|
Relational Disorder
According to Michael First of the DSM-5 working committee the focus of a relational disorder, in contrast to other DSM-IV disorders, "is on the relationship rather than on any one individual in the relationship".Michael B. First, MD. A Research Agenda for DSM-V: ''Summary of the DSM-V Preplanning White Papers''. Published in May 2002. Relational disorders involve two or more individuals and a disordered "juncture", whereas typical Axis I psychopathology describes a disorder at the individual level. An additional criterion for a relational disorder is that the disorder cannot be due solely to a problem in one member of the relationship, but requires pathological interaction from each of the individuals involved in the relationship. For example, if a parent is withdrawn from one child but not another, the dysfunction could be attributed to a relational disorder. In contrast, if a parent is withdrawn from both children, the dysfunction may be more appropriately attributable to a dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael First
Michael B. First (born 1956) is an American psychiatrist who focuses on diagnostic criteria for mental disorders. He is Professor of Clinical Psychiatry at Columbia University. First was one of the editors of DSM-IV-TR, the Editor of Text and Criteria for the DSM-IV, and the editor of the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV. He also served as consultant to the World Health Organization for the revision of ICD-11. Life and career First earned a bachelor's degree in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from Princeton University in 1978. He then graduated from University of Pittsburgh with a master's degree, also in Computer Science, and a Doctor of Medicine degree in 1983. He did his psychiatric residency at Columbia-Presbyterian Medical Center and a fellowship in biometrics at the New York State Psychiatric Institute. He is certified with the American Board of Psychiatry & Neurology. First frequently writes on diagnostic criteria, particularly diagnostic con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSM IV
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (''DSM''; latest edition: ''DSM-5-TR'', published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common language and standard criteria. It is an internationally accepted manual on the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders, though it may be used in conjunction with other documents. Other commonly used principal guides of psychiatry include the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders (CCMD), and the ''Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual''. However, not all providers rely on the DSM-5 as a guide, since the ICD's mental disorder diagnoses are used around the world, and scientific studies often measure changes in symptom scale scores rather than changes in DSM-5 criteria to determine the real-world effects of mental health interventions. It is used by researchers, psychiatric drug regulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husband
A husband is a man involved in a marital relationship, commonly referred to as a spouse. The specific rights, responsibilities, and societal status attributed to a husband can vary significantly across different cultures and historical periods, reflecting a global perspective on this role. In many parts of the world, heterosexual monogamous marriage is the prevailing norm, where a husband and wife form the basic unit of a family. Legal systems in numerous countries enforce monogamy and prohibit bigamy and polygamy. Traditionally, husbands often held the position of being the head of the household and the primary provider, a role that was often considered Paternalism, paternalistic. However, the evolving dynamics of modern society have led to a shift in these roles. Today, a husband is not automatically designated as the sole breadwinner, especially when his spouse pursues a more financially rewarding career. This change reflects a global trend in the changing dynamics of Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wife
A wife (: wives) is a woman in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until their marriage is legally dissolved with a divorce judgment; or until death, depending on the kind of marriage. On the death of her partner, a wife is referred to as a widow. The rights and obligations of a wife to her partner and her status in the community and law vary between cultures and have varied over time. Etymology The word is of Germanic origin from the Proto-Germanic word ''wībam'', which translates into "woman". In Middle English, it had the form ''wif'', and in Old English ''wīf'', "woman or wife". It is related to Modern German ''Weib'' (woman, female), Danish ''viv'' (wife, usually poetic), and Dutch ''wijf'' (woman, generally pejorative, cf. ''bitch''). The original meaning of the phrase "wife" as simply "woman", unconnected with marriage or a husband/wife, is preserved in words such as "midwife", "goodwife", " fishwife" and " sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or academic difficulties), relationship problems (such as breakups or divorces), or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; improving economic conditions; and dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT). Although crisis hotlines, like 988 in North America and 13 11 14 in Australia, are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied. Suicide is the 10th leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately 1.5% of total deaths. In a given year, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Freak
Control freak is a colloquialism for a person who feels a psychological need to constantly be in charge of things and people around them. A control freak can become distressed when they feel things are going out of control. The feel of the need to control is often attributed to the underlying fear of losing control over their lives. This expression was introduced around the 1960s and it is not a clinical one. Characteristics Control freaks tend to have a psychological need to be in charge of things and people – even circumstances that cannot be controlled. The need for control, in extreme cases, stems from deeper psychological issues such as obsessive–compulsive personality disorder (OCPD), anxiety disorders, or personality disorders. Control freaks are often insecure and perfectionists. Additionally, they may even manipulate or pressure others to change to avoid having to change themselves. They may have had an overbearing mother or father. Furthermore, control freaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Advisory Council On Violence Against Women
The National Advisory Council on Violence Against Women was created in 1995 by the United States Department of Health and Human Services and the United States Department of Justice. It consists of experts from law enforcement, media, business, sports, health and social services, and victim advocacy. The council works with both the public and private sectors to promote greater awareness about the problem of violence against women and its victims, to help devise solutions, and to advise the federal government on these issues. The NACVAW does not advise on issues of violence against men, as it is a ''gender specific'' advocacy for women alone. The NACVAW created the promotional "Toolkit To End Violence Against Women" to provide concrete guidance to communities, policy leaders, and individuals engaged in activities to end violence against women. As described, "each Toolkit chapter focuses on a particular audience or environment and includes recommendations for strengthening prevention e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
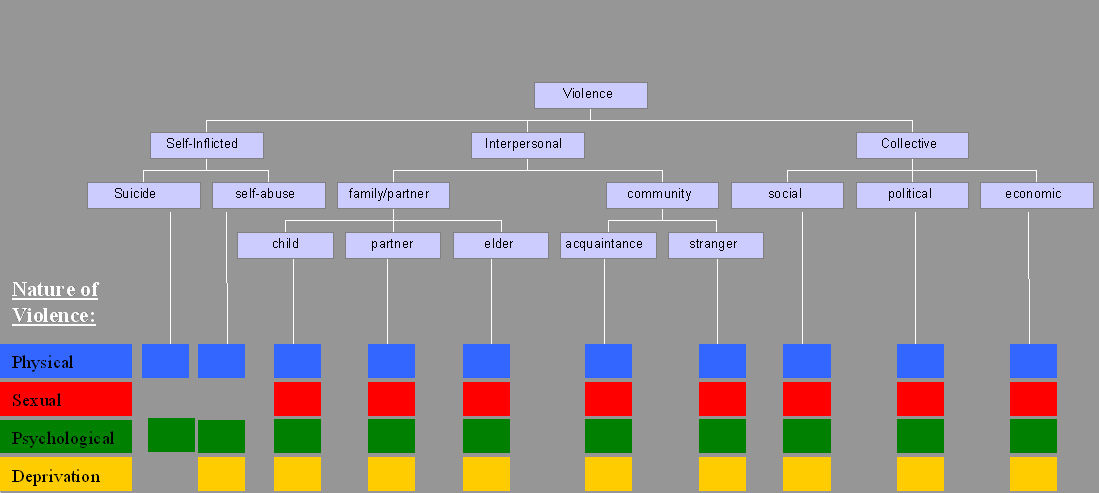
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinician
A clinician is a health care professional typically employed at a skilled nursing facility or clinic. Clinicians work directly with patients rather than in a laboratory, community health setting or in research. A clinician may diagnose, treat and care for patients as a psychologist, clinical pharmacist, clinical scientist, nurse, occupational therapist, speech-language pathologist, physiotherapist, dentist, optometrist, physician assistant, clinical officer, physician, paramedic, or chaplain. Clinicians undergo and take comprehensive training and exams to be licensed and some complete graduate degrees (master's or doctorates) in their field of expertise. The main function of a clinician is to manage a sick person in order to cure their illness, reduce pain and suffering, and extend life considering the impact of illness upon the patient and their family as well as other social factors. See also * List of healthcare occupations A listing of health care professions by m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognised union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children (if any), and between them and their Affinity (law), in-laws. It is nearly a cultural universal, but the definition of marriage varies between cultures and religions, and over time. Typically, it is an institution in which interpersonal relationships, usually sexual, are acknowledged or sanctioned. In some cultures, marriage is recommended or considered to be Premarital sex, compulsory before pursuing sexual activity. A marriage ceremony is called a wedding, while a private marriage is sometimes called an elopement. Around the world, there has been a general trend towards ensuring Women's rights, equal rights for women and ending discrimination and harassment against couples who are Interethnic marriage, interethnic, Interracial marriage, interracial, In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Psychology
Social psychology is the methodical study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others. Although studying many of the same substantive topics as its counterpart in the field of sociology, psychological social psychology places more emphasis on the individual, rather than society; the influence of social structure and culture on individual outcomes, such as personality, behavior, and one's position in social hierarchies. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the relationship between mental states and social situations, studying the social conditions under which thoughts, feelings, and behaviors occur, and how these variables influence social interactions. History 19th century In the 19th century, social psychology began to emerge from the larger field of psychology. At the time, many psychologists were concerned with developing concrete explanations for the different aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |