|
Rue Émile-Lepeu
''Ruta graveolens'', commonly known as rue, common rue or herb-of-grace, is a species of the genus ''Ruta'' grown as an ornamental plant and herb. It is native to the Mediterranean. It is grown throughout the world in gardens, especially for its bluish leaves, and sometimes for its tolerance of hot and dry soil conditions. It is also cultivated as a culinary herb, and to a lesser extent as an insect repellent and incense. Etymology The specific epithet ''graveolens'' refers to the strong-smelling leaves.J. D. Douglas and Merrill C. Tenney Description Rue is a woody, perennial shrub. Its leaves are oblong, blue green and arranged bipinnately with rounded leaflets; they release a strong aroma when they are bruised. The flowers are small with 4 to 5 dull yellow petals in cymes. The first flower in each cyme is pentamerous (five sepals, five petals, five stamens and five carpels. All the others are tetramerous (four of each part). They bear brown seed capsules when pollinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friuli-Venezia Giulia
Friuli-Venezia Giulia () is one of the 20 regions of Italy and one of five autonomous regions with special statute. The regional capital is Trieste on the Gulf of Trieste, a bay of the Adriatic Sea. Friuli-Venezia Giulia has an area of and about 1,194,095 inhabitants as of 2025. A natural opening to the sea for many central European countries, the region is traversed by the major transport routes between the east and west of Southern Europe. It encompasses the historical-geographical region of Friuli and a small portion of the historical region of —also known in English as the Julian March—each with its own distinct history, traditions and identity. Name ''Friuli'' comes from the Latin term (' Julius' forum'), a center for commerce in the Roman times, which today corresponds to the city of Cividale. The denomination ''Venezia Giulia'' ('Julian Venetia', not referring to the city of Venice but to the Roman province of Venetia et Histria) was proposed by the Italian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damson
The damson (), damson plum, or damasceneSamuel Johnson equates "damascene" and "damson" and for "damask plum" simply states "see Plum" (''A Dictionary of the English Language'', 1755, p. 532). Later expanded editions also distinguish between "damascene" and "damson", the latter being described as "smaller and [with] a peculiar bitter or roughness". (''Prunus domestica'' subsp. ''insititia'', sometimes ''Prunus insititia''),M. H. Porche"Sorting ''Prunus'' names" in "Multilingual multiscript plant names database, University of Melbourne. Plantnames.unimelb.edu.au. Retrieved on 2012-01-01. is an edible Drupe, drupaceous fruit, a subspecies of the plum tree. Varieties of ''insititia'' are found across Europe, but the name ''damson'' is derived from and most commonly applied to forms that are native to Great Britain. Damsons are small, ovoid, plum-like fruit with a distinctive, somewhat Astringent (taste), astringent taste, and are widely used for culinary purposes, particularly in fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakia
Rakia, rakija, rakiya, rachiu or rakı (), is the collective term for fruit spirits (or fruit brandy) popular in the Balkans. The alcohol content of rakia is normally 40% ABV, but home-produced rakia can be stronger (typically 50–80%). Overview Rakia is produced from fermented and distilled fruits, typically plums and grapes, but also apricots, pears, cherries or raspberries. Other fruits less commonly used are peaches, apples, Ficus, figs, blackberries, and quince. Common flavours are ''šljivovica'' and ''țuică'', produced from plums, ''kaysieva''/''kajsija'', produced from apricots, or ''grozdova''/''lozova'' in Bulgaria, ''raki rrushi'' in Albania, ''lozovača''/''komovica'' in Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina all produced from grapes. Plum and grape rakia are sometimes mixed with other ingredients, such as herbs, honey, sour cherries and walnuts, after distillation. By country Albania Raki ( sq-definite, rakia) (a type of ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grappa
Grappa is an alcoholic beverage: a fragrant, grape-based pomace brandy of Italian origin that contains 35 to 60 percent alcohol by volume (70 to 120 Alcohol proof, US proof). Grappa is a protected name in the European Union. Grappa is made by Distillation, distilling the skins, pulp, seeds, and stems (i.e., the pomace) left over from winemaking after Pressing (wine), pressing the grapes. It was originally made to prevent waste by using these leftovers. A similar drink, known as ''acquavite d'uva'', is made by distilling whole must. In Italy, grappa is primarily served as a ''Italian meal structure#Formal meal structure, digestivo'' or Apéritif and digestif, after-dinner drink. Its main purpose is to aid in the digestion of heavy meals. Grappa may also be added to espresso coffee to create a ''caffè corretto'', meaning "corrected" coffee. Another variation of this is the ''ammazzacaffè'': the espresso is drunk first, followed by a few ounces of grappa served in its own glass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriatic Sea to the southwest, which is part of the Mediterranean Sea. Slovenia is mostly mountainous and forested, covers , and has a population of approximately 2.1 million people. Slovene language, Slovene is the official language. Slovenia has a predominantly temperate continental climate, with the exception of the Slovene Littoral and the Julian Alps. Ljubljana, the capital and List of cities and towns in Slovenia, largest city of Slovenia, is geographically situated near the centre of the country. Other larger urban centers are Maribor, Ptuj, Kranj, Celje, and Koper. Slovenia's territory has been part of many different states: the Byzantine Empire, the Carolingian Empire, the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Republic of Venice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at the top of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Kvarner Gulf, the peninsula is shared by three countries: Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy,Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries'' John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe'' Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), 90% of its area being part of Croatia. Most of Croatian Istria is part of Istria County. Geography The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria mountain range; the rivers Dragonja/Dragogna, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicius
''Apicius'', also known as ''De re culinaria'' or ''De re coquinaria'' (''On the Subject of Cooking''), is a collection of Food and dining in the Roman Empire, Roman cookery recipes, which may have been compiled in the fifth century CE, or earlier. Its language is in many ways closer to Vulgar Latin, Vulgar than to Classical Latin, with later recipes using Vulgar Latin (such as ''ficatum'', ''bullire'') added to earlier recipes using Classical Latin (such as ''iecur'', ''fervere''). The book has been attributed to an otherwise unknown Caelius Apicius, an invention based on the fact that one of the two manuscripts is headed with the words "API CAE" or rather because a few recipes are attributed to Apicius in the text: Patinam Apicianam sic facies (IV, 14) Ofellas Apicianas (VII, 2). It has also been attributed to Marcus Gavius Apicius, a Roman gourmet who lived sometime in the 1st century CE during the reign of Tiberius. The book also may have been authored by a number of diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Sayyar Al-Warraq
() was an Arab author from Baghdad. He was the compiler of a tenth-century cookbook, the (, ''The Book of Dishes''). This is the earliest known Arabic cookbook. It contains over 600 recipes, divided into 132 chapters. The is the oldest surviving Arabic cookbook, written by al-Warraq in the 10th century. It is compiled from the recipes of the 8th and 9th century courts of the Abbasid Caliphate in Baghdad. Some scholars speculate that al-Warraq may have prepared the manuscript on behalf of a patron, the Hamdanid prince Sayf al-Dawla, who sought to improve the cultural prestige of his own court in Aleppo as the court in Baghdad had started to decline. Some recipes in the book, like (date-sweetened porridge), come from the relatively simple cuisine of the Arabian Peninsula The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest penin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
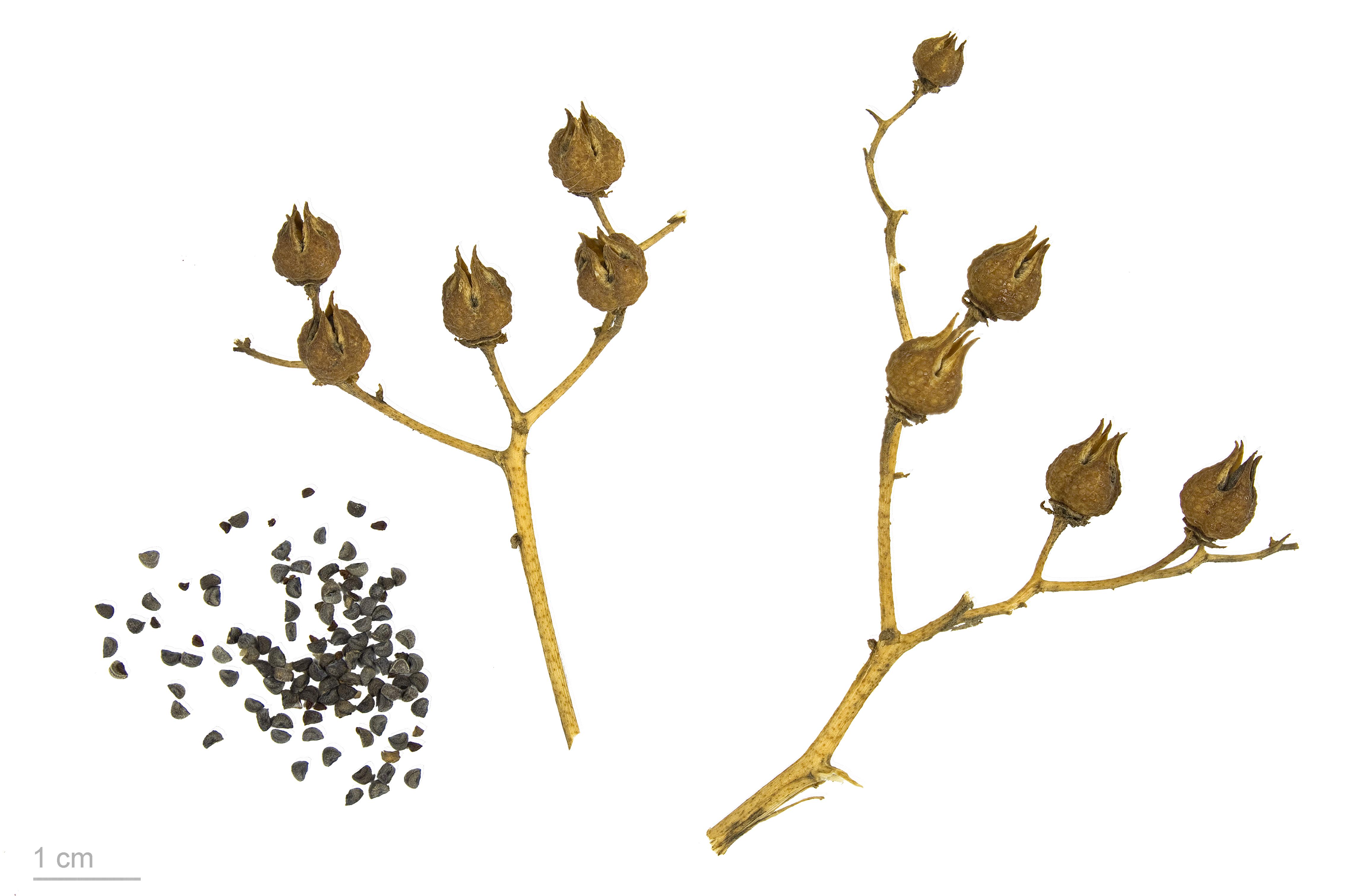
Ruta Graveolens MHNT
''Ruta'' (commonly known as rue) is a genus of strongly scented evergreen subshrubs, 20–60 cm tall, in the family Rutaceae, native to the Mediterranean region, Macaronesia and southwest Asia. About ten species are accepted in the genus. The most well-known species is '' Ruta graveolens'' (rue or common rue). The leaves are bipinnate or tripinnate, with a feathery appearance, and green to strongly glaucous blue-green in colour. The flowers are yellow, with 4–5 petals, about 1 cm diameter, and borne in cymes. The fruit is a 4–5-lobed capsule, containing numerous seeds. Species , Plants of the World Online accepted ten species: *'' Ruta angustifolia'' Pers. *'' Ruta chalepensis'' L. *'' Ruta corsica'' DC. *'' Ruta graveolens'' L. *'' Ruta lamarmorae'' Bacch., Brullo & Giusso *'' Ruta lindsayi'' Turrill *'' Ruta microcarpa'' Svent. *'' Ruta montana'' (L.) L. *'' Ruta oreojasme'' Webb *'' Ruta pinnata'' L.f. Medicinal uses Extracts from rue have been used to treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abortifacient
An abortifacient ("that which will cause a miscarriage" from Latin: '' abortus'' "miscarriage" and '' faciens'' "making") is a substance that induces abortion. This is a nonspecific term which may refer to any number of substances or medications, ranging from herbs to prescription medications. Common abortifacients used in performing medical abortions include mifepristone, which is typically used in conjunction with misoprostol in a two-step approach. Synthetic oxytocin, which is routinely used safely during term labor, is also commonly used to induce abortion in the second or third trimester. For thousands of years, writers in many parts of the world have described and recommended herbal abortifacients to women who seek to terminate a pregnancy, although their use may carry risks to the health of the woman. Medications Because "abortifacient" is a broad term used to describe a substance's effects on pregnancy, there is a wide range of drugs that can be described as abor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |