|
Rameses IX
Neferkare Setepenre Ramesses IX (also written Ramses) (originally named Amon-her-khepshef Khaemwaset) (ruled 1129–1111 BC) was the eighth pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. He was the third longest serving king of this Dynasty after Ramesses III and Ramesses XI. He is now believed to have assumed the throne on I Akhet day 21 based on evidence presented by Jürgen von Beckerath in a 1984 GM article. According to Papyrus Turin 1932+1939, Ramesses IX enjoyed a reign of 18 years and 4 months and died in his 19th Year in the first month of Peret between day 17 and 27. His throne name, Neferkare Setepenre, means "Beautiful Is The Soul of Re, Chosen of Re." Ramesses IX is believed to be the son of Mentuherkhepeshef, a son of Ramesses III, since Mentuherkhopshef's wife, the lady Takhat bears the prominent title of King's Mother on the walls of tomb KV10, which she usurped and reused in the late 20th Dynasty; no other 20th Dynasty king is known to have had a mother with this nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Egypt
, image = Decorated pillars of the temple at Karnac, Thebes, Egypt. Co Wellcome V0049316.jpg , alt = , caption = Pillars of the Great Hypostyle Hall, in '' The Holy Land, Syria, Idumea, Arabia, Egypt, and Nubia'' , map_type = Egypt , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = yes , coordinates = , location = Luxor, Luxor Governorate, Egypt , region = Upper Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = , epochs = , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event = , excavations = , archaeologists = , condition = , ownership = , management = , public_access = , website = , notes = , designation1 = WHS , designation1_offname = Ancient T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mentuherkhepeshef (son Of Ramesses III)
Montuherkhopshef or Montuhirkhopshef was a Prince of the 20th Dynasty of Egypt and one of the sons of Ramesses III and Iset Ta Hemdjert. He was thus a brother of Ramesses IV, Ramesses VI, Ramesses VIII and an uncle of Ramesses V and Ramesses VII. He was the "First Charioteer of His Majesty", and married the lady Takhat who bears the prominent title of "King's Mother." This development supports the hypothesis that they are most probably the parents of king Ramesses IX since no other Ramesside king had a mother by this name, also, Ramesses IX had a son named Montuherkhepeshef. Montuherkhepeshef is shown in the procession of princes in the Medinet Habu temple of Ramesses III. He is likely to be identical with the Prince Montuherkhepeshef buried in the tomb KV13 in the Valley of the Kings. He never became Pharaoh, unlike his son Ramses IX, or even crown prince because he died not only before his brother Ramses VIII but also before his nephew Ramses VII Usermaatre Setepenre Mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
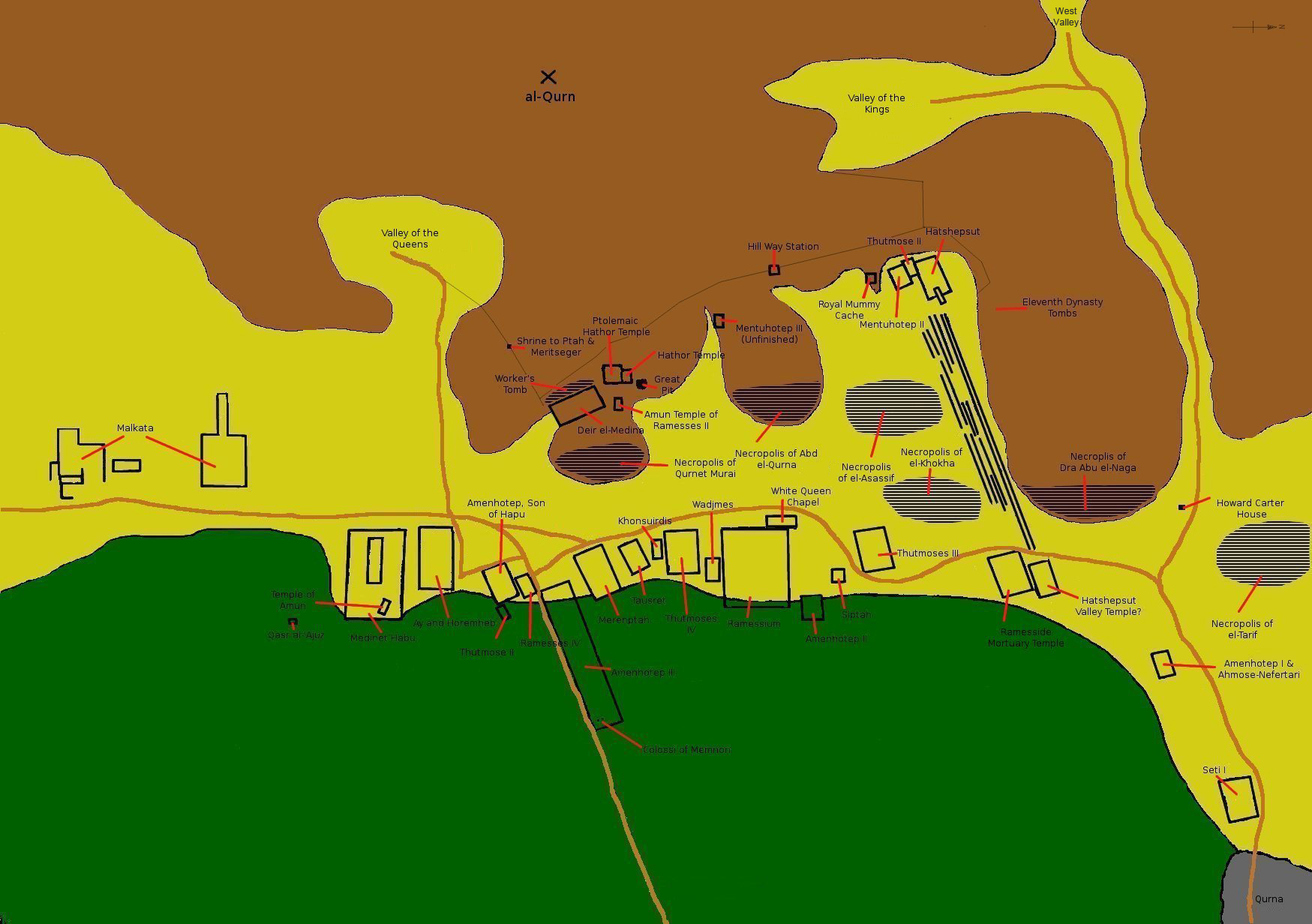
Valley Of The Kings
The Valley of the Kings ( ar, وادي الملوك ; Late Coptic: ), also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings ( ar, وادي أبوا الملوك ), is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th century BC, rock-cut tombs were excavated for the pharaohs and powerful nobles of the New Kingdom (the Eighteenth to the Twentieth Dynasties of Ancient Egypt). The valley stands on the west bank of the Nile opposite Thebes (modern Luxor), within the heart of the Theban Necropolis.Siliotti (1997), p.13 The wadi consists of two valleys: the East Valley (where the majority of the royal tombs are situated) and the West Valley (Valley of the Monkeys). With the 2005 discovery of a new chamber and the 2008 discovery of two further tomb entrances, the valley is known to contain 63 tombs and chambers (ranging in size from KV54, a simple pit, to KV5, a complex tomb with over 120 chambers). It was the principal burial place of the major royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paweraa
Paweraa (alt. Pewero) was the Mayor of Western Thebes during a series of tomb robberies that occurred in the Valley of the Kings during the late New Kingdom of Ancient Egypt. In official transcripts of a Tomb Robbery report from Year 16 of Ramesses IX, Paweraa was accused by Paser, the Mayor of Eastern Thebes, of either being involved in the series of Tomb robberies or being negligent in his duties in protecting the royal tombs from incursions by marauding Libyan bands or conventional Egyptian tomb robbers. The vizier Khaemwaset ordered an investigation by a commission of which Paweraa himself was the head. The investigation was considered corrupt by the people of Deir el-Medina. In the ensuing trial seventeen workmen from near-by temples were convicted and executed. Paweraa, however, was never charged due to the lack of clear evidence of his guilt. He continued to serve in office while Paser, his accuser, vanished from history, and the robberies continued.Michael Rice, ''Who's Who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as the means by which a mayor is elected or otherwise mandated. Depending on the system chosen, a mayor may be the chief executive officer of the municipal government, may simply chair a multi-member governing body with little or no independent power, or may play a solely ceremonial role. A mayor's duties and responsibilities may be to appoint and oversee municipal managers and employees, provide basic governmental services to constituents, and execute the laws and ordinances passed by a municipal governing body (or mandated by a state, territorial or national governing body). Options for selection of a mayor include direct election by the public, or selection by an elected governing council or board. The term ''mayor'' shares a linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sobekemsaf II
Sobekemsaf ''(sbk-m-z3=f;'' “Sobek is his protection”) is an ancient Egyptian theophoric name, popular during the Second Intermediate Period (mainly in the 17th Dynasty). Although it is grammatically masculine, it was also used for women; it was common during this era that the gender of a name did not correspond to that of its bearer.Ranke: ''Persönennamen,'' Band II, p.4 Notable bearers * Pharaoh Sobekemsaf I Sobekemsaf ''(sbk-m-z3=f;'' “Sobek is his protection”) is an ancient Egyptian theophoric name, popular during the Second Intermediate Period (mainly in the 17th Dynasty The Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVII, alternatively 17 ... * Pharaoh Sobekemsaf II * official of the 13th Dynasty Sobekemsaf * Queen Sobekemsaf, wife of Nubkheperre Intef * Princess Sobekemsaf C, daughter of Queen Sobekemsaf * obek?msaf A, mother of Pharaoh Rahotep Sources {{reflist Ancient Egyptian given names Theophoric names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theban Necropolis
The Theban Necropolis is a necropolis on the west bank of the Nile, opposite Thebes (Luxor) in Upper Egypt. It was used for ritual burials for much of the Pharaonic period, especially during the New Kingdom. Mortuary temples * Deir el-Bahri ** Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut ** Mortuary temple of Mentuhotep II ** Mortuary temple of Thutmose III * Medinet Habu ** Mortuary temple and palace of Ramesses III ** Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III ** Colossi of Memnon * Mortuary Temple of Merneptah * Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV * Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III * Mortuary Temple of Twosret * Temple of Nebwenenef * Qurna ** Mortuary Temple of Seti I * Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep II * Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II) Royal Necropolis * Valley of the Kings (Modern: "''Wadi el-Muluk''") * Valley of the Queens (Modern: "''Biban el-Harim''") * Royal Cache * Bab el-Gasus Necropolis * Deir el-Medina ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses VI
Ramesses VI Nebmaatre-Meryamun (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses, also known under his princely name of Amenherkhepshef C) was the fifth ruler of the Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt. He reigned for about eight years in the mid-to-late 12th century BC and was a son of Ramesses III and queen Iset Ta-Hemdjert. As a prince, he was known as Ramesses Amunherkhepeshef and held the titles of royal scribe and cavalry general. He was succeeded by his son, Ramesses VII Itamun, whom he had fathered with queen Nubkhesbed. After the death of the ruling pharaoh, Ramesses V, who was the son of Ramesses VI's older brother, Ramesses IV, Ramesses VI ascended the throne. In the first two years after his coronation, Ramesses VI stopped frequent raids by Libyan or Egyptian marauders in Upper Egypt and buried his predecessor in what is now an unknown tomb of the Theban necropolis. Ramesses VI usurped KV9, a tomb in the Valley of the Kings planned by and for Ramesses V, and had it enlarged and redecora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayer Papyri
The Mayer Papyri are two ancient Egyptian documents from the Twentieth Dynasty that contain records of court proceedings. Papyrus Mayer A The best known of the two is Papyrus Mayer A. It deals with court sessions held in the first two years of the Whm Mswt or Renaissance, an era which began in year 19 of king Ramesses XI. A panel consisting of the vizier of the South and three high officials cross-examined suspects charged with tomb robbery at Deir el-Bahri (cf. also the Abbott Papyrus and the Amherst Papyrus). The interrogation of both suspects and witnesses was preceded by a bastinado and an oath in the name of the king was administered. The confessions of the six suspects were corroborated by the testimony of the chief of police of the Theban Necropolis and other witnesses, among them the son of one of the thieves who had died in the meantime. This witness claims to have been a child at the time of the crime; still, he was beaten when he was being examined, as was a female w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recto
'''' is the "right" or "front" side and ''verso'' is the "left" or "back" side when text is written or printed on a leaf of paper () in a bound item such as a codex, book, broadsheet, or pamphlet. Etymology The terms are shortened from Latin: and ' (which translate as "on the right side of the leaf" and "on the back side of the leaf"). The two opposite pages themselves are called ' and ' in Latin, and the ablative ', ' already imply that the text on the page (and not the physical page itself) are referred to. Usage In codicology, each physical sheet (', abbreviated ''fol.'' or ''f.'') of a manuscript is numbered, and the sides are referred to as ' and ', abbreviated as ''r'' and ''v'' respectively. Editions of manuscripts will thus mark the position of text in the original manuscript in the form ''fol. 1r'', sometimes with the ''r'' and ''v'' in superscript, as in ''1r'', or with a superscript ''o'' indicating the ablative ', ', as in ''1ro''. This terminology has been stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amherst Papyrus
The ancient Egyptian document Papyrus Leopold II (originally Amherst Papyrus VI), is part of the original court records dealing with the tomb robberies under Ramesses IX and dates to Year 16 of Ramesses IX. It contains the confessions of eight men who had broken into the tomb of Sobekemsaf II and a description of the reconstruction of the crime. It throws light on the practices followed at ancient Egyptian courts: eliciting confessions by ''beating with a double rod, smiting their feet and hands'', reconstructing the crime on site, and imprisonment of suspects in the gatehouse of a temple. The document remains an important document for understanding the importance of burial and the afterlife in ancient Egypt as well as crime and punishment practices in Egypt during the 20th Dynasty.Spencer, p95 Background history The grave robbery described in the Amherst-Leopold document came during the 20th Dynasty of ancient Egypt and "a background of economic trouble and incipient national disun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |