|
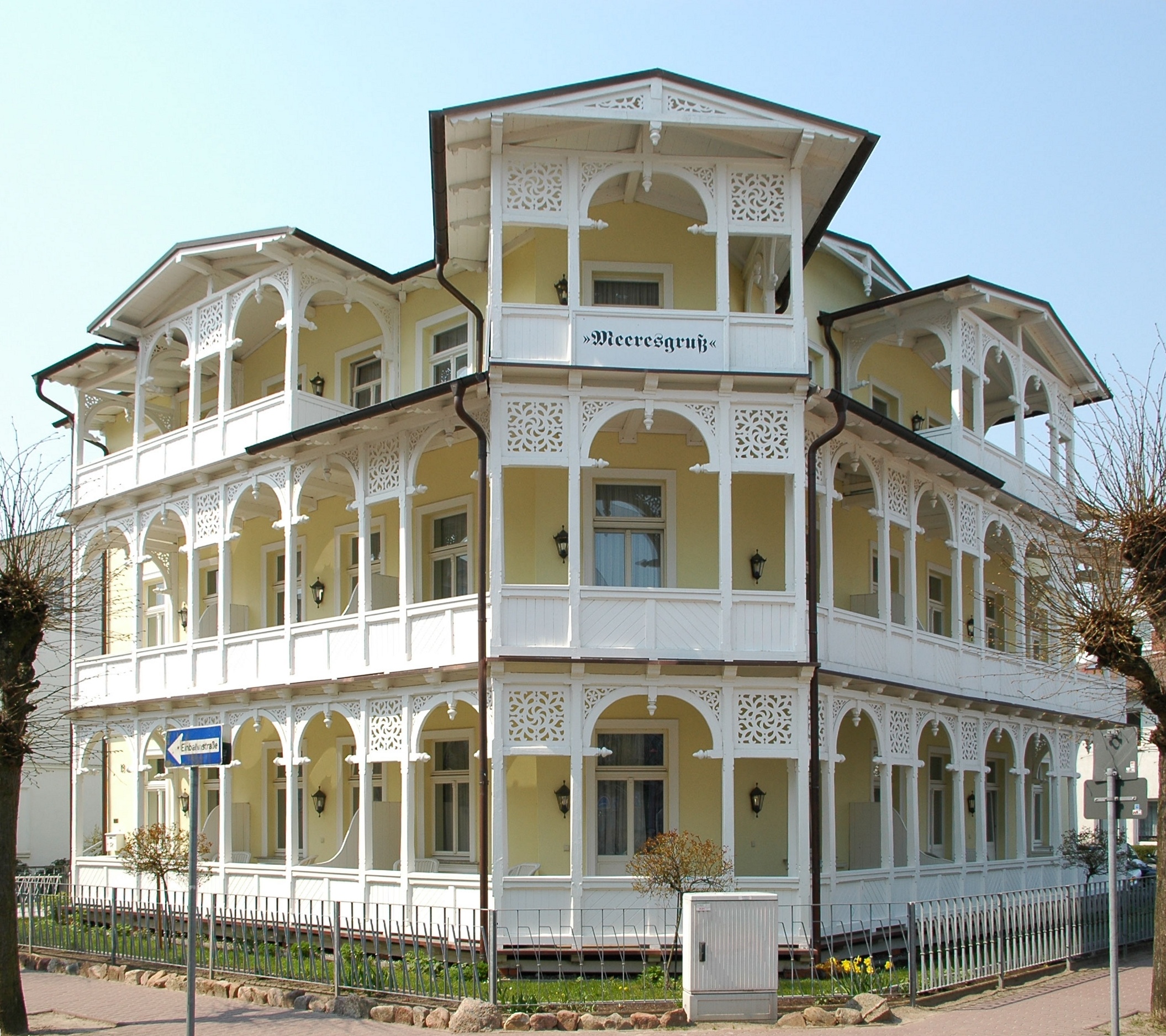
Resort Architecture
Resort architecture (german: Bäderarchitektur) is an architectural style that is especially characteristic of spas and seaside resorts on the German Baltic coast. The style evolved since the foundation of Heiligendamm in 1793, and flourished especially around the year 1870, when resorts were connected to big cities via railway lines. Until today, many buildings on the German coasts are built in the style or feature distinct elements of resort architecture. Single free-standing mansions featuring resort architecture are called ''Bädervilla'' (plural ''Bädervillen''), translating as Resort Mansion or Spa Villa. The architecture of inland health spas in Central Europe (i.e. those away from the coast), in Thuringia, the Czech Republic or Switzerland for instance, is generally referred to as spa architecture (''Kurarchitektur''). History The architectural style of resort architecture was initially developed since the foundation of Heiligendamm in Mecklenburg in 1793, the first con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesthetic concerns. The term gable wall or gable end more commonly refers to the entire wall, including the gable and the wall below it. Some types of roof do not have a gable (for example hip roofs do not). One common type of roof with gables, the gable roof, is named after its prominent gables. A parapet made of a series of curves (Dutch gable) or horizontal steps (crow-stepped gable) may hide the diagonal lines of the roof. Gable ends of more recent buildings are often treated in the same way as the Classic pediment form. But unlike Classical structures, which operate through trabeation, the gable ends of many buildings are actually bearing-wall structures. Gable style is also used in the design of fabric structures, with varying degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
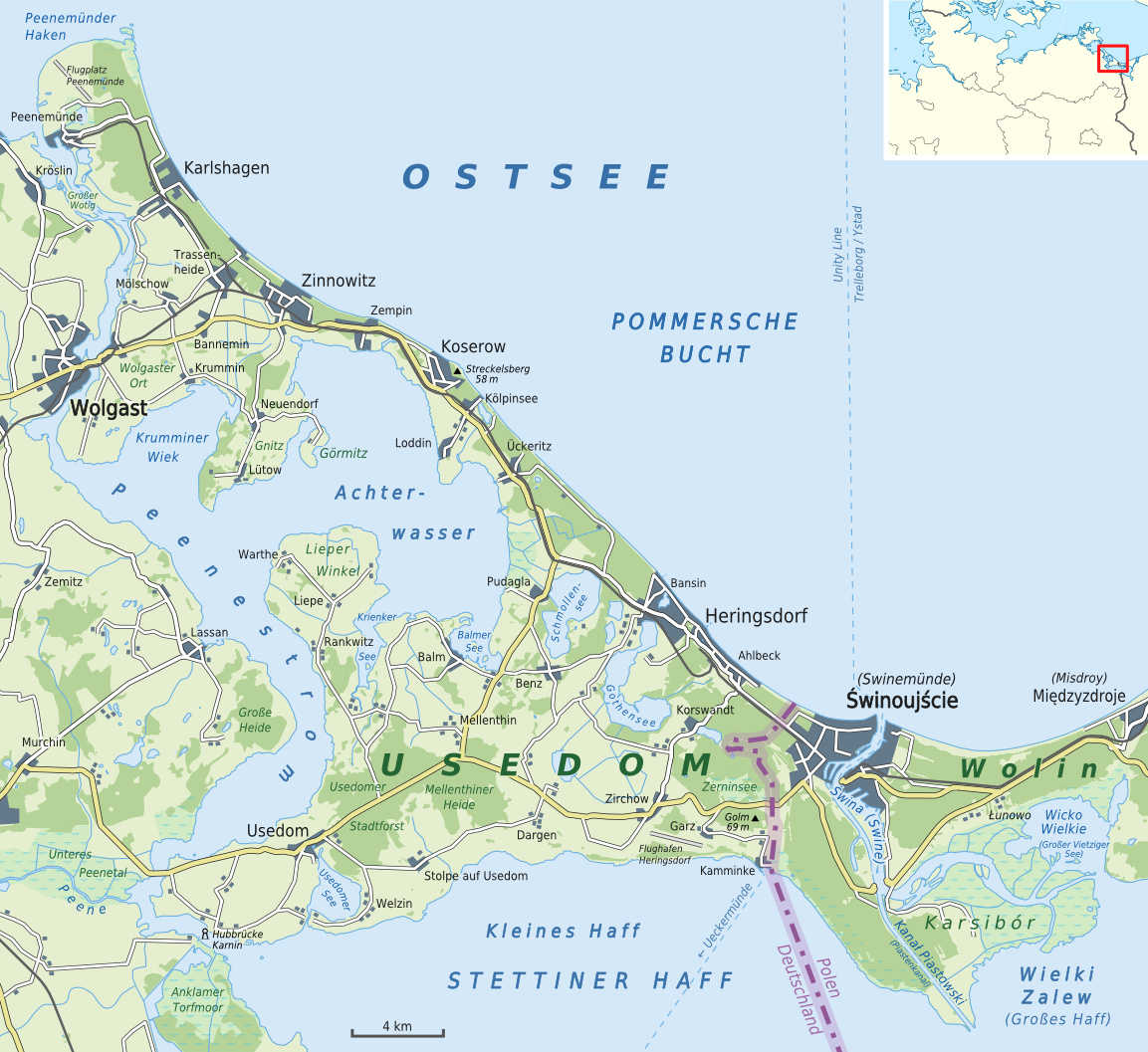
Usedom
Usedom (german: Usedom , pl, Uznam ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea. It is north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary of the Oder river. About 80% of the island belongs to the German district of Vorpommern-Greifswald in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The eastern part and the largest city on the island, Świnoujście, are part of the Polish West Pomeranian Voivodeship. The island's total area is – in the German part and in the Polish part. Its population is 76,500 (German part 31,500; Polish part 45,000). With an annual average of 1,906 hours of sunshine, Usedom is the sunniest region of both Germany and Poland, and it is also one of the sunniest islands in the Baltic Sea, hence its nickname "Sun Island" (german: Sonneninsel, pl, Wyspa Słońca). The island has been a tourist destination since the Gründerzeit in the 19th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heringsdorf
Heringsdorf is a semi-urban municipality and a popular seaside resort on Usedom Island in Western Pomerania, Germany. It is also known by the name Kaiserbad ('' en, Imperial Spa''). The municipality was formed in January 2005 out of the former municipalities of Heringsdorf, Ahlbeck and Bansin. Until January 2006, the municipality was called ''Dreikaiserbäder'', literally meaning ''Three Imperial Spas'', a reference to several vacation visits of the German emperor Wilhelm II until 1918. For the same reason, the fine sandy beach stretching about 12 km (7.5 miles) from Bansin over Heringsdorf to Ahlbeck and Swinemünde (nowadays a Polish spa), is also called ''Kaiserstrand'' (Imperial Beach). The continuous Baltic Sea beach of Usedom Island has an overall length of exactly 40 km (25 miles) and an average width of 40 m (130 feet). Tourism is the dominant economical sector of the Imperial Spas, with an increasing number of hotels and vacation homes every year. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Doberan
Bad Doberan () is a town in the district of Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Bad Doberan. In 2012, its population was 11,427. Geography Bad Doberan is situated just west of Rostock's city centre and is therefore part of one of the most developed regions in the north-eastern part of Germany. The town nestles between beautiful beech tree forests just 6 km from the Baltic Sea and is one of the earliest German settlements in Mecklenburg. Today the town is a very popular bathing resort, thanks to Heiligendamm, a district of Bad Doberan situated directly at the cliff line of the Baltic. Historically, Doberan used to be the summer residence for the Mecklenburg Dukes who resided in Schwerin, and for their entourage. Name The name Doberan, originally ''Dobran'', is a place name that probably derives from a Slavic Old Polabian personal name, meaning "good" (''dobry''). According to legend, the name Doberan originated when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göhren (Rügen)
Göhren may refer to the following places: ;Germany * Göhren (Tramm), a village in the municipality Tramm in the district Ludwigslust-Parchim, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern * Göhren, Rügen, a municipality in the district Vorpommern-Rügen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern * Göhren, Thuringia, a municipality in the district Altenburger Land, Thuringia ;Czech Republic * Klíny, a village in Most District ;See also * , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker {{geodis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binz
Binz is the largest seaside resort on the German island of Rügen. It is situated between the bay of Prorer Wiek and the ''Schmachter See'' (a lake) in the southeast of the island. To the north of Binz stretches the Schmale Heide (the "narrow heath"), a tongue of land which joins the Muttland region of Rügen to the Jasmund peninsula. The land to the south and east of Binz is hilly, reaching a height of over 100 metres above sea level. Binz is known for its well-kept historical resort architecture and natural scenery, close to the Jasmund National Park and its chalk cliffs. Geography Location Binz lies on the eastern coast of the island of Rügen between the bay of Prorer Wiek and the lake of Schmachter See. North of Binz is the Schmale Heide, a neck of land that links the Muttland – Rügen's central region – with the peninsula of Jasmund. East and south of the municipality, the land is rolling, in the southeast, in the Granitz, the land climbs to just over . The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sellin
Sellin is a municipality on the Island of Rügen, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. History First mentions of Sellin date to 1295. From 1880 on, the town gained importance as a Baltic Sea spa town. After the '' Wende'' in 1989, the building stock in the village was extensively renovated. In 1992, Sellin Pier was rebuilt and was officially opened on 2 April 1998. Culture and sights ''Wilhelmstraße'', with its houses from the resort architecture period (turn of the 19th and 20th century), runs up to the steep coast, up to 30 metres high - where there is a steep flight of steps or a lift to Sellin Pier or the promenade on the South Beach (''Südstrand''). Sellin has the longest pier on Rügen: 394 metres. Since 1991 the historic centre has been thoroughly renovated as part of a programme of urban development. Other sights are the ''Galerie Hartwich'' in the old fire station (''Feuerwehrhaus''), the Amber Museum with its associated workshop and the ''Gnadenkirche''. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where it is linked to the mainland by road and railway via the Rügen Bridge and Causeway, two routes crossing the two-kilometre-wide Strelasund, a sound of the Baltic Sea. Rügen has a maximum length of (from north to south), a maximum width of in the south and an area of . The coast is characterized by numerous sandy beaches, lagoons () and open bays (), as well as projecting peninsulas and headlands. In June 2011, UNESCO awarded the status of a World Heritage Site to the Jasmund National Park, famous for its vast stands of beeches and chalk cliffs like King's Chair, the main landmark of Rügen island. The island of Rügen is part of the district of Vorpommern-Rügen, with its county seat in Stralsund. The towns on Rügen are: Berg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern Style (British Art Nouveau style), Modern Style in English. It was popular between 1890 and 1910 during the Belle Époque period, and was a reaction against the academic art, eclecticism and historicism of 19th century architecture and decoration. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and flowers. Other characteristics of Art Nouveau were a sense of dynamism and movement, often given by asymmetry or whiplash lines, and the use of modern materials, particularly iron, glass, ceramics and later concrete, to create unusual forms and larger open spaces.Sembach, Klaus-Jürgen, ''L'Art Nouveau'' (2013), pp. 8–30 One major objective of Art Nouveau was to break down the traditional distinction between fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classicism
Classicism, in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for a classical period, classical antiquity in the Western tradition, as setting standards for taste which the classicists seek to emulate. In its purest form, classicism is an aesthetic attitude dependent on principles based in the culture, art and literature of ancient Greece and Rome, with the emphasis on form, simplicity, proportion, clarity of structure, perfection, restrained emotion, as well as explicit appeal to the intellect. The art of classicism typically seeks to be formal and restrained: of the ''Discobolus'' Sir Kenneth Clark observed, "if we object to his restraint and compression we are simply objecting to the classicism of classic art. A violent emphasis or a sudden acceleration of rhythmic movement would have destroyed those qualities of balance and completeness through which it retained until the present century its position of authority in the restricted repertoire of visual images." Classicism, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |