|
Renitovirus
''Torovirus'' is a genus of Viral envelope, enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Nidovirales'' and family ''Tobaniviridae''. They primarily infect vertebrates, especially cattle, pigs, and horses. Diseases associated with this genus include gastroenteritis, which commonly presents in mammals. ''Torovirus'' is the only genus in the Monotypic taxon, monotypic subfamily ''Torovirinae''. The discovery of the first torovirus can be traced back to 1970s. Equine torovirus (EToV) was accidentally found in the rectal sample from a horse who was experiencing severe diarrhea. The 'Breda' bovine torovirus was later found in 1979 while investigation in a dairy farm in Breda. They had several calves experiencing severe diarrhea for months. In 1984, torovirus-like particles were detected with Electron Microscope, electron microscope (EM) technique in the human patients with gastroenteritis. Virology Taxonomy Until recently, the toroviruses were not assigned any family. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torovirinae
''Torovirus'' is a genus of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order ''Nidovirales'' and family ''Tobaniviridae''. They primarily infect vertebrates, especially cattle, pigs, and horses. Diseases associated with this genus include gastroenteritis, which commonly presents in mammals. ''Torovirus'' is the only genus in the monotypic subfamily ''Torovirinae''. The discovery of the first torovirus can be traced back to 1970s. Equine torovirus (EToV) was accidentally found in the rectal sample from a horse who was experiencing severe diarrhea. The 'Breda' bovine torovirus was later found in 1979 while investigation in a dairy farm in Breda. They had several calves experiencing severe diarrhea for months. In 1984, torovirus-like particles were detected with electron microscope (EM) technique in the human patients with gastroenteritis. Virology Taxonomy Until recently, the toroviruses were not assigned any family. The recent molecular analysis of the virus revealed its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
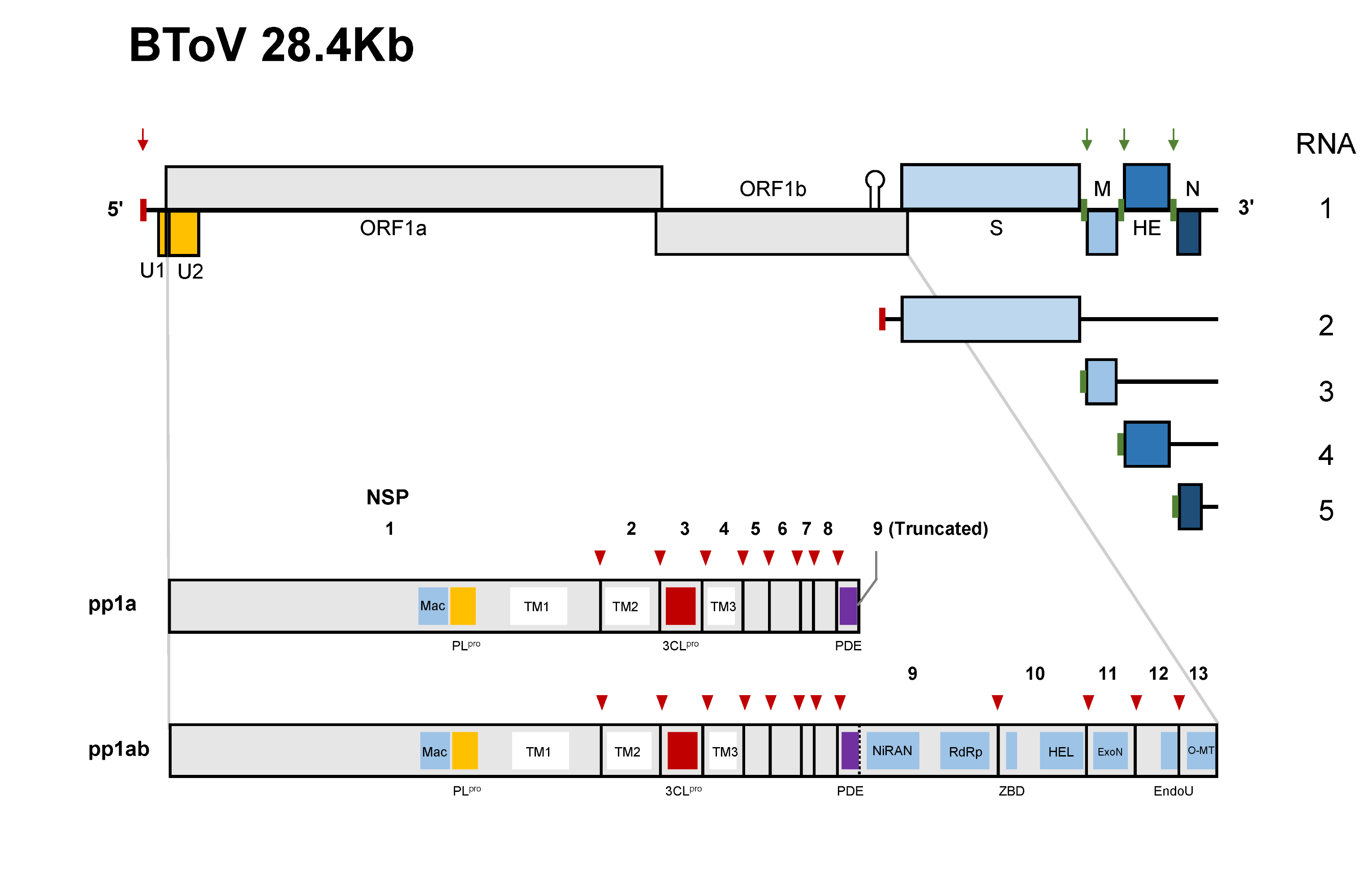
Open Reading Frames
In molecular biology, reading frames are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in translation). Such an open reading frame (ORF) may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In eukaryotic genes with multiple exons, introns are removed and exons are then joined together after transcription to yield ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Stuttering
Polymerase stuttering is the process by which a polymerase transcribes a nucleotide several times without progressing further on the mRNA chain. It is often used in addition of poly A tails or capping mRNA chains by less complex organisms such as viruses. Process A polymerase may undergo stuttering as a probability controlled event, hence it is not explicitly controlled by any mechanisms in the translation process. Generally, it is a result of many short repeated frameshifts on a slippery sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA strand. However, the frameshift is restricted to one (in some cases two) nucleotides with a pseudoknot or choke points on both sides of the sequence. Examples A polymerase that exhibits this behavior is RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, present in many RNA viruses. Reverse transcriptase A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to convert RNA genome to DNA, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal Frameshifting
Ribosomal frameshifting, also known as translational frameshifting or translational recoding, is a biological phenomenon that occurs during translation that results in the production of multiple, unique proteins from a single mRNA. The process can be programmed by the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and is sometimes affected by the secondary, 3-dimensional mRNA structure. It has been described mainly in viruses (especially retroviruses), retrotransposons and bacterial insertion elements, and also in some cellular genes. Small molecules, proteins, and nucleic acids have also been found to stimulate levels of frameshifting. In December 2023, it was reported that ''in vitro''-transcribed (IVT) mRNAs in response to BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) anti-COVID-19 vaccine caused ribosomal frameshifting. Process overview Proteins are translated by reading tri-nucleotides on the mRNA strand, also known as codons, from one end of the mRNA to the other (from the 5' to the 3' end) starting wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgenomic MRNA
Subgenomic mRNAs are essentially smaller sections of the original transcribed template strand. 3' to 5' DNA or RNA During transcription, the original template strand is usually read from the 3' to the 5' end from beginning to end. Subgenomic mRNAs are created when transcription begins at the 3' end of the template strand (or 5' of the to-be-newly synthesized template) and begins to copy towards the 5' end of the template strand before "jumping" to the end of the template and copying the last nucleotides of the 5' end of the template, (finishing the 3' tail for the newly created strand). As a result, the translated strand will have a similar 5' end to varying degrees with the original template (depending on which part of the template the transcription jumped over) and a similar 3' end to the template. 5' to 3' (positive sense) viral RNA Positive-sense (5' to 3') viral RNA which may be directly translated into the desired viral proteins, undergoes a similar process as described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variati ...), is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) or one thousand million (long scale) of a metre, meter (0.000000001 m) and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as 1 × 10−9 m and as m. History The nanometre was formerly known as the "''millimicrometre''" – or, more commonly, the "''millimicron''" for short – since it is of a micrometre, micrometer. It was often de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleomorphism (microbiology)
In microbiology, pleomorphism (from Ancient Greek , ''pléō'', "more", and , ''morphḗ'', form), also pleiomorphism, is the ability of some microorganisms to alter their morphology, biological functions or reproductive modes in response to environmental conditions. Pleomorphism has been observed in some members of the Deinococcaceae family of bacteria. The modern definition of pleomorphism in the context of bacteriology is based on ''variation'' of morphology or functional methods of the individual cell, rather than a heritable ''change'' of these characters as previously believed. Bacteria In the first decades of the 20th century, the term "pleomorphism" was used to refer to the idea that bacteria change morphology, biological systems, or reproductive methods dramatically according to environmental cues. This claim was controversial among microbiologists of the time, and split them into two schools: the monomorphists, who opposed the claim, and the pleomorphists such as Antoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |