|
Rho Scorpii
Rho Scorpii (ρ Scorpii, abbreviated Rho Sco, ρ Sco) is a double star in the constellation of Scorpius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.87, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located approximately 472 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the system is reduced by 0.07 due to extinction from interstellar dust. It is a member of the Upper Scorpius OB association. It has two components, designated Rho Scorpii A and B. Rho Scorpii A is itself a single-lined spectroscopic binary whose components are designated Rho Scorpii Aa (formally named Iklil , traditionally the name for several neighboring stars) and Ab. Nomenclature ''ρ Scorpii'' ( Latinised to ''Rho Scorpii'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the three constituents as ''Rho Scorpii A'' and ''B'', and those of ''A's'' components - ''Rho Scorpii Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpius (constellation)
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra (constellation), Libra to the west and Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation whose recognition predates Greek culture; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. Notable features Stars Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; Beta Scorpii, β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; Delta Scorpii, δ Sco (Dschubba, "the forehead"); Theta Scorpii, θ Sco (Sargas, of Sumerian origin); Nu Scorpii, ν Sco (Jabbah); Xi Scorpii, ξ Sco; Pi Scorpii, π Sco (Fang); Sigma Scorpii, σ Sco (Alniyat); and Tau Scorpii, τ Sco (Paikauhale). Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are Lambda Scorpii, λ Sco (Shaula) and Upsilon Scorpii, υ Sco (Lesat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
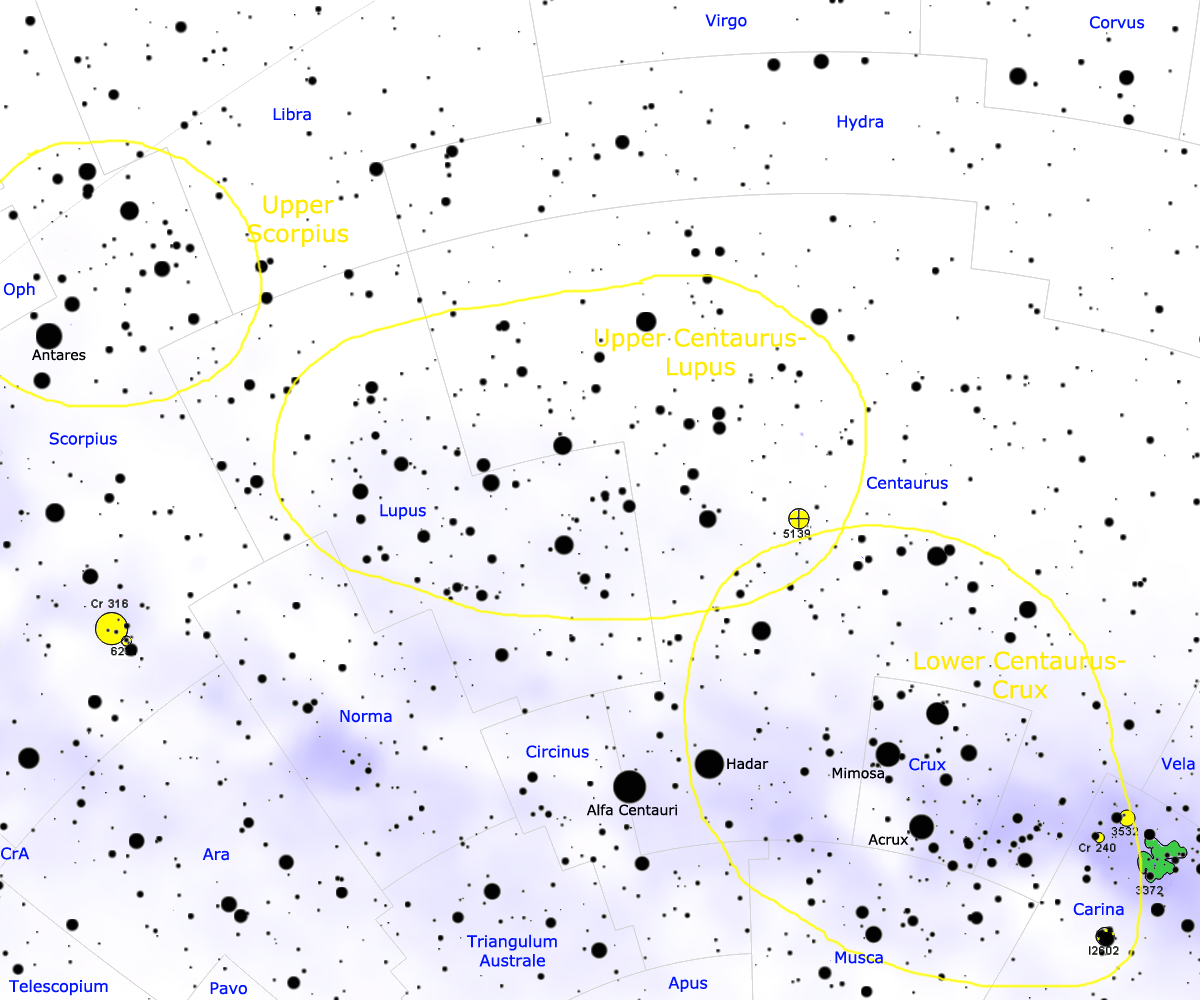
Scorpius–Centaurus Association
The Scorpius–Centaurus association (sometimes called Sco–Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearest OB association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups (Upper Scorpius, Upper Centaurus–Lupus, and Lower Centaurus–Crux) and its distance is about 130 parsecs or 420 light-years. Analysis using improved Hipparcos data has brought the number of known members to 436. The cluster shows a continuous spread of stars with no apparent need for subclassification. The Sco–Cen subgroups range in age from 11 million years (Upper Scorpius) to roughly 15 million years (Upper Centaurus–Lupus and Lower Centaurus–Crux). Many of the bright stars in the constellations Scorpius, Lupus, Centaurus, and Crux are members of the Sco–Cen association, including Antares (the most massive member of Upper Scorpius), and most of the stars in the Southern Cross. Hundreds of stars have been identified as members of Sco-Cen, with masses ranging from roughly 15 solar masses (Antares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta1 Scorpii
Beta Scorpii is a multiple star system in the southern zodiac constellation of Scorpius. It bore the traditional proper name of Acrab , though the International Astronomical Union now regards that name as applying only to the β Scorpii Aa component. Components Observed through a small telescope, Beta Scorpii appears as a binary star with a separation between the two components of 13.5 arcseconds and a combined apparent magnitude of 2.50. This pair, designated β¹ Scorpii and β² Scorpii, form the top branches of a hierarchy of six orbiting components. Hierarchy of orbits in the β Scorpii system β¹ Scorpii, the brighter of the pair, consists of two sub-components, designated β Scorpii A and β Scorpii B, orbiting at an angular separation of 0.3 arcseconds with an orbital period of 610 years. β Scorpii A is itself a spectroscopic binary, with the two components designated β Scorpii Aa (also named Acrab) and β Scorpii Ab. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Scorpii
Delta Scorpii (Latinisation of names, Latinised from δ Scorpii, abbreviated Delta Sco, δ Sco) is a binary star (the presence of a third star in the system is being debated) in the constellation of Scorpius. The primary star is named Dschubba . Observation Delta Scorpii is 2.0 degrees south of the ecliptic. It is a binary star with two components of magnitudes 2.4 and 4.6 separated by . In 1981 it was occultation, occulted by Rings of Saturn, Saturn's rings as seen by Voyager 2, with starlight unexpectedly blocked even by the apparently empty gaps, indicating that "there is very little empty space anywhere in the main ring system." Variability Delta Scorpii A is a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable star. This type of star shows irregular slow brightness variations of a few hundredths of a magnitude due to material surrounding the star. In June 2000 Delta Scorpii was observed by Sebastian Otero to be 0.1 magnitudes brighter than normal; its brightness has varied since then a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pi Scorpii
Pi Scorpii or π Scorpii, is a triple star system in the southern constellation of Scorpius. With a combined apparent magnitude of 2.9, it can be easily seen with the naked eye. Parallax measurements yield an estimated distance of around from the Sun. It consists of a binary pair, designated Pi Scorpii A, with a more distant third companion, B. A's two components are themselves designated Pi Scorpii Aa (formally named Fang) and Ab. Nomenclature ''π Scorpii'' ( Latinised to ''Pi Scorpii'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the three constituents as ''Pi Scorpii A'' and ''B'' and those of ''A's'' components - ''Pi Scorpii Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). In Chinese, (), meaning ''Room'', refers to an asterism consisting of Pi Scorpii, Rho Scorpii, Delta Scorpii, Beta¹ Scorpii and Beta² Scorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room (Chinese Constellation)
The Room mansion (房宿, pinyin: Fáng Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the eastern mansions of the Azure Dragon The Azure Dragon ( zh, c=青龍, p=Qīnglóng) is one of the Dragon King, Dragon Gods who represent the mount or Chthonic deities, chthonic forces of the Wufang Shangdi, Five Regions' Highest Deities (). It is also one of the Four Symbols o .... Asterisms {{DEFAULTSORT:Room (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The Ancient China, ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE). They flourished during the Han period (202 BCE – 220 CE) and subsequent dynasties with the publication of star catalogues. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observational astronomy, observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified star pattern, and therefore are a more general concept than the IAU designated constellations, 88 formally defined constellations. Constellations are based upon asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations are defined regions with official boundaries which together encompass the entire sky. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. The patterns of stars seen in asterisms are not necessarily a product of any physical association between the stars, but are rather the result of the particular perspectives of their observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dschubba
Delta Scorpii ( Latinised from δ Scorpii, abbreviated Delta Sco, δ Sco) is a binary star (the presence of a third star in the system is being debated) in the constellation of Scorpius. The primary star is named Dschubba . Observation Delta Scorpii is 2.0 degrees south of the ecliptic. It is a binary star with two components of magnitudes 2.4 and 4.6 separated by . In 1981 it was occulted by Saturn's rings as seen by Voyager 2, with starlight unexpectedly blocked even by the apparently empty gaps, indicating that "there is very little empty space anywhere in the main ring system." Variability Delta Scorpii A is a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable star. This type of star shows irregular slow brightness variations of a few hundredths of a magnitude due to material surrounding the star. In June 2000 Delta Scorpii was observed by Sebastian Otero to be 0.1 magnitudes brighter than normal; its brightness has varied since then and has reached at least as high as magnitude 1.6, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Mansion
Often called lunar mansion, a lunar station or lunar house is a segment of the ecliptic through which the Moon passes in orbit of the Moon, its orbit around the Earth. The concept was used by several ancient cultures as part of their calendrical system. Stations in different cultures In general, though not always, the zodiac is divided into 27 or 28 segments relative to the March Equinox, vernal equinox point or the fixed stars – one for each day of the lunar month. (A Lunar month#Sidereal month, sidereal month lasts about days.) The Moon's position is charted with respect to those fixed segments. Since the Moon's position at any given stage will vary according to Earth's position in Earth's orbit, its own orbit, lunar stations are an effective system for keeping track of the passage of seasons. Various cultures have used sets of lunar stations astrology, astrologically; for example, the Jyotisha astrological ''nakshatras'' of Hindu culture, the Arabic manzils (''ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded on 28 July 1919 in Brussels, Belgium and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. the Union had 85 national members and 12,734 individual members, spanning 90 countries and territories. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star System
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravity, gravitational attraction. It may sometimes be used to refer to a single star. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking, they are also star systems. Star systems are not to be confused with planetary systems, which include planets and similar bodies (such as comets). Terminology A star system of two stars is known as a ''binary star'', ''binary star system'' or ''physical double star''. Systems with four or more components are rare, and are much less commonly found than those with 2 or 3. Multiple-star systems are called ''triple'', ''ternary'', or ''trinary'' if they contain three stars; ''quadruple'' or ''quaternary'' if they contain four stars; ''quintuple'' or ''quintenary'' with five stars; ''sextuple'' or ''sextenary'' with six stars; ''septuple'' or ''septenary'' with seven stars; and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |