|
Regular Satellite
In astronomy, a regular moon is a natural satellite following a relatively close and prograde orbit with little orbital inclination or eccentricity. They are believed to have formed in orbit about their primary, as opposed to irregular moons, which were captured. There are at least 57 regular satellites of the eight planets: one at Earth, eight at Jupiter, 23 named regular moons at Saturn (not counting hundreds or thousands of moonlets), 18 known at Uranus, and 7 small regular moons at Neptune (Neptune's largest moon Triton appears to have been captured). It is thought that Pluto's five moons and Haumea's two were formed in orbit about those dwarf planets out of debris created in giant collisions. Most regular moons are known to be tidally locked to their parent planet; the one known exception is Saturn's Hyperion, which exhibits chaotic rotation. See also *Irregular moon *Inner moon In astronomy, an inner moon or inner natural satellite is a natural satellite follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'', a derivation from the Moon of Earth. In the Solar System, there are six planetary satellite systems containing 209 known natural satellites altogether. Seven objects commonly considered dwarf planets by astronomers are also known to have natural satellites: , Pluto, Haumea, , Makemake, , and Eris. , there are 442 other minor planets known to have natural satellites. A planet usually has at least around 10,000 times the mass of any natural satellites that orbit it, with a correspondingly much larger diameter. The Earth–Moon system is a unique exception in the Solar System; at 3,474 kilometres (2,158 miles) across, the Moon is 0.273 times the diameter of Earth and about of its mass. The next largest ratios are the Neptune– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
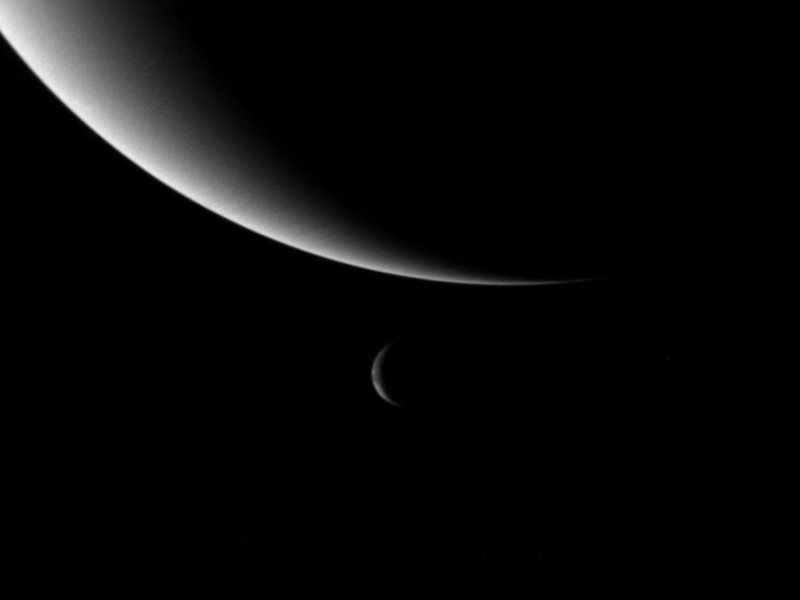
Moons Of Neptune
The planet Neptune has 14 known moons, which are named for minor water deities in Greek mythology. By far the largest of them is Triton, discovered by William Lassell on October 10, 1846, 17 days after the discovery of Neptune itself; over a century passed before the discovery of the second natural satellite, Nereid. Neptune's outermost moon Neso, which has an orbital period of about 26 Julian years, orbits farther from its planet than any other moon in the Solar System. Triton is unique among moons of planetary mass in that its orbit is retrograde to Neptune's rotation and inclined relative to Neptune's equator, which suggests that it did not form in orbit around Neptune but was instead gravitationally captured by it. The next-largest satellite in the Solar System suspected to be captured, Saturn's moon Phoebe, has only 0.03% of Triton's mass. The capture of Triton, probably occurring some time after Neptune formed a satellite system, was a catastrophic event for Neptune's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Moon
In astronomy, an irregular moon, irregular satellite or irregular natural satellite is a natural satellite following a distant, inclined, and often eccentric and retrograde orbit. They have been captured by their parent planet, unlike regular satellites, which formed in orbit around them. Irregular moons have a stable orbit, unlike temporary satellites which often have similarly irregular orbits but will eventually depart. The term does not refer to shape as Triton is a round moon, but is considered irregular due to its orbit. As of December 2022, 149 irregular moons are known, orbiting all four of the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune). The largest of each planet are Himalia of Jupiter, Phoebe of Saturn, Sycorax of Uranus, and Triton of Neptune. It is currently thought that the irregular satellites were captured from heliocentric orbits near their current locations, shortly after the formation of their parent planet. An alternative theory, that they or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperion (moon)
Hyperion , also known as Saturn VII, is a moon of Saturn discovered by William Cranch Bond, his son George Phillips Bond and William Lassell in 1848. It is distinguished by its irregular shape, its chaotic rotation, and its unexplained sponge-like appearance. It was the first non- round moon to be discovered. Name The moon is named after Hyperion, the Titan god of watchfulness and observation – the elder brother of Cronus, the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Saturn. It is also designated ''Saturn VII''. The adjectival form of the name is ''Hyperionian''. Hyperion's discovery came shortly after John Herschel had suggested names for the seven previously known satellites of Saturn in his 1847 publication ''Results of Astronomical Observations made at the Cape of Good Hope''. William Lassell, who saw Hyperion two days after William Bond, had already endorsed Herschel's naming scheme and suggested the name Hyperion in accordance with it. He also beat Bond to pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Locking
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change in its rotation rate over the course of a complete orbit. In the case where a tidally locked body possesses synchronous rotation, the object takes just as long to rotate around its own axis as it does to revolve around its partner. For example, the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth, although there is some variability because the Moon's orbit is not perfectly circular. Usually, only the satellite is tidally locked to the larger body. However, if both the difference in mass between the two bodies and the distance between them are relatively small, each may be tidally locked to the other; this is the case for Pluto and Charon. Alternative names for the tidal locking process are gravitational locking, captured rotation, and spin–orbit locking. The effect arises between two bodies when their gravitational interaction s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collisional Family
In astronomy, a collisional family is a group of objects that are thought to have a common origin in an impact (collision). They have similar compositions and most share similar orbital elements. Numerous asteroid families, most of the irregular satellites of the outer planets, the Earth and the Moon and the dwarf planets Pluto, Eris and Haumea and its satellites could be included among the known or putative collisional families. Known or suspected collisional families include numerous asteroid families, most of the irregular moons of the outer planets, the Earth and the Moon, and the dwarf planets Pluto, Eris, and Haumea , discoverer = , discovered = , earliest_precovery_date = March 22, 1955 , mpc_name = (136108) Haumea , pronounced = , adjectives = Haumean , note = yes , alt_names = , named_after = Haumea , mp_category = , orbit_ref = , epoc ... and their moons. See also * Satellite collision * Origin of the Moon References Minor planet groups and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to planetary geologists is that they may be geologically active bodies, an expectation that was borne out in 2015 by the ''Dawn'' mission to and the '' New Horizons'' mission to Pluto. Astronomers are in general agreement that at least the nine largest candidates are dwarf planets: Pluto, , , , , , , , and . Of these and the tenth-largest candidate , all but Sedna have either been visited by spacecraft (Pluto and Ceres) or have at least one known moon (Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Salacia), which allows their masses and thus an estimate of their densities to be determined. Mass and density in turn can be fit into geophysical models in an attempt to determine the nature of these worlds. Some astronomers include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moons Of Haumea
The Solar System#Trans-Neptunian region, outer Solar System planetoid Haumea has two known Natural satellite, moons, Hiʻiaka (moon), Hiʻiaka and Namaka (moon), Namaka, named after Hawaiian mythology, Hawaiian goddesses. These small moons were discovered in 2005, from observations of Haumea made at the large telescopes of the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii. Haumea's moons are unusual in a number of ways. They are thought to be part of Haumea family, its extended collisional family, which formed billions of years ago from icy debris after a large impact disrupted Haumea's volatiles, ice Mantle (geology), mantle. Hiʻiaka, the larger, outermost moon, has large amounts of pure water ice on its surface, which is rare among Kuiper belt objects. Namaka, about one tenth the mass, has an orbit with surprising dynamics: it is unusually Orbital eccentricity, eccentric and appears to be greatly influenced by the larger satellite. History Two small natural satellite, satellites were dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
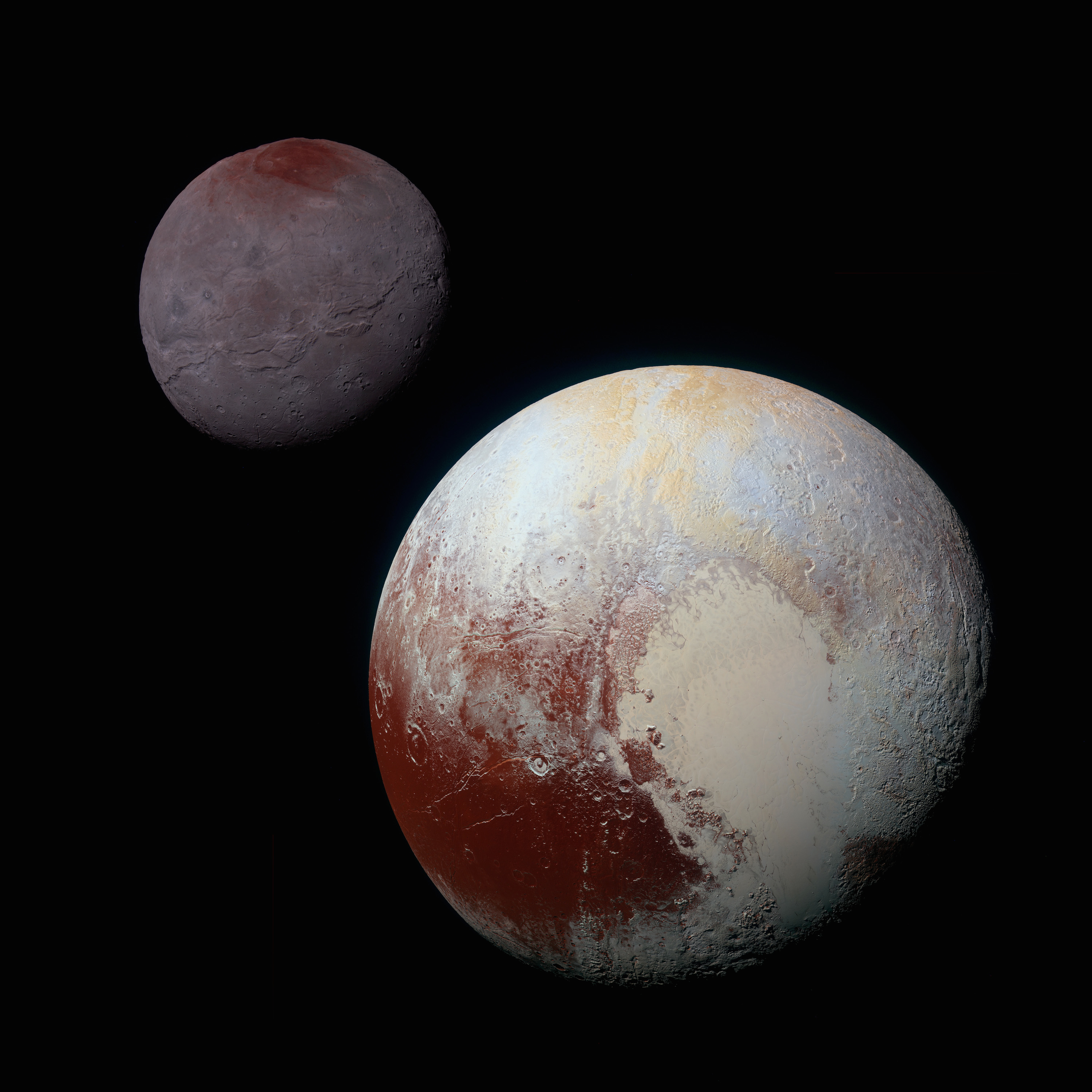
Moons Of Pluto
The dwarf planet Pluto has five natural satellites. In order of distance from Pluto, they are Charon, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. Charon, the largest, is mutually tidally locked with Pluto, and is massive enough that Pluto–Charon is sometimes considered a double dwarf planet. History The innermost and largest moon, Charon, was discovered by James Christy on 22 June 1978, nearly half a century after Pluto was discovered. This led to a substantial revision in estimates of Pluto's size, which had previously assumed that the observed mass and reflected light of the system were all attributable to Pluto alone. Two additional moons were imaged by astronomers of the Pluto Companion Search Team preparing for the ''New Horizons'' mission and working with the Hubble Space Telescope on 15 May 2005, which received the provisional designations S/2005 P 1 and S/2005 P 2. The International Astronomical Union officially named these moons Nix (or Pluto II, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triton (moon)
Triton is the largest natural satellite of the planet Neptune, and was the first Neptunian moon to be discovered, on October 10, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, an orbit in the direction opposite to its planet's rotation. Because of its retrograde orbit and composition similar to Pluto, Triton is thought to have been a dwarf planet, captured from the Kuiper belt. At in diameter, it is the seventh-largest moon in the Solar System, the only satellite of Neptune massive enough to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, the second-largest planetary moon in relation to its primary (after Earth's Moon), and larger than Pluto. Triton is one of the few moons in the Solar System known to be geologically active (the others being Jupiter's Io and Europa, and Saturn's Enceladus and Titan). As a consequence, its surface is relatively young, with few obvious impact craters. Intricate cryovolcanic and tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
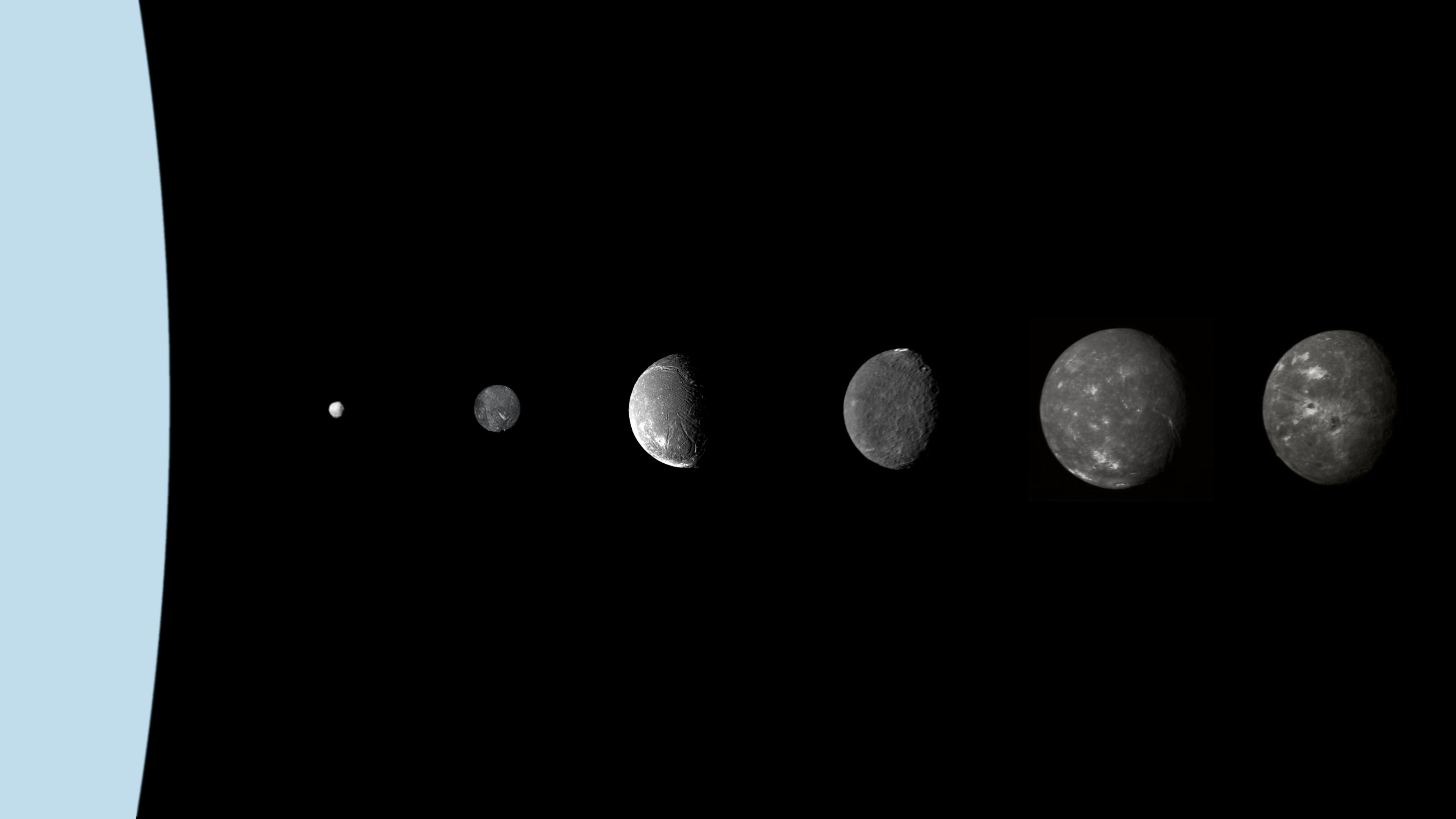
Moons Of Uranus
Uranus, the seventh planet of the Solar System, has 27 known moons, most of which are named after characters that appear in, or are mentioned in, the works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope. Uranus's moons are divided into three groups: thirteen inner moons, five major moons, and nine irregular moons. The inner and major moons all have prograde orbits, while orbits of the irregulars are mostly retrograde. The inner moons are small dark bodies that share common properties and origins with Uranus's rings. The five major moons are ellipsoidal, indicating that they reached hydrostatic equilibrium at some point in their past (and may still be in equilibrium), and four of them show signs of internally driven processes such as canyon formation and volcanism on their surfaces. The largest of these five, Titania, is 1,578 km in diameter and the eighth-largest moon in the Solar System, about one-twentieth the mass of the Earth's Moon. The orbits of the regular moons are nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prograde Orbit
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or nutation of an object's rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also refer to an object other than the primary if so described. The direction of rotation is determined by an inertial frame of reference, such as distant fixed stars. In the Solar System, the orbits around the Sun of all planets and most other objects, except many comets, are prograde. They orbit around the Sun in the same direction as the sun rotates about its axis, which is counterclockwise when observed from above the Sun's north pole. Except for Venus and Uranus, planetary rotations around their axes are also prograde. Most natural satellites have prograde orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |