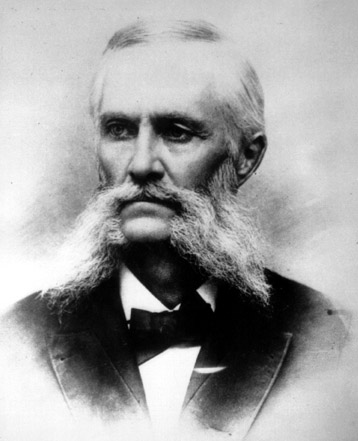|
Rogers Pass (British Columbia)
Rogers Pass is a high mountain pass through the Selkirk Mountains of British Columbia, but the term also includes the approaches used by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) and the Trans-Canada Highway. In the heart of Glacier National Park (Canada), Glacier National Park, this National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site has been a tourist destination since 1886. Topography Rogers Pass is the lowest route between the Sir Donald and Hermit ranges of the Selkirks, providing a shortcut along the southern perimeter of the Big Bend Country, Big Bend of the Columbia River from Revelstoke, British Columbia, Revelstoke on the west to Donald, British Columbia, Donald, near Golden, British Columbia, Golden, on the east. The pass is formed by the headwaters of the Illecillewaet River to the west and by the Beaver River (Columbia River), Beaver River to the east. These rivers are tributaries of the Columbia, which arcs to the north. Railway Proposal & planning During the 1870 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway (Canadian French, French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the Atlantic Ocean on the east coast. The main route spans across the country, one of the longest routes of its type in the world. The highway system is recognizable by its distinctive white-on-green maple leaf route shield, route markers, although there are small variations in the markers in some provinces. While by definition the Trans-Canada Highway is a highway ''system'' that has several parallel routes throughout most of the country, the term "Trans-Canada Highway" often refers to the main route that consists of Highway 1 (British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba), Highways 11 & 17/417 (Ontario), Autoroutes 40, 25, 20, 85 & 185 (Quebec), Highway 2 (New Brunswick), Highways 104 and 105 (Nova Scotia), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowhead Pass
The Yellowhead Pass is a mountain pass across the Continental Divide of the Americas in the Canadian Rockies. It is on the provincial boundary between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and British Columbia, and lies within Jasper National Park and Mount Robson Provincial Park. Due to its modest elevation of and its gradual approaches, the pass was recommended by Sir Sandford Fleming as a route across the Rocky Mountains for the planned Canadian Pacific Railway. The proposal was rejected in favour of a more direct and southerly route, through the more difficult Kicking Horse Pass, which was opened in 1886. Later the Grand Trunk Pacific and Canadian Northern Railways used the Yellowhead Pass for their main lines, built c. 1910–1913, and the main line of their successor, the Canadian National Railway, still follows the route. Via Rail's premier passenger train, the ''Canadian''; the Jasper – Prince Rupert train; and the Jasper section of the '' Rocky Mountaineer' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine Hat
Medicine Hat is a city in Southern Alberta, southeast Alberta, Canada. It is located along the South Saskatchewan River. It is approximately east of Lethbridge and southeast of Calgary. This city and the adjacent Town of Redcliff, Alberta, Redcliff to the northwest are within Cypress County. Medicine Hat was the List of cities in Alberta, eighth-largest city in Alberta in 2021 with a population of 63,271. It is also the sunniest place in Canada according to Environment and Climate Change Canada, averaging 2,544 hours of sunshine a year. Started as a railway town, today Medicine Hat is served by the Trans-Canada Highway (Alberta Highway 1, Highway 1) and the eastern terminus of the Crowsnest Highway (Alberta Highway 3, Highway 3). Nearby communities considered part of the Medicine Hat area include the Town of Redcliff (abutting the city's northwest boundary) and the hamlets of Desert Blume, Dunmore, Alberta, Dunmore, Irvine, Alberta, Irvine, Seven Persons, and Veinervil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastbound Over SCB
''Eastbound'' (originally released in 2012 as ) is a book by French author Maylis de Kerangal, published in translation in 2023 by Archipelago Books. The novel tells the story of Aliocha, a 20 year old Russian conscript who is attempting desertion from the army as he travels on a trans-Siberian train heading east. On board the train he meets Helene, a passenger in first class. Helene is a 35 year old French woman who is leaving her Russian lover. Helene does not speak Russian and the two communicate with hand gestures and other non-verbal cues. Helene assists Aliocha in evading capture from his Sergeant as he attempts to flee. The novel was named one of the best books of 2023 by ''The New York Times'' and ''The New Yorker''. Reception Writing in the ''New York Times'', author Ken Kalfus believed that the book's setting, on board a speeding train in the vastness of Siberia, complemented the characters' relationship elegantly. Halfus stated: "Siberia’s immensity dwarfs human pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Cornelius Van Horne
Sir William Cornelius Van Horne, (February 3, 1843September 11, 1915) was an American businessman, industrialist and railroad magnate who spent most of his career in Canada. He is famous for overseeing the construction of the first Canadian Transcontinental railroad, transcontinental railway, a project that was completed in 1885, in under half the projected time. He succeeded George Stephen, 1st Baron Mount Stephen, Lord Mount Stephen as president of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) in 1888. Van Horne was responsible for launching the CP Ships, sea transport division of the CPR, which inaugurated regular service between Vancouver and Hong Kong in 1891. He also presided over the expansion of the CPR into the luxury hotel business in the 1890s. Van Horne was also a prominent member of the syndicate that created the Cuba Railroad Company in 1900. He lived at the Van Horne Mansion in Montreal's Golden Square Mile. Ancestry and early life Born on February 3, 1843, in rural Illinois, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalanche Mountain
Avalanche Mountain is a summit in Glacier National Park in the Selkirk Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. Its nearest higher peak is Mount Macdonald, to the north. Mount Sir Donald is to the southeast, and Eagle Peak is to the south-southeast. The Avalanche Glacier is situated on the east side of the peak, and the Connaught Tunnel lies partially beneath Avalanche Mountain. The peak is visible from eastbound Highway 1, the Trans-Canada Highway approaching Rogers Pass. During winter and spring of each year the western slope, named Avalanche Crest, generates avalanches which can threaten the highway. History The mountain's name was applied by Major A.B. Rogers and stems from its history of avalanches from its western slopes onto Rogers Pass. The 1910 Rogers Pass avalanche, the deadliest avalanche in Canadian history, resulted in the deaths of 62 Canadian Pacific Railway workers and was the impetus which forced the railway to build the Connaught Tunnel. In 1881, Rogers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Macdonald
Mount Macdonald is a mountain peak located in the Selkirk Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, immediately east of Rogers Pass in Glacier National Park. It is notable as the location of the Canadian Pacific Railway's Connaught and Mount Macdonald Tunnels. At 14.7 km, the Mount Macdonald tunnel is the longest railway tunnel in the western hemisphere. The original name of the peak was ''Mount Carroll'' (for a member of the CPR engineering team under A. B. Rogers), but was renamed to honor the first Prime Minister of Canada, Sir John A. Macdonald, by a Privy Council Order in Council #551 on 4 April 1887. __NOTOC__ Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, this mountain is located in a subarctic climate zone with cold, snowy winters and mild summers. Temperatures can drop below −20 °C with wind chill factors below −30 °C. Precipitation runoff from the mountain drains into tributaries of the Beaver River. Gallery Mt MacDonald at Rogers Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Sir Donald
Mount Sir Donald is a mountain summit located in the Rogers Pass area of Glacier National Park in the Selkirk Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. Its good rock quality and classic Matterhorn shape make it popular for alpine rock climbers, and the Northwest Arete route is included in the popular book '' Fifty Classic Climbs of North America''. It was originally named Syndicate Peak in honor of the group who arranged the finances for the completion of the Canadian Pacific Railway, but was later renamed after Donald Smith, 1st Baron Strathcona and Mount Royal, head of the syndicate. The first ascent was made in 1890 by Emil Huber and Carl Sulzer of Switzerland and porter Harry Cooper. As of the 1910s, an average of three or four ascents per year were being made. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, the mountain has a subarctic climate with cold, snowy winters, and mild summers. Temperatures can drop below −20 °C with wind chill factors below −30&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eagle Pass, British Columbia
Eagle Pass (elevation ) is a mountain pass through the Gold Range of the Monashee Mountains in British Columbia, Canada. It divides the Columbia River drainage basin from that of the Fraser River (via the Shuswap Lakes and the Thompson River). Eagle Pass was chosen as the route of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR), and later the Trans-Canada Highway, over the Monashees. The line over the Eagle Pass was the last section of the CPR to be completed; the last spike was driven at a location known as Craigellachie in 1885. The pass was discovered by Walter Moberly in his role as Assistant Surveyor General of British Columbia in 1865. The nearest city to Eagle Pass is Revelstoke, 20 kilometres to the east. See also *Eagle River (Shuswap) The Eagle River is a river in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The river was named by Walter Moberly after following the flight of eagles and finding Eagle Pass. Course The Eagle River originates in the mountains west of Revelsto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Moberly (engineer)
Walter Moberly (August 15, 1832 – May 15, 1915) was a civil engineer and surveyor who played a large role in the early exploration and development of British Columbia, Canada, including discovering Eagle Pass, now used by the Canadian Pacific Railway and the Trans-Canada Highway. Early life and education He was born in Steeple Aston, Oxfordshire, England in 1832. In 1834, Walter moved with his family to Penetanguishene, Upper Canada (now Ontario), where his father, Capt. John Moberly, R. N. was appointed Post Commander. Walter received his primary education at the Base and later went to grammar school in Barrie. Career During the construction of the railway to Collingwood, Walter worked clearing bush and following that, chose a career of Lumberman, with timber holdings in Essa and Tossorontio, near Angus, and on the Severn River, in Muskoka. Most of his survey work was in British Columbia, and Utah. It is thought that Walter was lured to the West, following a brief visit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Bowman Rogers
Albert Bowman Rogers (28 May 1829 – 4 May 1889), commonly known as Major A.B. Rogers, was an American surveyor now best remembered for his discovery of the Rogers Pass in British Columbia, Canada. He also has the distinction of having Rogers Pass in the U.S. state of Montana named after him, following his description of the pass in 1887. Early life Born in Orleans, Massachusetts in 1829, he attended Brown University, but transferred after one year to Yale University, where he obtained a degree in Engineering. Rogers served with the U.S. Cavalry during the Indian Wars, attaining the rank of major during the 1862 Dakota Sioux uprising. Surveys for the Canadian Pacific Railway His initial engineering experience was primarily on the American prairies surveying for the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. Nevertheless, James Jerome Hill of the Canadian Pacific Railway hired Rogers in April 1881 to find a rail route through the Selkirk and Rocky Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |