|
Robert Gordon University
Robert Gordon University, commonly called RGU (), is a public university in the city of Aberdeen, Scotland. It became a university in 1992, and originated from an educational institution founded in the 18th century by Robert Gordon (philanthropist), Robert Gordon, an Aberdeen merchant, and various institutions which provided adult and technical education in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It is one of two universities in the city, the other being the University of Aberdeen. RGU is a campus university in Garthdee, in the south-west of the city. The university awards degrees in a wide range of disciplines from Bachelor's degree, BA/BSc to PhD, primarily in professional, technical, health and artistic disciplines and those most applicable to business and industry. A number of traditional academic degree programmes are also offered, such as in the social sciences. In addition, the university's academic and research staff produce research in a number of areas. History The univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public University
A public university, state university, or public college is a university or college that is State ownership, owned by the state or receives significant funding from a government. Whether a national university is considered public varies from one country (or region) to another, largely depending on the specific education landscape. In contrast a private university is usually owned and operated by a private corporation (not-for-profit or for profit). Both types are often regulated, but to varying degrees, by the government. Africa Algeria In Algeria, public universities are a key part of the education system, and education is considered a right for all citizens. Access to these universities requires passing the Baccalaureate (Bac) exam, with each institution setting its own grade requirements (out of 20) for different majors and programs. Notable public universities include the Algiers 1 University, University of Algiers, Oran 1 University, University of Oran, and Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the motion, movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, air navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks. All navigational techniques involve locating the navigator's Position (geometry), position compared to known locations or patterns. Navigation, in a broader sense, can refer to any skill or study that involves the determination of position and Relative direction, direction. In this sense, navigation includes orienteering and pedestrian navigation. For marine navigation, this involves the safe movement of ships, boats and other nautical craft either on or underneath the water using positions from navigation equipment with appropriate nautical char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Science
Home economics, also called domestic science or family and consumer sciences (often shortened to FCS or FACS), is a subject concerning human development, personal and family finances, consumer issues, housing and interior design, nutrition and food preparation, as well as textiles and apparel. Although historically mostly taught in secondary school or high school, dedicated home economics courses are much less common today. Home economics courses are offered around the world and across multiple educational levels. Historically, the purpose of these courses was to professionalize housework, to provide intellectual fulfillment for women, to emphasize the value of "women's work" in society, and to prepare them for the traditional roles of sexes. Family and consumer sciences are taught as an elective or required course in secondary education, as a continuing education course in institutions, and at the primary level. Beginning in Scotland in the 1850s, it was a woman-dominated co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Institution
{{Short description, Type of higher education institute in 20th and 21st century Scotland A central institution (CI) was a type of higher education institute in 20th and 21st-century Scotland, responsible for providing degree-level education but emphasising teaching rather than research. Some had a range of courses similar to polytechnics elsewhere in the United Kingdom while others were more specialised such as the art colleges and the conservatoire. Some subjects were not taught at CIs; for example, teacher training was only carried out by colleges of education, which later merged with universities. Amongst the most common names for individual CIs were ''college of agriculture'', ''college of art'', and ''institute of technology''. Of the five colleges of technology, Napier and Glasgow eventually changed their names to include the word ''polytechnic'', Paisley took the name Paisley College, while Dundee and Robert Gordon became institutes of technology. Another CI, Leith Nautic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
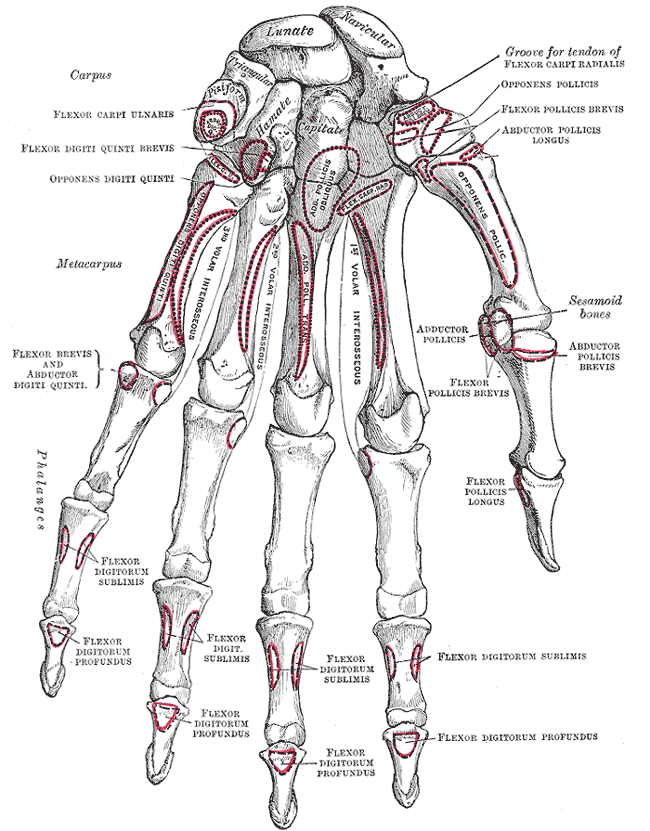
Gray's School Of Art
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter and first published in London in 1858. It has had multiple revised editions, and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive and ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coeducational
Mixed-sex education, also known as mixed-gender education, co-education, or coeducation (abbreviated to co-ed or coed), is a system of education where males and females are educated together. Whereas single-sex education was more common up to the 19th century, mixed-sex education has since become standard in many cultures, particularly in western countries. Single-sex education remains prevalent in many Muslim countries. The relative merits of both systems have been the subject of debate. The world's oldest co-educational school is thought to be Archbishop Tenison's Church of England High School, Croydon, established in 1714 in the United Kingdom, which admitted boys and girls from its opening onwards. This has always been a day school only. The world's oldest co-educational both day and boarding school is Dollar Academy, a junior and senior school for males and females from ages 5 to 18 in Scotland, United Kingdom. From its opening in 1818, the school admitted both boys and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Gordon's College
Robert Gordon's College is a co-educational private school for day pupils in Aberdeen, Scotland. The school caters for pupils from Nursery through to S6. History Background Robert Gordon, an Aberdeen merchant, made his fortune in 18th century Poland trading from the Baltic port of Danzig, (Gdansk). Upon his death in 1731, he left his entire estate in a '''Deed of Mortification, dated 13 December 1729, for the foundation of Robert Gordon's Hospital, a residential school for poor boys. The building, designed by William Adam, was completed by 1732, but lay empty until the Governors had sufficient funds to complete the interior. A statue of the Founder was added in 1753 in a niche above the door. During the Jacobite Rising in 1746, the building was requisitioned by Hanoverian troops under the command of the Duke of Cumberland and was known as Fort Cumberland. The hospital opened its doors to its first 14 pupils in July 1750. East and West wings with classical colonnades, desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bust Of John Gray
{{Disambiguation ...
Bust commonly refers to: * Breasts * Bust (sculpture), of head and shoulders * An arrest Bust may also refer to: Places *Bust, Bas-Rhin, a city in France *Lashkargah, Afghanistan, known as Bust historically Media * ''Bust'' (magazine) of feminist pop culture * ''Bust'' (TV series), 1987–1988 UK comedy-drama television series *"Bust", a 2015 song by rapper Waka Flocka Flame Other uses *Bust, in blackjack *Boom and bust economic cycle *Draft bust in sports, referring to an highly touted athlete that does not meet expectations See also *Busted (other) *Crimebuster (other) *Gangbuster (other) '' Gang Busters'' was an American radio series. Gangbuster(s) or Gang Busters might also refer to: * ''Gang Busters'' (serial), a movie serial based on the radio series * ''Gang Busters'', a 1955 crime film * "Gang Busters" (Tiny Toons episode) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a collegiate university, federal Public university, public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degree-awarding examination board for students holding certificates from University College London, King's College London and "other such institutions, corporate or unincorporated, as shall be established for the purpose of Education, whether within the Metropolis or elsewhere within our United Kingdom". It is one of three institutions to have claimed the title of the Third-oldest university in England debate, third-oldest university in England. It moved to a federal structure with constituent colleges in 1900. It is now incorporated by its fourth (1863) royal charter and governed by the University of London Act 2018 (c. iii). The university consists of Member institutions of the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkbeck College
Birkbeck, University of London (formally Birkbeck College, University of London), is a public research university located in London, England, and a member institution of the University of London. Established in 1823 as the London Mechanics' Institute by its founder Joseph Clinton Robertson and its supporters George Birkbeck, Jeremy Bentham, J. C. Hobhouse and Henry Brougham, Birkbeck is one of the few universities to specialise in evening higher education in the United Kingdom. Birkbeck's main building is in Bloomsbury, in the London Borough of Camden in Central London. Birkbeck offers more than 200 undergraduate and postgraduate programmes. Birkbeck's academic activities are organised into five constituent faculties, which are subdivided into nineteen departments. The university is a member of academic organisations such as the Association of Commonwealth Universities and the European University Association. The university is also a member of the Screen Studies Group, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Birkbeck
George Birkbeck (; 10 January 1776 – 1 December 1841) was an English physician, academic, philanthropist, pioneer in adult education and a professor of natural philosophy at the Andersonian Institute. He is the founder of Birkbeck, University of London and was head of the Chemical Society. He is one of the creators of the earliest chemistry laboratory for undergraduates at University College London, and is also known for the creation of mechanics' institutes in Scotland and London. He was President of the Medical and Chirurgical Society of London in 1825. Early life and education Birkbeck was born on 10 January 1776 to a Quaker family in Settle, West Riding of Yorkshire. His mother was Sarah and his father, William, was a merchant and banker. Birkbeck went to Sedbergh School and then studied medicine at Leeds and LondonPDF (Note: out of copy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |