|
Rhodeus Hondae
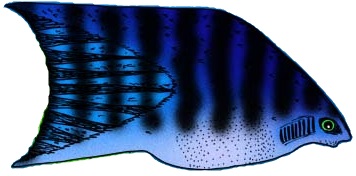
''Rhodeus hondae'' also known as Seoho bitterling () is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish in the genus ''Rhodeus''. It is endemic to South Korea. Named in honor of K. Honda, director, Agricultural Station at Suigen (Korea), "who obtained for us a fine collection from the pond at this station". Following this single specimen, two further specimens were collected in the same place in 1935 by T. Mori. As no further specimens have been collected since, it is now considered extinct Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and .... References hondae Taxa named by David Starr Jordan Fish described in 1913 Fish of East Asia Endemic fauna of South Korea {{Acheilognathinae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Starr Jordan
David Starr Jordan (January 19, 1851 – September 19, 1931) was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford University, he served as president of Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana University from 1885 to 1891. Jordan was also a strong supporter of eugenics, and his published views expressed a fear of "race-degeneration", asserting that cattle and human beings are "governed by the same laws of selection". He was an antimilitarist since he believed that war killed off the best members of the gene pool, and he initially opposed American involvement in World War I. Early life and education Jordan was born in Gainesville (town), New York, Gainesville, New York, and grew up on a farm in upstate New York. His parents made an unorthodox decision to educate him at a local girls' high school. His middle name, Starr, does not appear in early census records, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wiliam Metz
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (James (< Latin ''-us'', see Spanish/ Portuguese ''Carlos''). According to Julius Pokorny, the historical linguist and Indo-European studies, Indo-Europeanist, the root meaning of Charles is "old man", from Proto-Indo-European language, Indo-European *wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fish fin, fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spine (zoology), spines called ''lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister taxon, sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation (anatomy), articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodeus
''Rhodeus'' is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Acheilognathidae, the bitterlings. The scientific name is derived from the Greek word ', meaning "rose". Most species in the genus are restricted to Asia, but two species are found in Europe (''R. amarus'' and ''R. meridionalis''). Bitterlings are short-lived species, generally surviving only about five years. Their maximum size is 11 cm, but they are usually much shorter. Bitterlings inhabit slow-flowing or still waters, such as ponds, lakes, marshes, muddy and sandy pools, and river backwaters. Because they depend on freshwater mussels to reproduce, their range is restricted. Bitterlings are omnivorous, feeding on both invertebrates and plants. Bitterlings have a remarkable reproduction strategy where parents transfer responsibility for the care of their young to various species of freshwater mussels (Unionidae and Margaritiferidae). The female extends her long ovipositor into the mantle cavit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and the Sea of Japan to the east. Like North Korea, South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and List of islands of South Korea, adjacent islands. It has Demographics of South Korea, a population of about 52 million, of which half live in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, the List of largest cities, ninth most populous metropolitan area in the world; other major cities include Busan, Daegu, and Incheon. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Gojoseon, Its first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early seventh century BC. From the mid first century BC, various Polity, polities consolidated into the rival Three Kingdoms of Korea, kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje, and Sil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By David Starr Jordan
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1913
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of East Asia
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |