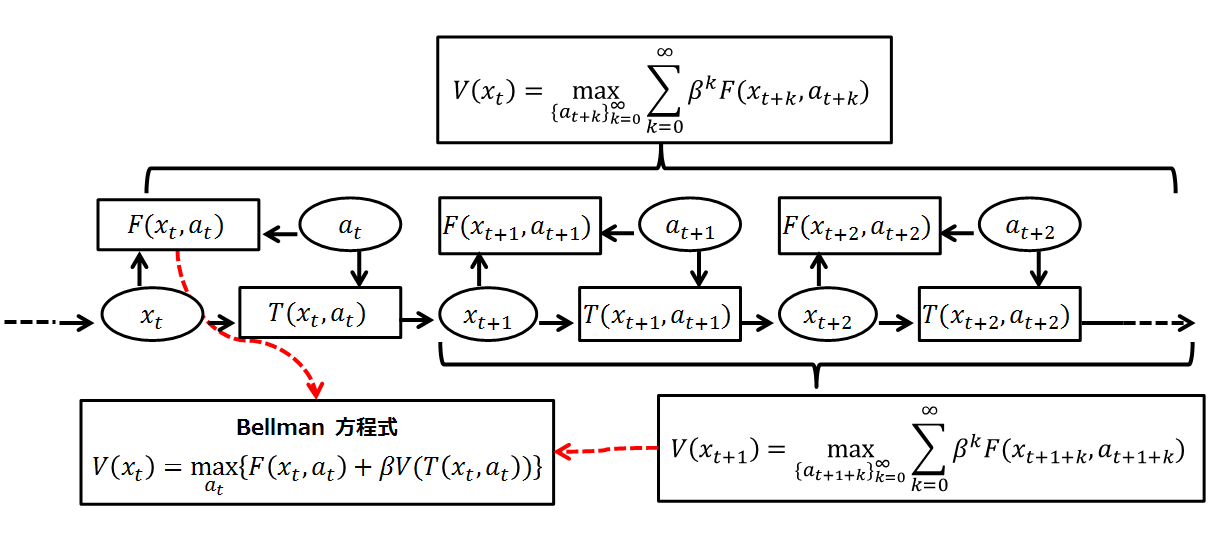
Bellman Equation
A Bellman equation, named after Richard E. Bellman, is a necessary condition for optimality associated with the mathematical optimization method known as dynamic programming. It writes the "value" of a decision problem at a certain point in time in terms of the payoff from some initial choices and the "value" of the remaining decision problem that results from those initial choices. This breaks a dynamic optimization problem into a sequence of simpler subproblems, as Bellman's “principle of optimality" prescribes. The equation applies to algebraic structures with a total ordering; for algebraic structures with a partial ordering, the generic Bellman's equation can be used. The Bellman equation was first applied to engineering control theory and to other topics in applied mathematics, and subsequently became an important tool in economic theory; though the basic concepts of dynamic programming are prefigured in John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern's '' Theory of Games and Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |