|
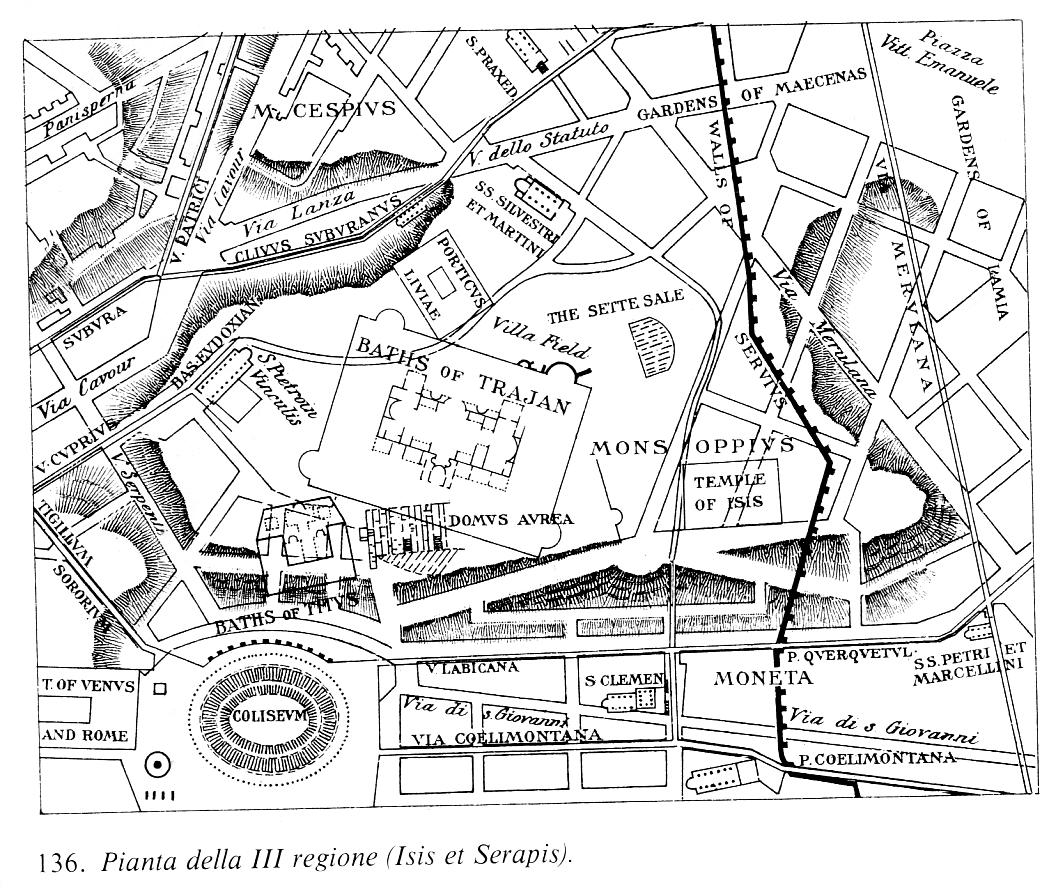
Regio III Isis Et Serapis
The Regio III Isis et Serapis was the third 14 regions of Augustan Rome, regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio III took its name from the double sanctuary of Isis and Serapis, in the area of the Via Praenestina, containing the valley that was to be the future site of the Colosseum, and parts of the Oppian Hill, Oppian and Esquiline Hill, Esquiline hills. Geographic extent and important features Centred on the Oppian Hill, Regio III was bordered to its south east by the Via Tusculana, to the north by the Clivus Suburanus, and to the west by the Via Labicana. A measurement taken at the end of the 4th century recorded that the perimeter of the region was 12,350 Roman feet (approximately 3.65km). Perhaps the most noticeable structure that resided within Regio III sat in the valley between the Caelian Hill, Caelian and Oppian Hills. This was the Flavian Amphitheatre, today referred to as the Colosseum. The most important ancient festival held there was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip The Arab
Philip the Arab ( la, Marcus Julius Philippus "Arabs"; 204 – September 249) was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. He was born in Aurantis, Arabia, in a city situated in modern-day Syria. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Philip, who had been Praetorian prefect, achieved power. He quickly negotiated peace with the Persian Sassanid Empire and returned to Rome to be confirmed by the Senate. During his reign, the city of Rome celebrated its millennium. Philip was betrayed and killed at the Battle of Verona in September 249 following a rebellion led by his successor, Gaius Messius Quintus Decius. Philip's reign of five years was uncommonly stable in a turbulent third century. During the late 3rd century and into the 4th, it was held by some churchmen that Philip had been the first Christian emperor; he was described as such in Jerome's '' Chronicon'' (''Chronicle''), which was well known during the Middle Ages, in Orosius' highly popular ''Historia Adversus Pagano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porticus Of Livia
The Porticus of Livia (Latin: porticus Liviae) was a portico in Regio III Isis et Serapis of ancient Rome. It was built by Augustus in honour of his wife Livia Drusilla and is located on the Esquiline Hill. Although little of its structure survives now, it was one of the most prominent porticos in the ancient city. The so-called Ara Concordia was located either in or near to the portico. Location The portico is located in Regio III of ancient Rome, which is named for a sanctuary of Isis in the area, and includes parts of the Esquiline and Oppian hills. The structure itself was found between the Via delle Sette Sale and the Via in Selci (the latter was called the "Clivus Suburanus" in ancient times). The structure was built on the estate of a rich freedman named Publius Vedius Pollio, who left his house and land to Augustus upon his death. His large estate was in the midst of the fairly crowded Subura neighbourhood, and the new leisure space was probably welcomed by the resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velarium
A ("curtain") was a type of awning used in Roman times. It stretched over the whole of the , the seating area in amphitheaters to protect spectators from the sun. Precisely how the awning was supported is a matter of conjecture.Suetonius, '' Life of Caligula'' 26Text. History Retractable awnings were relatively common throughout the Roman Empire, including on the wooden amphitheater that preceded the Colosseum. The Colosseum The Colosseum being the biggest amphitheater of Roman times, the that covered it was the biggest that ever was as well. It provided shade from the sun for up to one third of the arena. The also created a ventilation updraft, creating circulation and a cool breeze. It is believed that sailors from the Misenum fleet, with their background in sailmaking and rigging were employed to build, maintain and operate the . In modern times The Puy du Fou theme park An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misenum
Miseno is one of the ''frazioni'' of the municipality of Bacoli in the Italian Province of Naples. Known in ancient Roman times as Misenum, it is the site of a great Roman port. Geography Nearby Cape Miseno marks the northwestern end of the Bay of Naples. History According to mythology, Misenum was named after Misenus, a companion of Hector and trumpeter to Aeneas. Misenus is supposed to have drowned near here after a trumpet competition with the sea-god Triton, as recounted in Virgil's Aeneid. In 39 BC, Misenum was the site where a short-lived pact was made between Octavian (heir of Julius Caesar, who later became the emperor Augustus), and his rival Sextus Pompeius. Misenum was first established as a naval base ('' Portus Julius'') during the civil wars in 27 BC by Marcus Agrippa, the right-hand man of the emperor Augustus. It was then developed into the largest Roman port for the ''Classis Misenensis'', the most important fleet. With its gorgeous natural setting c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludus Dacicus
The ''Ludus Dacicus'' or The Dacian Gladiatorial Training School was one of the four gladiator training schools (''ludi'') in Ancient Rome. It was founded by Domitian (81–96), completed by Trajan (98–117), and was used to train gladiators drawn from among the Dacian prisoners taken by both emperors in their Dacian Wars. It was located east of the Colosseum, on the slopes of the Caelian Hill. History Dacian prisoners were taken many times by the Romans and very often they were forced to fight in the arenas. Dio Cassius mentions that around 31 BC, after the Battle of Actium, where the Dacian king Dicomes provided help to Mark Antony,Plutarch; Antonius, 63 Augustus took the Dacian prisoners and made them fight in the arena as gladiators, against Suebi captives, a spectacle that lasted many days with no interruption. See also * Ludus Magnus * Falx * Dacian warfare The history of Dacian warfare spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 2nd century AD in the region defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed. Domitian had a minor and largely ceremonial role during the reigns of his father and brother. After the death of his brother, Domitian was declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard. His 15-year reign was the longest since that of Tiberius. As emperor, Domitian strengthened the economy by revaluing the Roman coinage, expanded the border defenses of the empire, and initiated a massive building program to restore the damaged city of Rome. Significant wars were fought in Britain, where his general Agricola attempted to conquer Caledonia (Scotland), and in Dacia, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their lives and their legal and social standing by appearing in the arena. Most were despised as slaves, schooled under harsh conditions, socially marginalized, and segregated even in death. Irrespective of their origin, gladiators offered spectators an example of Rome's martial ethics and, in fighting or dying well, they could inspire admiration and popular acclaim. They were celebrated in high and low art, and their value as entertainers was commemorated in precious and commonplace objects throughout the Roman world. The origin of gladiatorial combat is open to debate. There is evidence of it in funeral rites during the Punic Wars of the 3rd century BC, and thereafter it rapidly became an essential fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludus Magnus
The Ludus Magnus (also known as the Great Gladiatorial Training School) was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian (r. 81–96 C.E.) in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects undertaken by him such as three other gladiatorial schools across the Roman Empire. The training school is situated directly east of the Colosseum in the valley between the Esquiline and the Caelian hills, an area already occupied by Republican and Augustan structures. While there are remains that are visible today, they belong to a reconstruction that took place under the emperor Trajan (r. 98–117) where the Ludus plane was raised by about 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in). The Ludus Magnus was essentially a gladiatorial arena where gladiators from across the Roman Empire would live, eat, and practice while undergoing gladiatorial training in preparation for fighting at the gladiatorial games held at the Colosseum. Etymology Location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domus Aurea
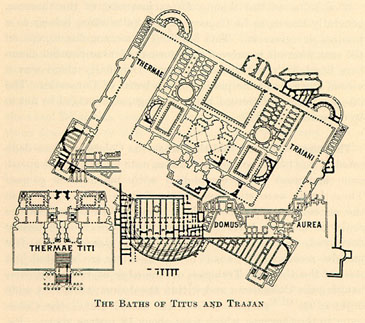
The Domus Aurea (Latin, "Golden House") was a vast landscaped complex built by the Emperor Nero largely on the Oppian Hill in the heart of ancient Rome after the great fire in 64 AD had destroyed a large part of the city.Roth (1993) It replaced and extended his Domus Transitoria that he had built as his first palace complex on the site. History The Domus Aurea was probably never completed. Otho and possibly Titus allotted money to finish at least the structure on the Oppian Hill; this continued to be inhabited, notably by emperor Vitellius in 69 but only after falling ill, until it was destroyed in a fire under Trajan in 104. A symbol of decadence that caused severe embarrassment to Nero's successors, the Domus Aurea was stripped of its marble, jewels, and ivory within a decade. Although the Oppian villa continued to be inhabited for some years, soon after Nero's death other parts of the palace and grounds, encompassing 2.6 km2 (c. 1 mi2), were filled with earth a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68. He was Adoption in Ancient Rome, adopted by the Roman emperor Claudius at the age of 13 and succeeded him on the throne. Nero was popular with the members of his Praetorian Guard and lower-class commoners in Rome and its provinces, but he was deeply resented by the Roman aristocracy. Most contemporary sources describe him as tyrannical, self-indulgent, and debauched. After being declared a public enemy by the Roman Senate, he committed suicide at age 30. Nero was born at Antium in AD 37, the son of Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (father of Nero), Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus and Agrippina the Younger, a great-granddaughter of the emperor Augustus. When Nero was two years old, his father died. His mother married the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |