|
Richard Arkwright
Sir Richard Arkwright (23 December 1732 – 3 August 1792) was an English inventor and a leading entrepreneur during the early Industrial Revolution. He is credited as the driving force behind the development of the spinning frame, known as the water frame after it was adapted to use water power; and he patented a rotary carding engine to convert raw cotton to 'cotton lap' prior to spinning. He was the first to develop factories housing both mechanised carding and spinning operations. Arkwright's achievement was to combine power, machinery, semi-skilled labour and the new raw material of cotton to create mass-produced yarn. His organisational skills earned him the accolade "father of the modern industrial factory system," notably through the methods developed in his mill at Cromford, Derbyshire (now preserved as part of the Derwent Valley Mills World Heritage Site). Life and family Richard Arkwright was born in Preston, Lancashire, England on 23 December 1732, the young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mather Brown
Mather Brown (baptized October 11, 1761 – May 25, 1831) was an American painter who was born in Boston, Massachusetts and was active in England. Early life Brown was the son of Gawen and Elizabeth (Byles) Brown, and descended from the Rev. Increase Mather on his mother's side. He was taught by his aunt and around 1773 (age 12) became a pupil of Gilbert Stuart. He arrived in London in 1781 to further his training in Benjamin West's studio, entered the Royal Academy schools in 1782 with plans to be a miniature painter, and began to exhibit a year later. Painting career In 1784, he painted two religious paintings for the church of St. Mary’s-in-the-Strand, which led Brown to found a partnership with the painter Daniel Orme for the commercialization of these and other works through exhibition and the sale of engravings. Among these were large paintings of scenes from English history, as well as scenes from Shakespeare's plays. However, despite their success he began to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susannah Arkwright, Mrs Charles Hurt (1762–1835) And Her Daughter Mary Anne, By Joseph Wright Of Derby
''Susannah'' is an opera in two acts by the American composer Carlisle Floyd, who wrote the libretto and music while a member of the piano faculty at Florida State University. Floyd adapted the story from the Apocryphal tale of Susannah and the Elders, though the latter story has a more positive ending. The story focuses on 18-year-old Susannah Polk, an innocent girl who is targeted as a sinner in the small mountain town of New Hope Valley, in the Southern American state of Tennessee. The opera was awarded the New York Music Critics Circle Award for Best New Opera in 1956 and was chosen to represent American music and culture at the World's Fair at Brussels in 1958, with a production (by Frank Corsaro) that featured Phyllis Curtin and Norman Treigle. It received its Metropolitan Opera premiere in 1999, with Renée Fleming singing the title role, Jerry Hadley singing Sam and Samuel Ramey singing Blitch. Ramey also recorded the complete opera with Cheryl Studer as Susannah and Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg , image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg , anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland") , image_map = , map_caption = , capital = Zagreb , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Croatian , languages_type = Writing system , languages = Latin , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2021 , religion = , religion_year = 2021 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Zoran Milanović , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Andrej Plenković , leader_title3 = Speaker of Parliament , leader_name3 = Gordan Jandroković , legislature = Sabor , sovereignty_type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagreb
Zagreb ( , , , ) is the capital and largest city of Croatia. It is in the northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the Medvednica mountain. Zagreb stands near the international border between Croatia and Slovenia at an elevation of approximately above sea level. At the 2021 census, the city had a population of 767,131. The population of the Zagreb urban agglomeration is 1,071,150, approximately a quarter of the total population of Croatia. Zagreb is a city with a rich history dating from Roman times. The oldest settlement in the vicinity of the city was the Roman Andautonia, in today's Ščitarjevo. The historical record of the name "Zagreb" dates from 1134, in reference to the foundation of the settlement at Kaptol in 1094. Zagreb became a free royal city in 1242. In 1851 Janko Kamauf became Zagreb's first mayor. Zagreb has special status as a Croatian administrative division - it comprises a consolidated city-county (but separate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivo Goldstein
Ivo Goldstein (; born 16 March 1958) is a historian, author and ambassador from Croatia. Goldstein is a recipient of the Order of Danica Hrvatska (2007) and the City of Zagreb Award (2005). Biography Education Ivo Goldstein graduated from the Classical Gymnasium in Zagreb and in 1976 he enrolled into undergraduate History studies at the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Zagreb where he graduated in 1979. In 1988, he received his doctorate from the Faculty of Philosophy, University of Belgrade in what was then Yugoslav constituent Socialist Republic of Serbia. His doctoral thesis was entitled ″''Byzantium on the Adriatic from Justinian I to Basil II (6th-9th Century)''″. At three separate occasions he spent a longer study abroad or research periods at the prestigious School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences in Paris (1981/1982), at the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens (1987/1988) and the Imre Kertész Kolleg at the Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
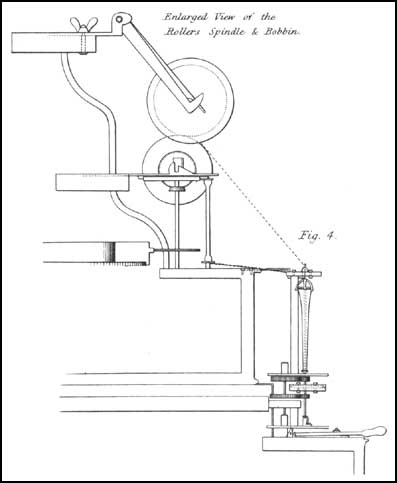
Lewis Paul
Lewis Paul (died 1759) was the original inventor of roller spinning, the basis of the water frame for spinning cotton in a cotton mill. Life and work Lewis Paul was of Huguenot descent. His father was physician to Lord Shaftesbury. He may have begun work on designing a spinning machine for cotton as early as 1729, but probably did not make practical progress until after 1732 when he met John Wyatt, a carpenter then working in Birmingham for a gun barrel forger. Wyatt had designed a machine, probably for cutting files, in which Paul took an interest. Roller spinning was certainly Paul's idea, and Wyatt built a machine (or model) for him. Paul obtained a patent for this on 24 June 1738. He then set about trying to license his machine, though some licences were granted in satisfaction of debts. In 1741, he set up a machine powered by two asses in the Upper Priory in Birmingham, near his house in Old Square. Mills using the roller spinning patent Edward Cave, a publisher, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromford Mill
Cromford Mill is the world's first water-powered cotton spinning mill, developed by Richard Arkwright in 1771 in Cromford, Derbyshire, England. The mill structure is classified as a Grade I listed building. It is now the centrepiece of the Derwent Valley Mills UNESCO World Heritage Site, and is a multi-use visitor centre with shops, galleries, restaurants and cafes. History Following the invention of the flying shuttle for weaving cotton in 1733, the demand for spun cotton increased enormously in England. Machines for carding and spinning had already been developed but were inefficient. Spun cotton was also produced by means of the spinning jenny but was insufficiently strong to form the warp of a fabric, for which it was the practice to use linen thread, producing a type of cloth known as fustian. In 1769, Richard Arkwright patented a water frame to use the extra power of a water mill after he had set up a horse-powered mill in Nottingham. He chose the site at Cromford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkwright House, Preston
Arkwright House is in Stoneygate, Preston, Lancashire, England. The house was built in 1728, and was later expanded and restored. It is notable as the place in which Richard Arkwright and colleagues worked in 1768 to develop the water frame, a machine for spinning yarn. The house is an example of Georgian architecture, and is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* listed building. History The house was built in 1728. It was the home of Revd Ellis Henry, who was the headmaster of the Free Grammar School in Stoneygate, and in 1768 Richard Arkwright was a lodger in the house. Arkwright was obsessed with the idea of creating a machine to spin yarn mechanically. During the time he was living in the house he worked with Thomas Highs and John Kay to develop a machine to do this. Their work was carried out in secrecy, the landlord thinking that they were working on a machine to measure the longitude. However it resulted in a machine kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kay (spinning Frame)
John Kay was an English inventor best known for the development of the spinning frame in 1767, which marked an important stage in the development of textile manufacturing during the Industrial Revolution. Born in Warrington in Lancashire, England, Kay was at least the co-constructor of the first spinning frame, and was a claimant to having been its inventor. He is sometimes confused with the unrelated John Kay from Bury, Lancashire, who had invented the flying shuttle, a weaving machine, some thirty years earlier. John Kay and Thomas Highs In 1763, Kay was working as a clockmaker in Leigh. A neighbour of his, Thomas Highs, was an inventor, and the two collaborated in investigations of machinery for the manufacture of textiles, including the spinning of thread by means of rollers. By 1763 weaving was already automated, but spinning was still done by hand. Lewis Paul had made a machine using mechanical rollers in 1738, but this had not been a commercial success. John Kay and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinning (textiles)
Spinning is a twisting technique to form yarn from fibers. The fiber intended is drawn out, twisted, and wound onto a bobbin. A few popular fibers that are spun into yarn other than cotton, which is the most popular, are viscose (the most common form of rayon), and synthetic polyester. Originally done by hand using a spindle whorl, starting in the 500s AD the spinning wheel became the predominant spinning tool across Asia and Europe. The spinning jenny and spinning mule, invented in the late 1700s, made mechanical spinning far more efficient than spinning by hand, and especially made cotton manufacturing one of the most important industries of the Industrial Revolution. Process The yarn issuing from the drafting rollers passes through a thread-guide, round a traveller that is free to rotate around a ring, and then onto a tube or bobbin, which is carried on to a spindle, the axis of which passes through a center of the ring. The spindle is driven (usually at an angular velocit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Arkwright Junior
Richard Arkwright junior (19 December 1755 – 23 April 1843), the son of Sir Richard Arkwright of Cromford, Derbyshire, was a mills owner, turned banker, investor and financier (creditor) of many successful state and private entreprises of the British Industrial Revolution which his father had helped to catalyse. Among his debtors were Samuel Oldknow of Marple and Mellor, his friend. He was one of ten known British millionaires in 1799. Biography Richard was born in Bolton. His mother, Patience Holt, died when he was only a few months old, and his father, Sir Richard Arkwright, raised him on his own until he was six, then married Margaret Biggens, with whom he had a daughter, Susan and Mary Anne. His father patented the water frame, a roller- spinning machine powered by water. This was the patented prototype and archetype of a revolutionary wave of mass-production machines for cloth manufacture. Recognition followed of the economy of scale of bulk, quality textiles among consu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolton
Bolton (, locally ) is a large town in Greater Manchester in North West England, formerly a part of Lancashire. A former mill town, Bolton has been a production centre for textiles since Flemish weavers settled in the area in the 14th century, introducing a wool and cotton-weaving tradition. The urbanisation and development of the town largely coincided with the introduction of textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution. Bolton was a 19th-century boomtown and, at its zenith in 1929, its 216 cotton mills and 26 bleaching and dyeing works made it one of the largest and most productive centres of cotton spinning in the world. The British cotton industry declined sharply after the First World War and, by the 1980s, cotton manufacture had virtually ceased in Bolton. Close to the West Pennine Moors, Bolton is north-west of Manchester and lies between Manchester, Darwen, Blackburn, Chorley, Bury and Salford. It is surrounded by several neighbouring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_and_her_daughter_Mary_Anne%2C_by_Joseph_Wright_of_Derby.jpg)




%2C_by_George_Philip_Reinagle_PCF3.jpg)
