|
Rpath
In computer science, rpath designates the run-time search path hard-coded in an executable file or library. Dynamic linking loaders use the rpath to find required libraries. Specifically, it encodes a path to shared libraries into the header of an executable (or another shared library). This RPATH header value (so named in the Executable and Linkable Format header standards) may either override or supplement the system default dynamic linking search paths. The rpath of an executable or shared library is an optional entry in the .dynamic section of the ELF executable or shared libraries, with the type DT_RPATH, called the DT_RPATH attribute. It can be stored there at link time by the linker. Tools such as chrpath and patchelf can create or modify the entry later. Use of the DT_RPATH entry by the dynamic linker The different dynamic linkers for ELF implement the use of the DT_RPATH attribute in different ways. GNU ld.so The dynamic linker of the GNU C Library searches f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
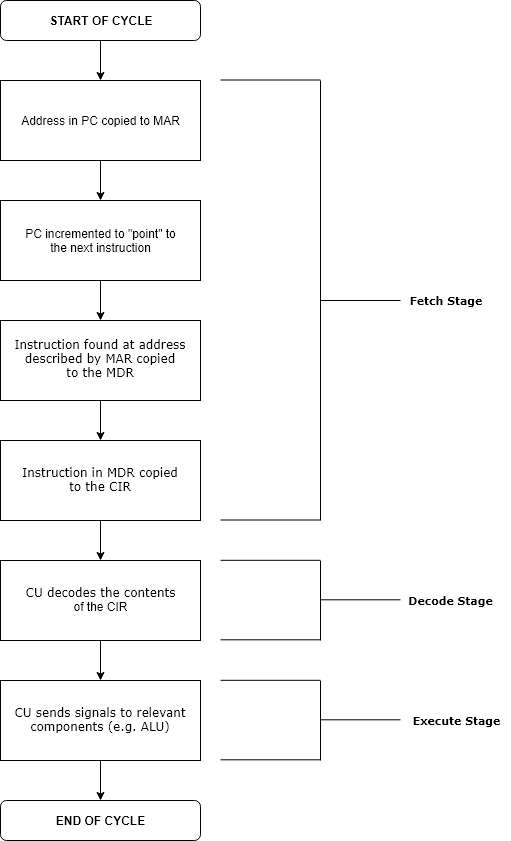
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Path
PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like operating systems, DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, specifying a set of directories where executable programs are located. In general, each executing process or user session has its own PATH setting. History Multics originated the idea of a search path. The early Unix shell only looked for program names in /bin, but by Version 3 Unix the directory was too large and /usr/bin, and a search path, became part of the operating system. Unix and Unix-like On POSIX and Unix-like operating systems, the $PATH variable is specified as a list of one or more directory names separated by colon (:) characters. Directories in the PATH-string are not meant to be escaped, making it impossible to have directories with : in their name. The /bin, /usr/bin, and /usr/local/bin directories are typically included in most users' $PATH setting (although this varies from implementation to implementation). The superuser also typically has /sbin and /usr/sbin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executable File
In computer science, executable code, an executable file, or an executable program, sometimes simply referred to as an executable or binary, causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions", as opposed to a data file that must be interpreted ( parsed) by an interpreter to be functional. The exact interpretation depends upon the use. "Instructions" is traditionally taken to mean machine code instructions for a physical CPU. In some contexts, a file containing scripting instructions (such as bytecode) may also be considered executable. Generation of executable files Executable files can be hand-coded in machine language, although it is far more convenient to develop software as source code in a high-level language that can be easily understood by humans. In some cases, source code might be specified in assembly language instead, which remains human-readable while being closely associated with machine code instructions. The high-level langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library (computer Science)
In computing, a library is a collection of resources that can be leveraged during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library consists of executable code such as compiled functions and classes, or a library can be a collection of source code. A resource library may contain data such as images and text. A library can be used by multiple, independent consumers (programs and other libraries). This differs from resources defined in a program which can usually only be used by that program. When a consumer uses a library resource, it gains the value of the library without having to implement it itself. Libraries encourage software reuse in a modular fashion. Libraries can use other libraries resulting in a hierarchy of libraries in a program. When writing code that uses a library, a programmer only needs to know how to use it not its internal details. For example, a program could use a library that abstracts a complicated system call so that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Linking
In computing, a dynamic linker is the part of an operating system that loads and links the shared libraries needed by an executable when it is executed (at " run time"), by copying the content of libraries from persistent storage to RAM, filling jump tables and relocating pointers. The specific operating system and executable format determine how the dynamic linker functions and how it is implemented. Linking is often referred to as a process that is performed when the executable is compiled, while a dynamic linker is a special part of an operating system that loads external shared libraries into a running process and then binds those shared libraries dynamically to the running process. This approach is also called dynamic linking or late linking. Implementations Microsoft Windows Dynamic-link library, or DLL, is Microsoft's implementation of the shared library concept in the Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems. These libraries usually have the file ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loader (computing)
In computing, computer systems a loader is the part of an operating system that is responsible for loading computer program, programs and Library (computing), libraries. It is one of the essential stages in the process of starting a program, as it places programs into memory and prepares them for execution. Loading a program involves either memory-mapped file, memory-mapping or copying the contents of the executable, executable file containing the program instructions into memory, and then carrying out other required preparatory tasks to prepare the executable for running. Once loading is complete, the operating system starts the program by passing control to the loaded program code. All operating systems that support program loading have loaders, apart from highly specialized computer systems that only have a fixed set of specialized programs. Embedded systems typically do not have loaders, and instead, the code executes directly from ROM or similar. In order to load the operatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executable And Linkable Format
In computing, the Executable and Linkable FormatTool Interface Standard (TIS) Portable Formats SpecificationVersion 1.1'' (October 1993) (ELF, formerly named Extensible Linking Format) is a common standard file format for executable files, object code, Shared library, shared libraries, and core dumps. First published in the specification for the application binary interface (ABI) of the Unix operating system version named System V Release 4 (SVR4), and later in the Tool Interface Standard,Tool Interface Standard (TIS) Executable and Linking Format (ELF) SpecificationVersion 1.2'' (May 1995) it was quickly accepted among different vendors of Unix systems. In 1999, it was chosen as the standard binary file format for Unix and Unix-like systems on x86 processors by the #86open, 86open project. By design, the ELF format is flexible, extensible, and cross-platform. For instance, it supports different endiannesses and address sizes so it does not exclude any particular central process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Linker
In computing, a dynamic linker is the part of an operating system that loads and links the shared libraries needed by an executable when it is executed (at " run time"), by copying the content of libraries from persistent storage to RAM, filling jump tables and relocating pointers. The specific operating system and executable format determine how the dynamic linker functions and how it is implemented. Linking is often referred to as a process that is performed when the executable is compiled, while a dynamic linker is a special part of an operating system that loads external shared libraries into a running process and then binds those shared libraries dynamically to the running process. This approach is also called dynamic linking or late linking. Implementations Microsoft Windows Dynamic-link library, or DLL, is Microsoft's implementation of the shared library concept in the Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems. These libraries usually have the file exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU C Library
The GNU C Library, commonly known as glibc, is the GNU Project implementation of the C standard library. It provides a wrapper around the system calls of the Linux kernel and other kernels for application use. Despite its name, it now also directly supports C++ (and, indirectly, other programming languages). It was started in the 1980s by the Free Software Foundation (FSF) for the GNU operating system. glibc is free software released under the GNU Lesser General Public License. The GNU C Library project provides the core libraries for the GNU system, as well as many systems that use Linux as the kernel. These libraries provide critical APIs including ISO C11, POSIX.1-2008, BSD, OS-specific APIs and more. These APIs include such foundational facilities as open, read, write, malloc, printf, getaddrinfo, dlopen, pthread_create, crypt, login, exit and more. History The glibc project was initially written mostly by Roland McGrath, working for the Free Sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Compiler Collection
The GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) is a collection of compilers from the GNU Project that support various programming languages, Computer architecture, hardware architectures, and operating systems. The Free Software Foundation (FSF) distributes GCC as free software under the GNU General Public License (GNU GPL). GCC is a key component of the GNU toolchain which is used for most projects related to GNU and the Linux kernel. With roughly 15 million lines of code in 2019, GCC is one of the largest free programs in existence. It has played an important role in the growth of free software, as both a tool and an example. When it was first released in 1987 by Richard Stallman, GCC 1.0 was named the GNU C Compiler since it only handled the C (programming language), C programming language. It was extended to compile C++ in December of that year. Compiler#Front end, Front ends were later developed for Objective-C, Objective-C++, Fortran, Ada (programming language), Ada, Go (programming la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Variable
An environment variable is a user-definable value that can affect the way running processes will behave on a computer. Environment variables are part of the environment in which a process runs. For example, a running process can query the value of the TEMP environment variable to discover a suitable location to store temporary files, or the HOME or USERPROFILE variable to find the directory structure owned by the user running the process. They were introduced in their modern form in 1979 with Version 7 Unix, so are included in all Unix operating system flavors and variants from that point onward including Linux and macOS. From PC DOS 2.0 in 1982, all succeeding Microsoft operating systems, including Microsoft Windows, and OS/2 also have included them as a feature, although with somewhat different syntax, usage and standard variable names. Design In all Unix and Unix-like systems, as well as on Windows, each process has its own separate set of environment vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |