|
Rate Of Climb
In aeronautics, the rate of climb (RoC) is an aircraft's vertical speed, that is the positive or negative rate of altitude change with respect to time. In most ICAO member countries, even in otherwise metric countries, this is usually expressed in feet per minute (ft/min); elsewhere, it is commonly expressed in metres per second (m/s). The RoC in an aircraft is indicated with a vertical speed indicator (VSI) or instantaneous vertical speed indicator (IVSI). The temporal rate of decrease in altitude is referred to as the rate of descent (RoD) or sink rate. A negative rate of climb corresponds to a positive rate of descent: RoD = −RoC. Speed and rate of climb There are a number of designated airspeeds relating to optimum rates of ascent, the two most important of these are ''VX'' and ''VY''. ''VX'' is the indicated forward airspeed for best angle of climb. This is the speed at which an aircraft gains the most altitude in a given horizontal , typically used to avoid a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Rate
In mathematics, a rate is the ratio between two related quantities in different units. If the denominator of the ratio is expressed as a single unit of one of these quantities, and if it is assumed that this quantity can be changed systematically (i.e., is an independent variable), then the numerator of the ratio expresses the corresponding ''rate of change'' in the other (dependent) variable. One common type of rate is "per unit of time", such as speed, heart rate and flux. Ratios that have a non-time denominator include exchange rates, literacy rates, and electric field (in volts per meter). In describing the units of a rate, the word "per" is used to separate the units of the two measurements used to calculate the rate (for example a heart rate is expressed "beats per minute"). A rate defined using two numbers of the same units (such as tax rates) or counts (such as literacy rate) will result in a dimensionless quantity, which can be expressed as a percentage (for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descent (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, a descent is any time period during air travel where an aircraft decreases altitude, and is the opposite of an ''ascent'' or '' climb''. Descents are part of normal procedures, but also occur during emergencies, such as rapid or explosive decompression, forcing an emergency descent to below and preferably below , respectively the maximum temporary safe altitude for an unpressurized aircraft and the maximum safe altitude for extended duration. An example of explosive decompression is Aloha Airlines Flight 243. Involuntary descent might occur from a decrease in power, decreased lift (wing icing), an increase in drag, or flying in an air mass moving downward, such as a terrain induced downdraft, near a thunderstorm, in a downburst, or microburst. Normal descents Intentional descents might be undertaken to land, avoid other air traffic or poor flight conditions (turbulence, icing conditions, or bad weather), clouds (particularly under visual flight rules), to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
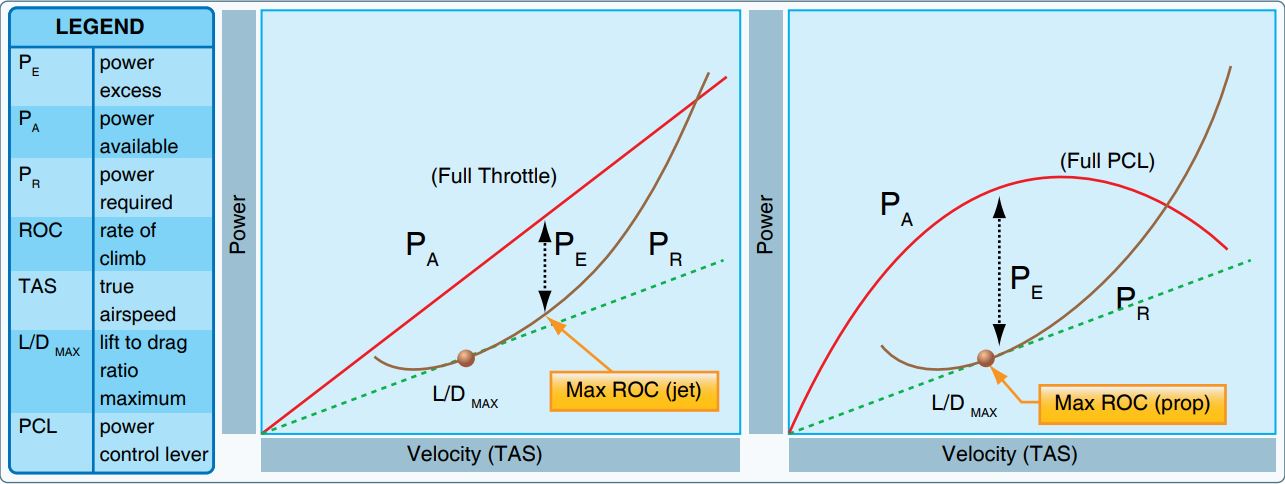
Climb (aeronautics)
An Iberia Airbus A321 on the climbout from London Heathrow Airport ">London_Heathrow_Airport.html" ;"title="Airbus A321 on the climbout from London Heathrow Airport">Airbus A321 on the climbout from London Heathrow Airport In aviation, a climb or ascent is the operation of increasing the altitude of an aircraft. It is also the logical phase of a typical flight (the ''climb phase'' or ''climbout'') following [ akeoff and preceding the cruise. During the climb phase there is an increase in altitude to a predetermined level. The opposite of a climb is a '' descent''. Climb operation A steady climb is carried out by using excess thrust, the amount by which the thrust from the power plant exceeds the drag on the aircraft. L. J. Clancy (1975): ''Aerodynamics''. Pitman Publishing Limited, London, The aircraft will climb steadily until the excess thrust falls to zero. Excess thrust might fall to zero as a result of the pilot's deliberate action in control of the output of the engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. ICAO headquarters are located in the '' Quartier International'' of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation. ICAO defines the protocols for air accident investigation that are followed by transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Chicago Convention on International Civil Aviation. The Air Navigation Commission (ANC) is the technical body within ICAO. The commission is composed of 19 commissioners, nominated by the ICAO's contracting states and ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicated Airspeed
Indicated airspeed (IAS) is the airspeed of an aircraft as measured by its pitot-static system and displayed by the airspeed indicator (ASI). This is the pilots' primary airspeed reference. This value is not corrected for installation error, instrument error, or the actual encountered air density, being instead calibrated to always reflect the adiabatic compressible flow of the International Standard Atmosphere at sea level. It uses the difference between total pressure and static pressure, provided by the system, to either mechanically or electronically measure dynamic pressure. The dynamic pressure includes terms for both density and airspeed. Since the airspeed indicator cannot know the density, it is by design calibrated to assume the sea level standard atmospheric density when calculating airspeed. Since the actual density will vary considerably from this assumed value as the aircraft changes altitude, IAS varies considerably from true airspeed (TAS), the relative vel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cessna 172
The Cessna 172 Skyhawk is an American four-seat, single-engine, high wing, fixed-wing aircraft made by the Cessna Aircraft Company."Cessna Skyhawk" (2013), . Retrieved 2013-04-12. First flown in 1955, more 172s have been built than any other aircraft. It was developed from the 1948 but with |
Absolute Ceiling
With respect to aircraft performance, a ceiling is the maximum density altitude an aircraft can reach under a set of conditions, as determined by its flight envelope. Service ceiling Service ceiling is where the rate of climb drops below a prescribed value. The service ceiling is the maximum usable altitude of an aircraft. Specifically, it is the density altitude at which flying in a clean configuration, at the best rate of climb airspeed for that altitude and with all engines operating and producing maximum continuous power, will produce a given rate of climb. A typical value might be climb, or on the order of climb for jet aircraft. The one-engine inoperative (OEI) service ceiling of a twin-engine, fixed-wing aircraft is the density altitude at which flying in a clean configuration, at the best rate of climb airspeed for that altitude with one engine producing maximum continuous power and the other engine shut down and feathered, will produce a given rate of climb, usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excess Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's third law. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction, the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction to be applied to that system. The force applied on a surface in a direction perpendicular or normal to the surface is also called thrust. Force, and thus thrust, is measured using the International System of Units (SI) in newtons (symbol: N), and represents the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. In mechanical engineering, force orthogonal to the main load (such as in parallel helical gears) is referred to as static thrust. Examples A fixed-wing aircraft propulsion system generates forward thrust when air is pushed in the direction opposite to flight. This can be done by different means such as the spinning blades of a propeller, the propelling jet of a jet engine, or by ejecting hot gases from a rocke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamic Drag
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Climb
In aerodynamics, climb gradient is the ratio between distance travelled over the ground and altitude gained, and is expressed as a percentage. The angle of climb can be defined as the angle between a horizontal plane representing the Earth's surface and the actual flight path followed by the aircraft during its ascent. The speed of an aircraft type at which the angle of climb is largest is called VX. It is always slower than VY, the speed for the best rate of climb. As the latter gives the quickest way for gaining altitude levels, regardless of the distance covered during such a maneuver, it is more relevant to cruising. The maximum angle of climb on the other hand is where the aircraft gains the most altitude in a given distance, regardless of the time needed for the maneuver. This is important for clearing an obstacle, and therefore is the speed a pilot uses when executing a "short field" takeoff. VX increases with altitude and VY decreases with altitude until they converge at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
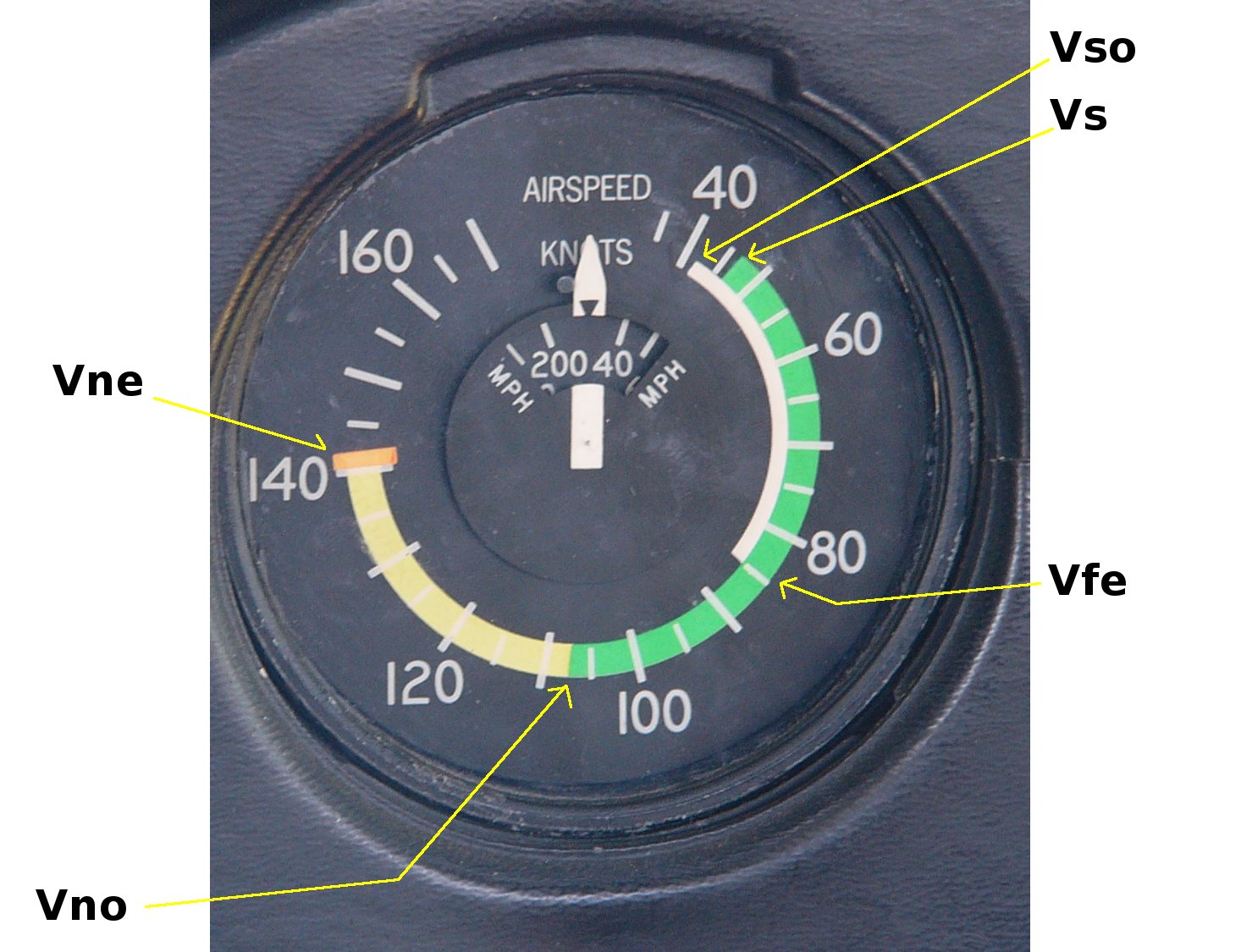
V Speeds
In aviation, V-speeds are standard terms used to define airspeeds important or useful to the operation of all aircraft. These speeds are derived from data obtained by aircraft designers and manufacturers during flight testing for aircraft type-certification. Using them is considered a best practice to maximize aviation safety, aircraft performance, or both. The actual speeds represented by these designators are specific to a particular model of aircraft. They are expressed by the aircraft's indicated airspeed (and not by, for example, the ground speed), so that pilots may use them directly, without having to apply correction factors, as aircraft instruments also show indicated airspeed. In general aviation aircraft, the most commonly used and most safety-critical airspeeds are displayed as color-coded arcs and lines located on the face of an aircraft's airspeed indicator. The lower ends of the white arc and the green arc are the stalling speed with wing flaps in landing con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |